Banking System in India- History of Banking in India, Role of Banks, Types of Banks in India, RBI, Merger of Banks
1. Structure of Banking System in India
Banks are special institutions that accomplish the seemingly simple duty of accepting deposits and lending them out. A country's banking system is an important pillar that supports the financial system of the country's economy.
1.1. Bank and its functions
The important role of banks in the financial system is to facilitate payment and settlement services for their customers.
Nowadays Banking sector is not only functioning to deposit money or lend loans but also provides services like issuing debit and credit cards, providing safe custody of valuables, lockers, ATM services, and other services like online transfer of funds across the country/world.
Functions of Banks
Banks have two types of functions: Primary Function and Secondary Function
1.1.1. Primary Functions of Banks
- Accepting of Deposits- Savings Account, Current Account, Fixed Deposit, Recurring Deposit. Fixed Deposits and Recurring deposit accounts are called term deposit or time deposit accounts. Saving Banks account and current account are called Demand Deposit accounts.
- Issue Loans- Term loans, Cash Credit, Overdrafts
- Funds transfer
- Credit Creation
- Discounting of bills
1.1.2. Secondary Functions of Banks
- Collection of cheques, drafts, promissory notes, etc.
- Accepting and collecting bills of exchange
- Undertaking safe custody of valuables- lockers facility
- Issuing letters of credit and travellers cheque
- Buy and sell shares, securities, debentures
- Providing consumer finance- educational loans
- Disperses salary to employees on the behalf of the employer
- On permission of RBI, the bank purchases or sells foreign exchange
1.1.3. Modern Functions of Banks
- ATM services
- Home Banking
- Green Card- Credit facility to farmers
- Factoring business- Under this, the bills drawn by customers on the buyer will be handed over to the bank for collection. The bank will pay 80% of the value of the bill to the customer and the balance 20% will be paid after realising the bill from the buyer. For this purpose, the bank will be paid factoring commission.
- Mutual Funds
- Electronic Clearing System (ECS)- Telephone charges are paid through this system.
- Gold or Platinum Card- credit card facility given to customers as per their credit worthiness.
- Gold Deposit Scheme
- E-banking
- Core Banking- A device in which all branches of a bank are linked through a network system. Customer can operate his account across any of the branches of a bank.
1.2. History of Banking System
Bank of Bombay was the first Joint-stock bank of India. It was established in the year 1720 in Bombay.
After the Bank of Bombay, the Bank of Hindustan was established in 1770 in Calcutta. It was established by the agency house. The Bank of Hindustan was shut down in 1832.
After the proposal of Governor (later Governor-General) Warren Hastings, the General Bank of Bengal and Bihar was established in the year 1773. The bank was closed soon.
1.2.1. Presidency Banks
The first 'Presidency Bank' of India was the Bank of Bengal. It was established on 2 June 1806 in Calcutta.
The second 'Presidency Bank' of India was the Bank of Bombay. It was established in the year 1840 in Bombay.
The third 'Presidency bank' of India was the Bank of Madras. It was established in July 1843 in Madras (now Chennai).
1.2.2. Imperial Bank
All three Presidency banks were merged to form a single bank in 1921. The bank so formed was named the Imperial bank of India. The bank worked as the central bank of India, before the establishment of RBI in 1935.
Imperial Bank of India functioned as commercial bank, central bank and banker to the government. In 1929, to inspect the extensive problems of Indian banking the Indian Central Banking Enquiry Committee was set up and the committee advised to establish a central bank in the country.
1.2.3. Indian owned Commercial Banks
Allahabad Bank was established in 1865 in Allahabad. It was the first Indian-owned bank. It was the oldest joint stock bank in India. Punjab National Bank was founded on 12 April 1894 in Lahore. It was the second Indian-owned bank. Bank of India was founded in 1906 in Mumbai. It was the third Indian-owned bank.
After the Swadeshi Movement of 1906, many Indian owned commercial banks were established such as
- Central Bank of India was founded on 21 December 1911 in Mumbai.
- Bank of Baroda was founded on 20 July 1908 in Vadodara, Gujarat.
- Canara Bank was established in Mangalore in 1906.
- Indian Bank was founded in 1907 in Chennai.
