16 Mahajanapadas- Capital, Location, History
How did Mahajanapadas emerge from Janapadas?
- The term "Janapada" literally means the foothold of a tribe. It represents a settled way of life for tribe.
- Janapadas further evolved into larger political entities by the process of land-grabbing.
- It led to the formation of kingdoms known in Buddhist traditions as the Mahajanapadas or the great nations.
- The sixth century BC is known as an era of ‘Second Urbanisation’ in the Indian Subcontinent.
- The later Vedic period is known as Mahajanapada Period.
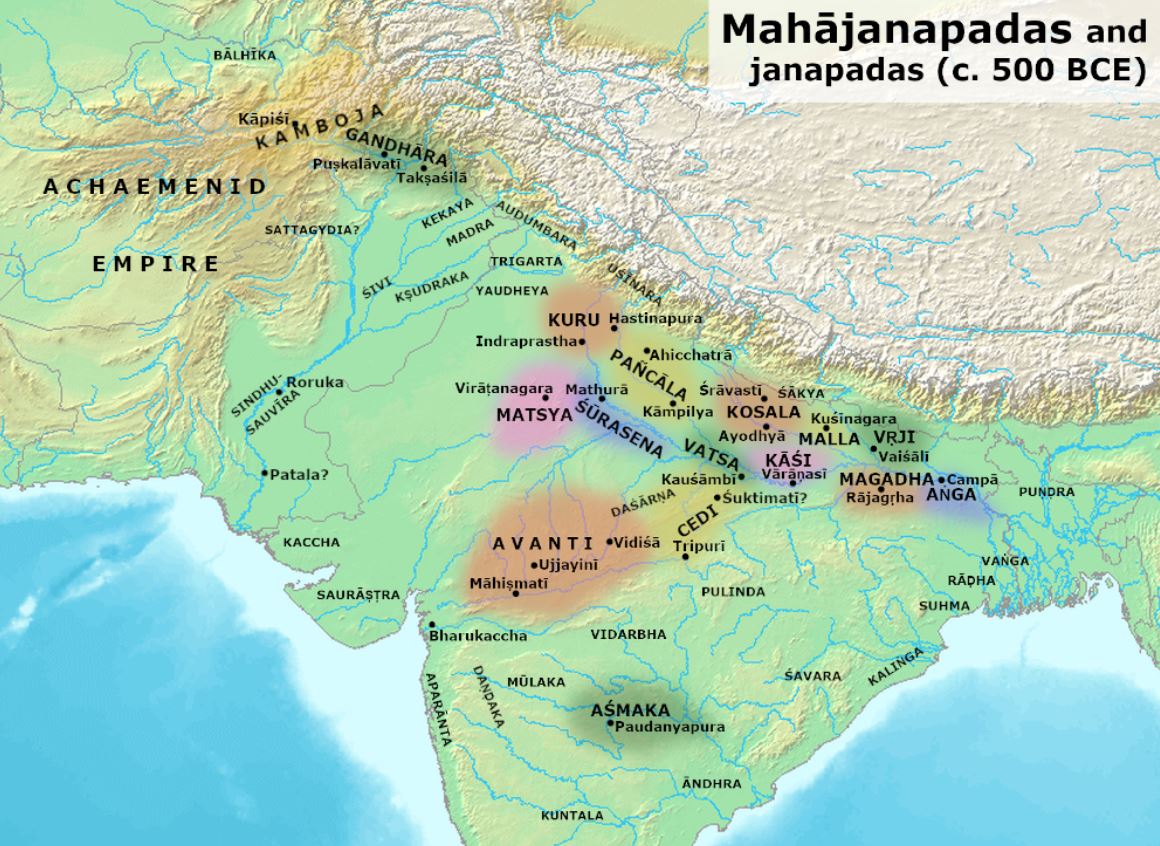
- The Mahajanapadas were a set of sixteen kingdoms that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE.
- These Mahajanapadas were monarchical in nature and had an oligarchical system of governance (small group of people hold most or all political power).
- Two of the Mahajanapadas were most probably gaṇasanghas (oligarchic republics) and others had forms of monarchy.
- The administration was run by an elected king with the help of a large council or assemblies comprising heads of all important clans and families.
