Highlights of Union Budget 2025-26
Union Minister of Finance, Nirmala Sitharaman, presented the Union Budget 2025-26 in Parliament with the theme “Sabka Vikas” stimulating balanced growth of all regions.
The Finance Minister outlined the broad Principles of Viksit Bharat, these are as follows:
- Zero-poverty
- Hundred per cent good quality school education
- Access to high-quality, affordable, and comprehensive healthcare
- 100% skilled labour with meaningful employment
- 70 % women in economic activities
- Farmers making our country the ‘food basket of the world’.
Union Budget highlights that Agriculture, MSME, Investment, and Exports are four engines in the journey to Viksit Bharat.
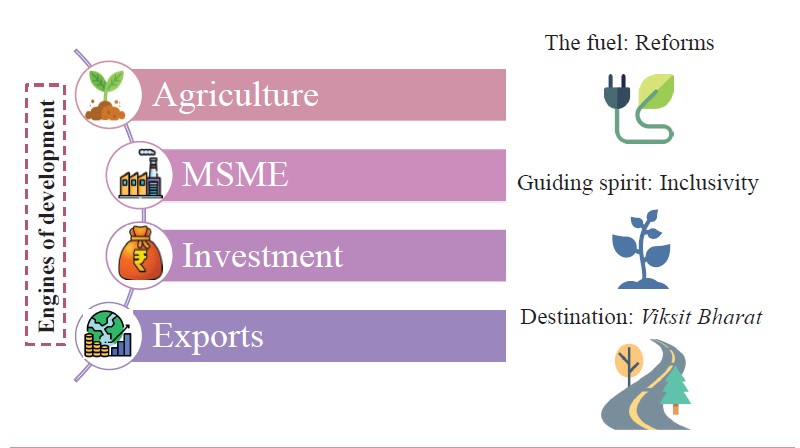
1st Engine: Agriculture
- ‘Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana’ has been announced in the budget.
- It will be implemented in partnership with states by covering 100 districts to increase productivity, adopt crop diversification, augment post-harvest storage, and facilitate the availability of long-term and short-term credit.
- ‘Rural Prosperity and Resilience’ programme will be launched to resolve the issue of underemployment in agriculture through skilling, investment, technology, and invigorating the rural economy.
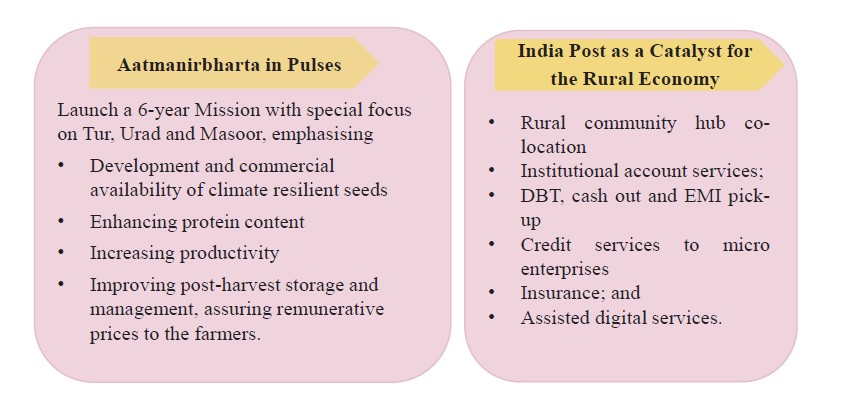
- The government will launch a 6-year “Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses” with a special focus on Tur, Urad and Masoor.
- The loans limit taken through Kisan Credit Cards has been increased from Rs 3 lakh to Rs 5 lakh.
- A Makhana Board will be established in Bihar to improve the production, processing, value addition, and marketing of makhana.
- A National Mission on High Yielding Seeds will be launched to strengthen the research ecosystem, targeted development and propagation of seeds with high yield, and commercial availability of more than 100 seed varieties.
- A 5-year Mission for Cotton Productivity has been announced for improvements in the productivity and sustainability of cotton farming, and to promote extra-long staple cotton varieties.