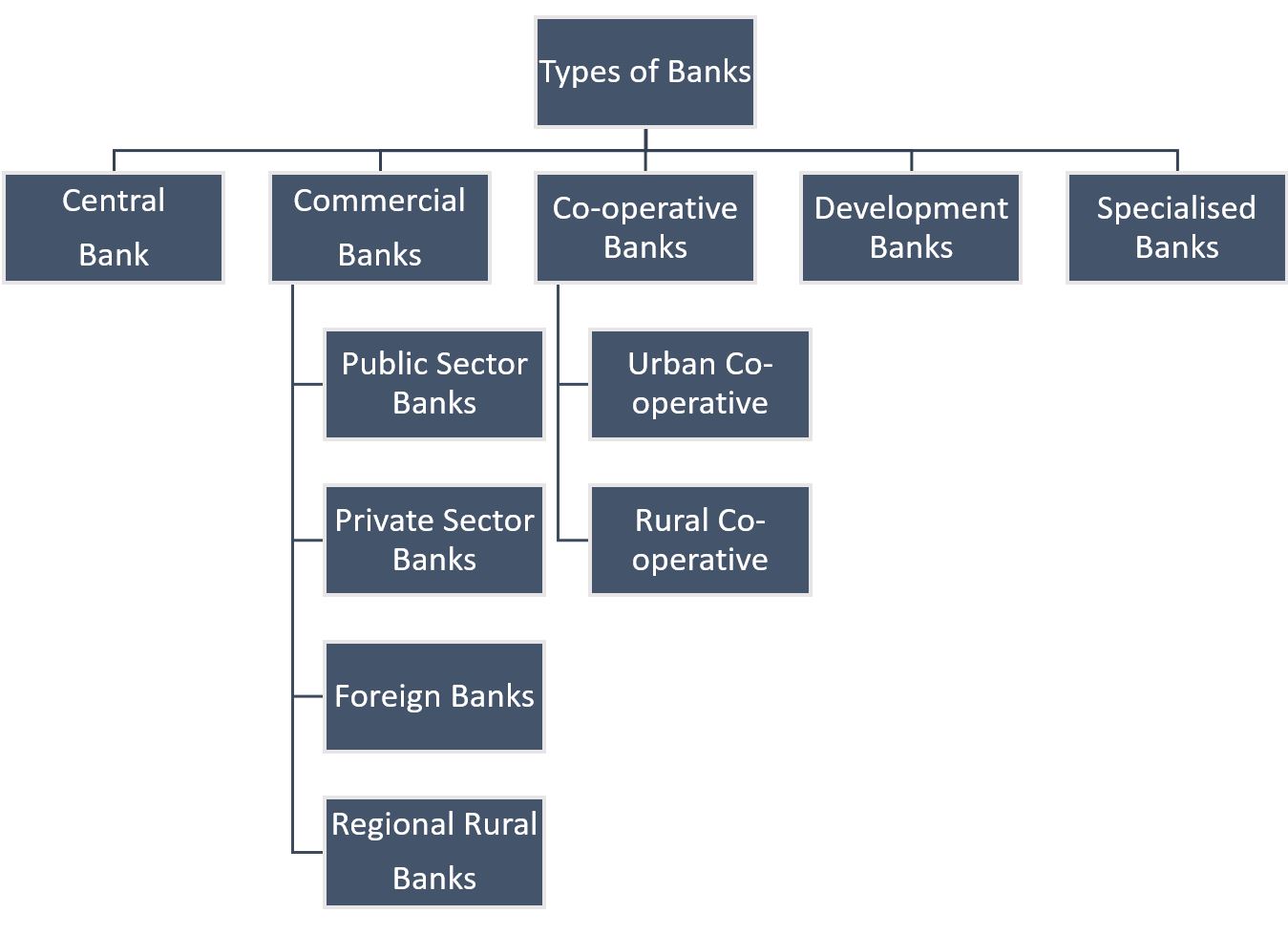
2. Types of Banks in India
In India, banks are divided into two categories: scheduled and non-scheduled banks. Let us discuss the different types of banks in India.
2.1. Scheduled banks
- The banks which are introduced in the second schedule of the RBI Act, 1934 are known as Scheduled banks.
- All these types of banks are having paid-up capital and reserves of an aggregate value of more than Rs 5 lakhs. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends loans to these banks at bank rates as and when they are needed.
- Types of Scheduled banks:
- Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks
- State Cooperative Banks
- Urban Cooperative Banks
2.2. Non-Scheduled banks
- These are those banks that do not need to comply with the provisions specified by the RBI. They are not listed in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934.