List of Mahajanapadas, their Capital and their Modern location
| S. No | Mahajanapadas | Capital | Modern location |
| 1 | Anga | Champa | Munger and Bhagalpur |
| 2 | Magadha | Girivraja / Rajagir | Gaya and Patna |
| 3 | Kasi | Kasi | Banaras |
| 4 | Vatsa | Kausambi | Allahabad |
| 5 | Kosala | Sravasti | Eastern Uttar Pradesh |
| 6 | Saurasena | Mathura | Mathura |
| 7 | Panchala | Ahichchatra and Kampilya | Western Uttar Pradesh |
| 8 | Kuru | Indraprastha | Merrut and S.E. Haryana |
| 9 | Matsya | Viratnagar | Jaipur |
| 10 | Chedi | Sothivati / Banda | Bundelkhanda |
| 11 | Avanti | Ujjain / Mahismati | Madhya Pradesh & Malwa |
| 12 | Gandhar | Taxila | Rawalpindi |
| 13 | Kamboj | Pooncha | Rajori & Hajra (Kashmir) |
| 14 | Asmaka | Pratisthan / Paithan | Bank of Godavari |
| 15 | Vajji | Vaishali | Vaishali |
| 16 | Malla | Kusinara | Deoria & U.P. |
List of 16 Mahajanapadas in India
Anga
- The first reference to the Angas is found in the Atharvaveda along with the Magadhas.
- It was located at the confluence of the Ganga and Champa rivers.
- The present day bhagalpur and munger districts of eastern bihar was part of the anga.
- Its capital was Champa, which was one of the greatest cities of the sixth century BCE.
- Champa was surrounded by defensive fortifications including a moat.
Magadha
- It was spread over the areas of modern day Patna and Gaya districts of Bihar.
- It was bounded by the Ganga, Son and Champa rivers on the north, west, and east respectively.
- Its first capital was Girivraja or Rajagriha, modern Rajgir. Later, its capital shifted to Pataliputra.
- It was ruled by the Brihadratha dynasty, the Haryanka dynasty (544–413 BCE), the Shaishunaga dynasty (413–345 BCE), the Nanda dynasty (345–322 BCE), the Mauryan dynasty (322–184 BCE), the Shunga dynasty (184–73 BCE) and the Kanva dynasty (73–28 BCE).
- The earliest reference to the Magadha people was found in the Atharvaveda.
- Magadha reference is also presence in the Ramayana, the Mahabharata and the Puranas.
Avanti
- It was one of the most powerful Mahajanapadas in the 6th century B.C.
- The core area of this kingdom is present Ujjain district of Madhya Pradesh.
- It was divided into two parts by the Vindhyas, the northern part had its capital at Ujjayini and the southern part had its centre at Mahishmati.
Matsya
- The Matsyas were located in the Jaipur-Bharatpur-Alwar region of Rajasthan.
- The Matsya tribe was first mentioned in the Ṛigveda.
- Their capital was at Viratnagara famed as the hiding place of the Pandavas.
- Matsya kingdom are mentioned in various texts such as the Satapatha Brahmana, the Kausitaki Upanisad, and the Mahabharata.
Mallas
- The Mallas were a confederacy of nine clans. The Mallas were close allies of the Vajjis.
- There were two main political centres- Kusinara and the capital Pava.
- Kusinara has been identified with Kasia, Janapadas and Mahajanapadas about 77 km east of Gorakhpur.
Vajji
- It is spread over the area of Basadh, near Muzaffarpur area in Bihar.
- Gandak River marking its western boundary and the Koshi and Mahananda Rivers defining its eastern limit.
- Vajji confederation emerged as a republic during the time of Mahavira and Gautama Buddha.
- Magadha king Bimbisara also established marriage alliances with the Vrijji ganasangha.
- Vajjis as a confederacy of eight or nine clans. In this confederacy the clans maintained an equal, and independent status.
Chedi
- It was situated in the eastern part of Bundelkhand in Central India.
- It was ruled by Sisupala, an ally of Jarasandha of Magadha.
- It is the place where Pandavas spend their 13 years of exile.
- Shuktimati was the capital of the Chedi Mahajanapada
Kashi
- It was located in the region around its capital Varanasi.
- It was one of the earliest mahajanapadas to gain political prominence.
- It was bound by the Varuna river in the north and the Asi river in the south.
- Later, Kashi was included into the Kosalan kingdom during the Buddha’s time.
Kosala
- It was bounded by the Sadanira (modern day Gandak) on the east and the Gomati on the west, the Sarpika or Syandika (Sai) on the south, and the Nepal hills to the north.