2nd Engine: MSMEs
- In the budget, a new scheme for 5 lakh women, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes first-time entrepreneurs has been announced to provide term-loans up to ₹ 2 crore in the next 5 years.
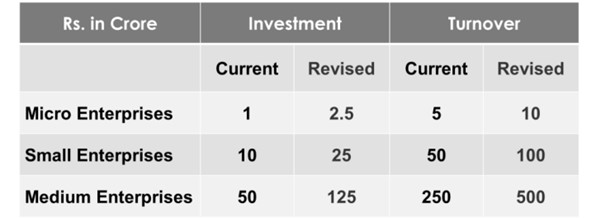
- The investment and turnover limits for classification of all MSMEs enhanced to 2.5 and 2 times.
- The Government will also implement a scheme to make India a global hub for toys representing the 'Made in India' brand.
- The Government will set up a National Manufacturing Mission for covering small, medium and large industries.
- A new Fund of Funds, with an expanded scope and a fresh contribution of ₹ 10,000 crore, will be set up by the government for the Indian startup sector.
3rd Engine: Investment
- The government announced that 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs will be set up in Government schools in the next 5 years.
- Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme will be implemented to provide digital-form Indian language books for school and higher education.
- Under the Bharatnet project, broadband connectivity will be provided to all government secondary schools and primary health centres in rural areas.
- A Centre of Excellence in Artificial Intelligence for education will be set up with a total outlay of 500 crore.
- Five National Centres of Excellence for skilling will be set up in partnership with global experts.
- For capital expenditure and incentives for reforms, an outlay of Rs 1.5 lakh crore was proposed for the 50-year interest free loans to states.
- Jal Jeevan Mission will be extended till 2028 by focussing on the quality of infrastructure and Operation & Maintenance of rural piped water supply schemes through “Jan Bhagidhari”.
- Urban Challenge Fund of Rs.1 lakh crore will be set up by the government to implement the proposals for ‘Cities as Growth Hubs’, ‘Creative Redevelopment of Cities’ and ‘Water and Sanitation’.
- The government will set up Day Care Cancer Centres in all district hospitals in the next 3 years, with 200 Centres in 2025-26.
- ₹20,000 crore has been allocated for private sector-driven Research, Development and Innovation initiatives.
- The Gyan Bharatam Mission has been proposed for the survey, documentation and conservation of more than 1 crore manuscripts in collaboration with academic institutions, museums, libraries, and private collectors.
- Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme announced to provide digital-form Indian language books for school and higher education.
- A National Digital Repository of Indian knowledge systems for knowledge sharing has been also proposed in the budget.
- PM SVANidhi scheme for street vendors will be revamped with enhanced loans from banks and UPI-linked credit cards with Rs 30,000 limit.
- The Nuclear Energy Mission for research & development of Small Modular Reactors (SMR) will be set up with an outlay of ₹20,000 crore.
- Under this Mission, 5 indigenously developed SMRs to become operational by 2033.
- A Maritime Development Fund with a corpus of ₹ 25,000 crore will be set up.
- A policy for the recovery of critical minerals from tailings will be brought by the government.
- 2nd Gene Bank with 10 lakh germplasm lines will be set up for future food and nutritional security.
- A National Geospatial Mission has been announced to develop foundational geospatial infrastructure and data.
4th Engine: Exports
- ‘BharatTradeNet’ (BTN) for international trade will be set up as a unified platform for trade documentation and financing solutions.
- The government will set up an Export Promotion Mission with the help of Ministries of Commerce, MSME, and Finance.
- For promoting Global Capability Centres in emerging tier 2 cities, a national framework will be formed to guide states.
REFORMS AS FUEL: FINANCIAL SECTOR REFORMS AND DEVELOPMENT
Major Reforms proposed in the Budget:
- For those companies which invest the entire premium in India, the FDI limit for the insurance sector will be raised from 74 to 100 per cent.
- Public Sector Banks will develop a ‘Grameen Credit Score’ framework to full fill the credit needs of SHG members and people in rural areas.
- An Investment Friendliness Index of States will be launched in 2025 to enhance the spirit of competitive cooperative federalism.