- They need to maintain a cash reserve requirement (CRR), but with themselves and not the RBI. These banks have a reserve capital of less than Rs. 5 lakhs and are generally local area banks. Unlike Scheduled banks, they cannot borrow money from the RBI, except in emergency situations.
- A few examples of non-scheduled banks operating in India are:
- Akhand Anand Co-operative Bank Limited
- Alavi Co-Operative Bank Limited
The banks can also be classified on the basis of their functions and ownership:
2.3. Central Bank of India - Reserve Bank of India
About RBI: India's central bank is known as the Reserve Bank of India. It is also called the banker's Bank. It is a regulatory body under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It takes responsibility to regulate the Indian banking system and issue and supply Indian rupees. RBI has the responsibility to manage all payment-related systems and works to promote its economic development.
RBI was constituted:
- To regulate and issue the banknotes
- To maintain the Indian reserves to secure monetary stability
- To maintain and operate the credit and currency system of the country
2.3.1. History of RBI
- Royal Commission on Indian Currency and Finance, also known as Hilton-Young Commission, was the first to recommend opening the central bank for India in 1926. RBI was established on 1 April 1935 under the RBI Act of 1934 with a capital of 5 crore. RBI started its operation on 1 April 1935 as the Central Bank of India.
- The headquarters of the Reserve Bank of India was initially established in Calcutta. RBI headquarters was permanently moved to Mumbai in 1937.
- RBI was the first nationalized bank of India, which was nationalized with effect from 1st January 1949 under the Reserve Bank of India (Transfer to Public Ownership) Act, 1948.
2.3.2. Role and Functions of RBI
- The main function of the Reserve Bank over these years has been the formulation and implementation of monetary policy.
- The goal of RBI is to maintain financial stability. Hence, it acts as the Regulator and supervisor of the financial system.
- RBI is responsible for designing and implementing the regulatory policy framework for banking and non-banking financial institutions.
- The function of RBI is to regulate the commercial banking sector.
- The Cooperative banks and Regional rural banks come under the jurisdiction of the Reserve Bank after the amendments to the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- RBI acts as the Issuer of Bank Notes.
- It is the Banker to the Government. It also acts as the Banker to banks in India.
- It is the Custodian of the Country’s Foreign Currency Reserves.
2.3.3. Organisational Structure of RBI
There are 21 central boards of directors in RBI, which are:
