Advent of Europeans in India
1. Beginning of Europeans entry in India:
Merchants of Western European States, especially of Spain and Portugal, started to search new sea routes to India and the East Indies (name of Indonesia’s Spice Islands) to avoid old trading routes. Two facts are important in relation to the Beginning of Europeans entry into India:
- In 1492, Spain’s Columbus started the journey to arrive in India. However, he reached America.
- In 1498, Portugal’s Vasco da Gama discovered a new sea route via Cape of Good Hope to reach India from Europe.
2. Portuguese in India:
2.1 Coming of Portuguese in India:
- Vasco da Gama of Portugal sailed around Africa and arrived at Calicut (Western side of India) on 17 May 1498.
- Currently, Calicut is the name of Kozhikode city in Kerala. Calicut’s Hindu ruler having the title of Zamorin let him in India.
- Vasco da Gama is known to have stayed for nearly three months and returned to India again in 1502 AD.
2.2 Portuguese Settlement in India:
- Vasco da Gama established a trading station in Cannanore (today known as Kannur in Kerala). Trading stations were also created at Calicut and Cochin.
- Cochin was the Portuguese capital in India. Goa took its place later and became the Portuguese capital in India.
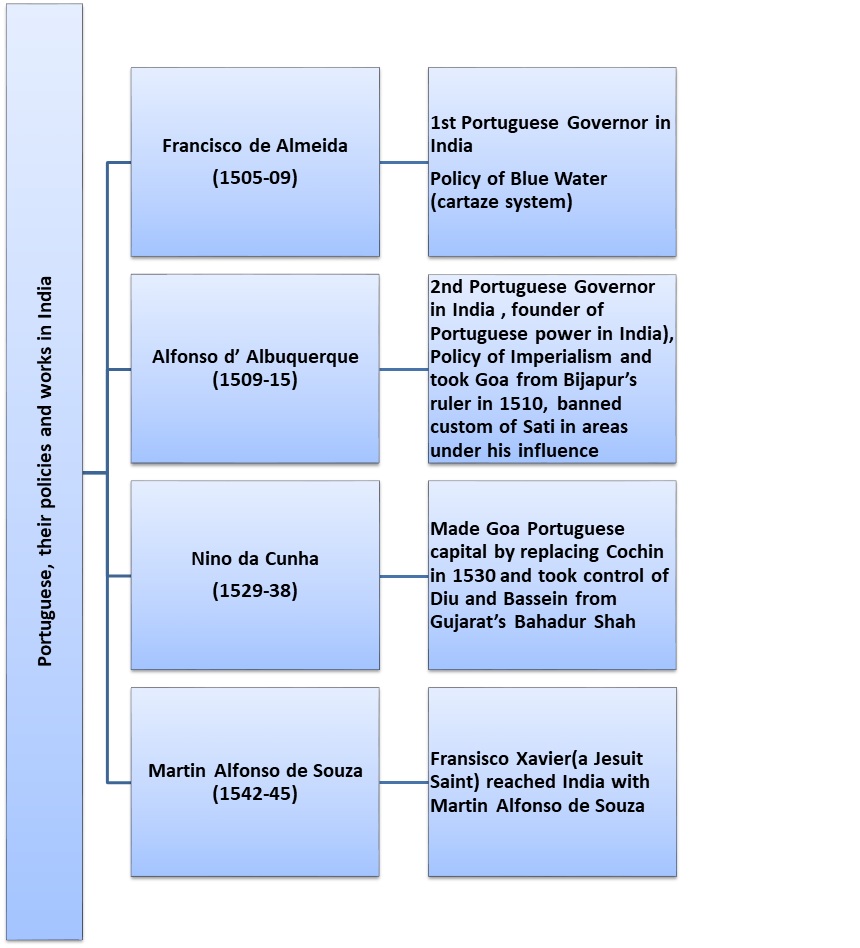
- In addition to Vasco da Gama, some other people from the time of Portuguese in India and their work are given in the next table.
|
Name |
Years |
Policies and Works |
|
Francisco de Almeida (1st Portuguese Governor in India) |
1505-09 |
Policy of Blue Water (cartaze system) |
|
Alfonso d’ Albuquerque (2nd Portuguese Governor in India and founder of Portuguese power in India) |
1509-15 |
Policy of Imperialism- took Goa from Bijapur’s ruler in 1510, banned the custom of Sati in areas under his influence. |
|
Nino da Cunha |
1529-38 |
Made Goa Portuguese capital by replacing Cochin in 1530 and took control of Diu and Bassein from Gujarat’s Bahadur Shah. |
|
Martin Alfonso de Souza |
1542-45 |
Fransisco Xavier(a Jesuit Saint) reached India with Martin Alfonso de Souza. |
2.3 Decline of Portuguese by 16th century end:
- 1631: Portuguese lost Hugli at the hands of Qasim Khan (Shahjahan’s Mughal noble).
- 1661: Bombay was given by the King of Portugal to England’s Charles II as dowry.
- 1739: Portuguese lost Salsette and Bassein to Marathas.
- Portuguese retained Goa, Diu and Daman till 1961.
3. Dutch in India:
3.1 Coming of Dutch into India:
- In March 1602, the Dutch parliament formed the Dutch East India Company (United East India Company) through a charter.
- The company was also called Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie (VOC).
- Dutch refers to people belonging to Holland (Currently Netherlands). They ended the Portuguese monopoly in India.
3.2 Dutch Settlement in India:
- In 1605, Dutch set up their first factory in Masulipattam, Andhra Pradesh.