- It incorporated the territory of the Shakya clan in the 5th century.
- The capital of north Kosala was Shravasti. The capital of south Kosala was Kushavati.
- Saket and Ayodhya were the other two important centres within the kingdom.
- Pasenadi (also known as Prasenajit) was the most popular ruler of Kosala, and was contemporary to the Buddha.
- Lucknow, Gonda, Faizabad, Baharaich of present day Uttar Pradesh was part of the Kosala.
Kuru
- The people of Kuru were part of the Puru-Bharata family.
- Its area was near to modern Delhi and the adjoining doab region.
- Kauravas and Pandavas were associated with the Kuru Mahajanapadas.
- The capital of the Kurus was at Hastinapur.
- It was a highly important state during the later Vedic period.
Panchal
- Panchal kingdom was divided into: Uttara Panchala and Dakhsina Panchala.
- It was spread over the northern region of the Himalayas and included the river Charmanwati, Kuru, and Matsya kingdoms from the west and extended up to the Naimisha Forest to the east.
- Ahichchhatra was capital of northern Panchala and Kampilya was capital of southern Panchala.
- It was annexed into the Nanda Empire during the reign of Mahapadma Nanda.
Shurasena
- Shurasena Janapada got its name from the Shura, the father of Vasudeva and Kunti.
- It was located in the region of Brij region of Uttar Pradesh and west of Yamuna.
- In the Mahabharata and the Puranas the ruling family of Mdhura is referred to as Yadus. Krishna is associated with these ruling families.
- Mathura was located at the junction of two famous ancient Indian trade routes i.e. Uttarapatha and the Daksinapatha.
- It had its capital at Mathura.
- The coins in two denominations Half-Karshapana and Mashaka were issued by Shurasena Janapada.
- It was annexed by the Magadha Empire.
Vatsa
- It was a powerful mahajanapada under the leadership of the famous king Udayana.
- Vatsa with its capital at Kausambi was one of the most powerful principalities of the sixth century B.C.
- Kausambi was an important point on the trade routes connecting the Deccan, the Ganga valley and the north-west.
- Kausambi has been identified with modem Kosam or the river Yamuna near Allahabad.
- The Vatsas were a branch of the Kuru dynasty.
- The Vatsas were further divided into two branches—One at Mathura, and the other at Kaushambi.
Gandhara
- It was located on both sides of the Indus river.
- It is corresponded to the modern Rawalpindi District of modern-day Pakistani Punjab and Peshawar District.
- Gandhara was also conquered by Persian emperor Darius in around 6th Century BE.
- The capital of Gandhāra was Takṣasila.
- Gandharis tribe has been mentioned in Rigveda as a tribe that has sheep with good wool
Kamboja
- Kamboja was located somewhere close to Gandhara.
- Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people of the Kshatriya caste inhabiting the Kamboja Mahajanapada region.
- Kambojas inhabited the northeastern most part of the territory populated by Iranian tribes.
- Rajapura (Eastern branch) Kapisi (Western branch) was the capital of the Kamboja.
- The major Indian epic Mahabharata also mentions the Kambojas.
Asmaka
- "Asmaka" (Sanskrit) signifies "stony region" and was located in the Deccan region.
- It was existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE around Godavari river.
- It was located between Mulaka and Kalinga.
- The capital of Aśmaka was known as Podana, Potali, Paudanyapura, and Potana.
- During the Mahajanapada period, Asmaka annexed the small kingdom of Mulaka.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Rise of Mahajanapadas
How many Mahajanapadas were there during 6th Century B.C.?
The Mahajanapadas were a set of sixteen kingdoms that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE.
What was the first capital of the Magadha Mahajanapada?
The first capital of Magadha was Girivraja or Rajagriha, modern Rajgir. Later, its capital shifted to Pataliputra.
Which Mahajanapada’s Capital was Viratnagara?
Matsya Mahajanapada’s Capital was Viratnagara.
Which Mahajanapada was located near to modern Delhi?
Kuru was located near to modern Delhi and the adjoining doab region.
Udayana was the famous king of which Mahajanapada?
Vatsa was a powerful mahajanapada under the leadership of the famous king Udayana.
Which mahajanapada emerged as the most powerful mahajanapada?
Magadha mahajanapada emerged as the most powerful mahajanapada.




 Latest
Latest 



Comments