- A Governor
- Four Deputy governors
- Two finance ministry representatives (usually the Economic Affairs Secretary and the Financial Services Secretary)
- Ten government-nominated directors
- Four directors who represent local boards for Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, and Delhi.
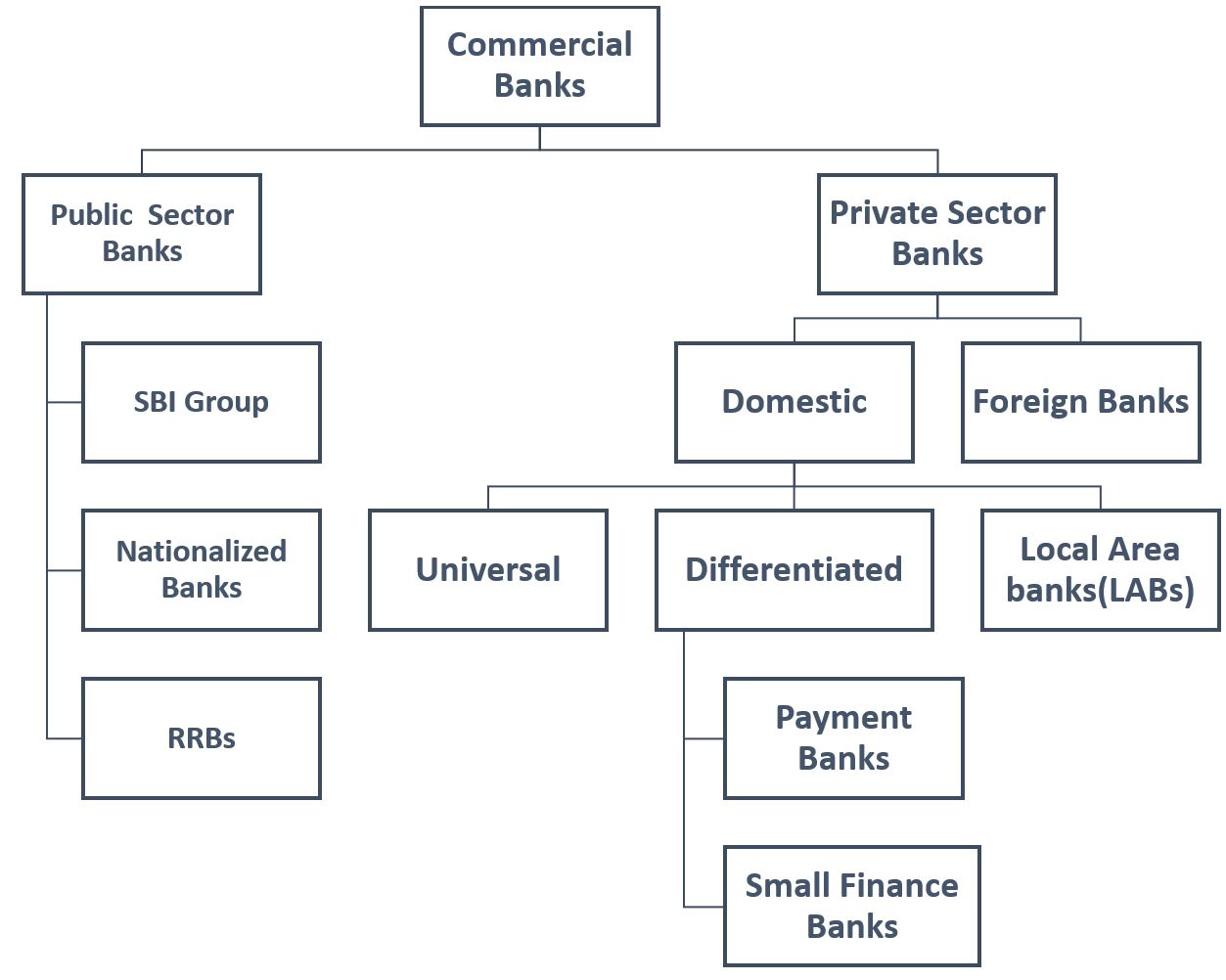
2.4. Commercial Banks
Commercial banks can be scheduled or non-scheduled commercial banks. These are regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
These banks are involved in the banking business, which deals with the general public, accepting deposits and making loans to large numbers of households and firms.
The process of accepting deposits and lending results in creating the flow of money in the economy.
Some examples of commercial banks are State Bank India, PNB, ICICI, HDFC, HSBC etc.
Types of Commercial Banks
On the basis of ownership and control over management, the commercial banks in India can be classified as below:
2.4.1. Public Sector Banks
- The Government of India has kept the majority of the stake in the Public Sector Banks.
- These bank's shares are listed on stock exchanges.
- State Bank of India, Nationalized Banks, and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) have been constituted under the respective Acts of Parliament. These banks come under Public sector Banks.
- As of 2022, there are total 12 Public sector Banks in India. These are:
- Union Bank of India
- UCO Bank
- State Bank of India
- Punjab National Bank
- Punjab and Sind Bank
- Indian Overseas Bank
- Indian Bank
- Central Bank of India
- Canara Bank
- Bank of Maharashtra
- Bank of India
- Bank of Baroda
2.4.1.1 State Bank of India Group
- State Bank of India (SBI) is a public sector bank of India. It is the largest commercial bank in India.
- All the Presidency banks merged to form the Imperial Bank of India. Later the Imperial Bank of India was turned into State Bank of India in 1955 under the enactment of the State Bank of India Act, 1955.
- Its headquarters is in Mumbai.
- Dinesh Kumar Khara is the current chairman of SBI.
2.4.1.2. Nationalized Banks
- The Nationalization of Banks was started from the nationalisation of Reserve bank of India in 1949.
- Reserve Bank of India was nationalization on 1st January 1949 under the Reserve Bank (Transfer of Public Ownership) Act, 1948.
- State Bank of India was nationalized in the year 1955 under the SBI Act of 1955.
- All the associated banks of SBI were nationalised as subsidiaries of the State Bank of India in 1959.
- On 19th July 1969, 14 major commercial banks with deposits exceeding Rs. 50 crores were nationalized.
- On 15th April 1980, 6 more commercial banks were nationalized which were having deposits above Rs.200 crores.