- Fort Geldria (Geldaria) in Pulicat (Tamil Nadu) was the main site of the first Dutch settlement in India. It was constructed in 1613.
- Dutch also set up factories at other places, as given below.
|
Years |
Dutch factories in India |
|
1600-1620 |
Pulicat in 1610 (main centre of Dutch in India till 1690) and Surat in 1616 |
|
1640-1650 |
Bimilipatam in 1641 and Karaikal in 1645 |
|
1653 |
Chinsura |
|
1658 |
Kasimbazar, Baranagore, Patna, Balasore, Negapatam (replaced Pulicat as the main centre of Dutch in India after 1690) |
|
1663 |
Cochin |
3.3 Decline of Dutch in India:
- In 1741, Dutch fought the Battle of Colachel with an army of the State of Travancore.
- English defeated the Dutch in the Battle of Bedera, Bengal, in 1759. This battle is also known as the Battle of Chinsurah or the Battle of Hoogly.
- Dutch East India Company was liquidated in 1798.
4. English in India:
4.1 Coming of English in India:
- In 1599, John Mildenhall was the first English to arrive in India.
- English East India Company was formed in 1600. It was formed by the charter of Queen Elizabeth I.
- Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East Indies was its name from 1600 to 1708.
4.2 English Settlement in India:
- In 1608, Captain William Hawkins came to get permission for a factory at Surat. He came for this purpose to the court of Mughal Emperor Jahangir in 1609. He stayed there till 1611 but could not get permission.
- In 1611, the Mughal governor of Surat allowed Captain Middleton to trade in Surat. English began trading at Masulipatam in 1611.
- In 1612, the Portuguese were defeated by Captain Thomas Best in the sea off the Surat.
- In early 1613, Jahangir permitted the English to set up a Surat factory under Thomas Aldworth. East India Company established its permanent factory at Surat in 1613.
- Sir Thomas Roe reached Jahangir’s court in 1615. His purpose was to get permission for factories in various parts of the Mughal Empire. He was the ambassador of James I. Jahangir and Prince Khurram gave two farmans to Thomas Roe by 1618.
- In 1616, East India Company’s first factory in the south was set up in Masulipatam.
- In 1632, the Sultan of Golconda issued Golden Farman to the company.
- In 1633, East India Company’s first factory in east India was set up at Hariharpur, Balasore in Orissa.
- In 1667, Aurangzeb issued Farman to the company and allowed it to trade in Bengal.
- In 1668, Bombay came under the control of the Company from Charles II on lease. Gerald Aungier became its first governor from 1669 to 1677.
- In 1690, a factory was set up at Sutanati by Job Charnock. British converted the Sultanati factory into the fort in 1696 and renamed it, Fort William, in 1700.
- In 1698, British took control Zamindari of Sutanati, Kalikata and Gobindpur. Sutanati, Kalikata and Gobindpur gave rise to Calcutta. English Company of Merchants Trading to the East Indies was also set up as a competitor of East India Company in 1698.
- In 1708, the English East India Company was officially titled as United Company of Merchants of England Trading to the East Indies, which continued to rule in India till 1858.
- In 1717, Farrukhsiyar gave Farman (called Magna Carta of Company) to John Surman.
5. Danes in India:
- The Danes were known for their missionary activities. They had their headquarters at Serampore in West Bengal and established their first factory in India at Tranquebar in Tamil Nadu in 1620.
- The Danish East India Company was formed in 1616.
6. French in India:
6.1 Coming of French in India:
- Colbert set up the French East India Company in 1664 as Compagnie des Indes Orientales during the rule of Louis XIV.
6.2 French Settlement in India:
- Francois Caron set up the first French Factory at Surat in 1668. In 1669, the factory was founded at Masulipatnam by Mercara, a Persian who came with Caron.
- In 1673, Shaista Khan permitted them to develop a township at Chandernagore. He was the Mughal Subahdar of Bengal.
- In 1674, Pondicherry was established and Francois Martin became French governor in place of Caron. In 1693, Pondicherry was captured by Dutch.
- Mahe, Karaikal, Balasore and Qasim Bazar were some of the French factories and trading centres.
- French got Pondicherry back through the Treaty of Ryswick signed in 1697.
- In 1720, the French company was organised in a new way as ‘Perpetual Company of the Indies.'
- French governors (Lenoir and Dumas) strengthened French power in India during 1720-1742.
6.3 Decline of French in India:
- Anglo-French wars (also called Carnatic wars) started after the coming of Dupleix as French governor in India in 1742.
- Coromandel Coast and areas located away from it were called Carnatic by Europeans.
- Anglo-French rivalry started in India with the beginning of the Austrian War of Succession. The rivalry stopped with the end of the Seven Years War (1756-63).
|
Anglo-French wars/ Carnatic wars |
Name of the Treaties that ended wars |
Outcomes of wars |
|
First Anglo-French war (1746-48)
|
Treaty of Aix-La-Chapelle |
French captured Madras and defeated the army of Nawab of Carnatic (Anwaruddin) at battle St. Thome (Madras) |
|
Second Anglo-French war (1749-54) |
Treaty of Pondicherry/ Treaty by Godehu (1754) Godehu was French governor replacing Dupleix |
Dupleix, Muzaffar Jung (Hyderabad), Chanda Sahib (Carnatic/Arcot) came together and killed Anwaruddin at the Battle of Ambur in 1749 Robert Clive of England won |
|
Third Anglo-French war (1758-63) |
Treaty of Paris (1763) |
British won at Wandiwash (Tamil Nadu) in 1760, Fort St David captured by French Count de Lally |




 Latest
Latest 



Comments