2.4.1.3. Regional Rural Banks
- These banks were established on the 26th September 1975 under the RRB Act, 1976. These are government owned scheduled commercial banks of India that operate at the regional level
- The main objective to establish the RRBs was to ensure sufficient institutional credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- Being a local level institution, RRBs were entrusted with an important role in the disbursement of agricultural and rural credit in association with commercial and co-operative banks.
- The Central Government, the respective State Government and the sponsor bank in the ratio of 50:15:35 contributes to the equity of RRB.
- Reserve Bank exercises the function of financial regulation over RRBs, and NABARD is vested with the supervisory powers.
2.4.2. Private Sector Banks
- The majority of shares of the Private sector banks are kept by private individuals.
- Private sector banks are treated as banking companies, as defined in the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- These banks are registered as companies with limited liability.
- Examples: ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, HDFC Bank, etc.
- As of 2022, there are a total of 22 Private sector Banks in India.
2.4.2.1. Domestic Banks
- The Reserve Bank had released the Framework for dealing with Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) on July 22, 2014.
- Starting in 2015, the Reserve Bank is required by the D-SIB framework to disclose the names of banks designated as D-SIBs and place them in appropriate buckets based on their Systemic Importance Scores (SISs).
- Depending on the bucket in which the D-SIB is placed, an additional common equity requirement will have to be applied.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has declared the State Bank of India (SBI), ICICI Bank, and HDFC Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) on January 4, 2022.
Universal banks
A universal bank is a financial services conglomerate that combines retail, wholesale, and investment banking services under one roof and reaping synergies between them. These banks would benefit from economies of scale in information technology and access to capital.
BNP Paribas, Deutsche Bank, Morgan Stanley, JP Morgan Chase, Citigroup, Bank of America, UBS, Credit Suisse, HSBC and Barclays are Universal Banks.
Differentiated banks
In 2014, the Reserve Bank of India released two guidelines for the licencing of two new types of banks: Payments Banks and Small Finance Banks.
- Small Finance Banks:
- Small Finance Banks is a public limited company under the Companies Act of 2013.
- Small financing banks will be granted a licence under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act of 1949.
- Small banks offer a whole range of banking services, including deposits and loans, but have a limited area of operation.
- Examples: AU Small Finance Banks, Equitas Small Finance Bank, Ujjivan Small Finance Bank, ESAF Small Finance Bank, Suryoday Small Finance Bank, etc.
- Payments Banks:
- Payments Bank is conceptualized by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 2015 on recommendation of Nachiket Mor Committee.
- The bank will be registered as a public limited company under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The bank will be licensed as payments banks under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Payments banks offer a limited range of products, such as demand deposit acceptance and fund remittances, but have a large network of access points, especially in remote areas.
- These can deposit an amount up to Rs.1,00,000 only. It does not provide loan or credit card facilities.
- Examples: Airtel Payments Bank, India Post Payments Bank, Fino Payments Bank, Paytm Payments Bank, Jio Payments Bank, etc.
Local Area Banks
Local Area Banks (LABs) were established as low-cost structures so that for providing efficient and competitive financial intermediation services in their areas of operation in the rural and semi-urban areas. These were introduced in 1996.
The scheme was launched with a minimum capital of Rs 5 crore and envisaged a local area bank, where the area of operation consisting of three contiguous districts.
Examples: Coastal Local Area Bank Ltd, Krishna Bhima Samruddhi LAB Ltd, Subhadra Local Bank Ltd
2.4.2.2. Foreign Banks
- Foreign banks are allowed to start his operation in India as branches or wholly owned subsidiaries (WOS).
- India’s commitment to WTO guides permission for opening of branches by foreign banks in India.
- These types of banks are regulated by both home and hosted countries.
- Its headquarters is based in the home country and branches are operated in the hosted country.
- Examples: HSBC, Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank, etc.
2.5. Co-operative banks
These are banks that are organised under the provisions of the cooperative society law of the state.
- They were originally set up to provide credit to the farmers at cheaper rates. However, the co-operative banks also function in the urban sectors.
- They generally provide services like loans, deposits, banking accounts, etc.
- These banks are the primary financiers of small and medium scale industries, agricultural activities & self-employed workers.
- Co-operative banks function on the basis of “no-profit no-loss”.
- The first mutual aid society in India, the 'Anyonya Sahakari Mandali,' was founded on February 5, 1889, in Gujarat at Baroda.
2.5.1. Characteristics of Co-operative Societies
- They have a restricted operating region.
- The Board of Directors is democratically elected by the shareholders.
- Borrowing from these institutions is limited to their members alone.
- There is share linking for borrowing, i.e. a part of the amount borrowed will be contributed to the share capital of the institution.
- Members can only vote once, regardless of how many shares they own.
- These institutions' shares cannot be listed or traded.
Traditionally, the cooperative structure is divided into two parts: 'Urban Co-operative' and 'Rural Co-operative'
2.5.2. Urban Co-operative Banks
- Urban Co-operative Banks cater to the financial needs of customers in urban and semi-urban areas.
- Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs) are primarily registered as co-operative societies under the provisions of the State Co-operative Societies Act of the State concerned.
- If the bank's operations extended in more than one state, it must be registered under the Multi State Co-operative Societies Act of 2002.
- These banks have been licensed by RBI to carry on banking business and are therefore under the dual control of RBI and Registrar of Co-operative Societies.
2.5.3. Rural Co-operative Banks
- Rural credit cooperatives were formed primarily as an institutional framework to offer farmers low-cost credit and to address the twin concerns of rural debt and poverty.
- They continue to play a critical role through the short-term and long-term structures like:
- Distribution of credit for enhancing production
- Guaranteeing food security
- Creating employment possibilities in rural regions
- Ensuring social and economic justice for the poor and vulnerable
- The long-term co-operative credit structure has the State Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (SCARDBs) at the apex level.
- Farmers and rural artisans largely use the country's short-term co-operative credit structure (STCCS) to meet their crop and operating capital needs.
2.6. Development Banks
- Development Banks are specialized financial institutions that are formed to promote economic development in the country.
- They provide medium-term and long-term loans to entrepreneurs at a comparatively low rate of interest rates.
- A development bank does not accept deposits from the public, like commercial banks and other financial institutions.
- India's first Development Bank, the Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI) was founded in 1948.
- Some examples of Development Banks are: Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), SIDBI
2.7. Specialized Banks
- Banks that mainly focus to provide overall support for setting up business in specific areas of activity are known as specialized banks.
- Examples of Specialized Banks are -EXIM Bank, SIDBI and NABARD.
- SIDBI provides a loan for a small-scale industry or enterprise.
- EXIM Bank helps to take loans or other financial aid for exporting or importing goods from other nations.
- NABARD helps with any type of financial support for rural, handicraft, village, and agricultural development.
3. Merger of Various Banks
- Dena and Vijaya Bank were merged with Bank of Baroda.
- Oriental Bank of Commerce and United Bank of India were merged with Punjab National Bank (PNB).
- Syndicate Bank was merged with Canara Bank.
- Andhra Bank and Corporation Bank were merged with Union Bank of India.
- Allahabad Bank was merged with Indian Bank.
- State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur, State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of Mysore, State Bank of Patiala, State Bank of Travancore, and Bharatiya Mahila Bank were merged with State Bank of India.
4. List of Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs)
| Types of Banks | Number of Banks |
| Public Sector Banks | 12 |
| Private Sector Banks | 22 |
| Regional Rural Banks | 43 |
| Foreign Banks | 46 |
| Payments Banks | 4 |
| Small Finance Banks | 11 |
Summary
Banks are special institutions that accomplish the seemingly simple duty of accepting deposits and lending them out.
Bank of Bombay was the first Joint-stock bank of India. It was established in the year 1720 in Bombay.
Bank of Bengal and Bank of Bombay and Bank of Madras were the three “Presidency Banks” of India.
All three Presidency bank was merged into a single bank in 1921 and named it Imperial bank of India.
In India, banks are divided into two categories: scheduled and non-scheduled banks.
India's central bank is known as the Reserve Bank of India, which is a regulatory body under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It takes responsibility to regulate the Indian banking system and issue and supply Indian rupees.
Commercial banks are categorised into scheduled and non-scheduled commercial banks, which are regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Co-operative banks are banks that are organised under the provisions of the cooperative society law of the state.
Development Banks are specialised financial institutions that are formed to provide medium-term and long-term loans to entrepreneurs.
Specialized banks are banks that primarily focus on providing total support for setting up a business in certain areas of operation.




 Latest
Latest 



Comments