- The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 will decriminalize more than 100 provisions in various laws.
- High-Level Committee for Regulatory Reforms will be formed to review all non-financial sector regulations, certifications, licenses, and permissions. The committee will make recommendations within a year.
- A mechanism will be set up under the Financial Stability and Development Council to evaluate the impact of current financial regulations.
Main Tax Proposals in the Finance Bill
- The annual limit for TDS on rent will be six lakh rupees.
- The limit of TCS on remittances has increased from seven lakh rupees to Rs 10 lakh.
- Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC) has been introduced in the budget.
- For several tax exemptions, the starting date of operations of an IFSC unit has been extended to March 31, 2030.
- Eligible start-ups established before April 1, 2030, would get a tax incentive for three consecutive years out of ten years from incorporation.
- The budget proposes to remove seven tariffs, apply appropriate cess to maintain effective duty incidence, and levy not more than one cess or surcharge as part of the rationalization of Customs tariffs of industrial goods.
- The budget proposed to extend the date of investing in Sovereign Wealth Funds and Pension Funds by five more years till 31st March 2030.
Revised tax rate structure
- Under the new regime, no personal income tax is payable up to an income of Rs 12 lakh.
- This limit will be Rs 12.75 lakh for salaried taxpayers, due to a standard deduction of Rs 75,000.
- The new Income-Tax Bill will be brought to make income tax simple to understand for taxpayers and tax administration.
| Tax Rate | Current Income Slab | New Income Slab |
| Nil | Up to ₹3 lakh | Up to ₹4 lakh |
| 5% | ₹3 lakh – ₹7 lakh | ₹4 lakh – ₹8 lakh |
| 10% | ₹7 lakh – ₹10 lakh | ₹8 lakh – ₹12 lakh |
| 15% | ₹10 lakh – ₹12 lakh | ₹12 lakh – ₹16 lakh |
| 20% | ₹12 lakh – ₹15 lakh | ₹16 lakh – ₹20 lakh |
| 25% | Not Applicable | ₹20 lakh – ₹24 lakh |
| 30% | Above ₹15 lakh | Above ₹24 lakh |
Budget Estimates 2025
- GDP: The government has estimated a nominal GDP growth rate of 10.1% in 2025-26.
- Expenditure: The government expenditure is estimated to be Rs 50,65,345 crore in 2025-26, 7.4% higher than the revised estimate of 2024-25.
- Expenditure on pension: The government has estimated to spend Rs 2,76,618 crore on pension in 2025-26, which is 0.6% higher than the revised estimate of 2024-25.
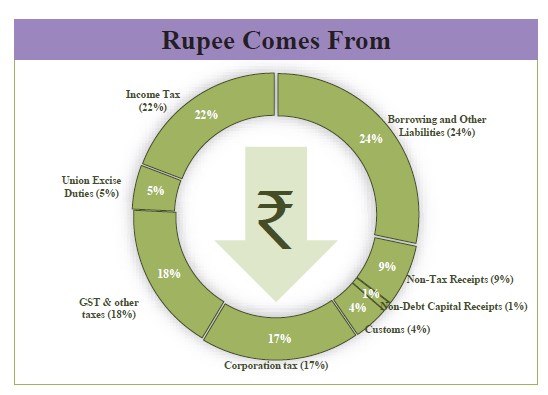
- Receipts: The receipts (other than borrowings) in 2025-26 are estimated to be Rs 34,96,409 crore, which is 11.1% more than the revised estimate of 2024-25.
- Capital receipts: It is estimated to be Rs 76,000 crore (excluding borrowings), an increase of 28.8% over the revised estimates for 2024-25.

(Source: PIB)
- Tax Revenue:
- Gross tax revenue is budgeted to increase by 10.8% in 2025-26.
- Corporation tax and income tax for 2025-26 are expected to increase over the revised estimates of 2024-25 by about 10.4% and 14.4%, respectively.
- Indirect taxes: Total indirect tax collections are estimated to be Rs 17,35,100 crore in 2025-26, out of which the government has estimated to raise Rs 11,78,000 crore from GST.
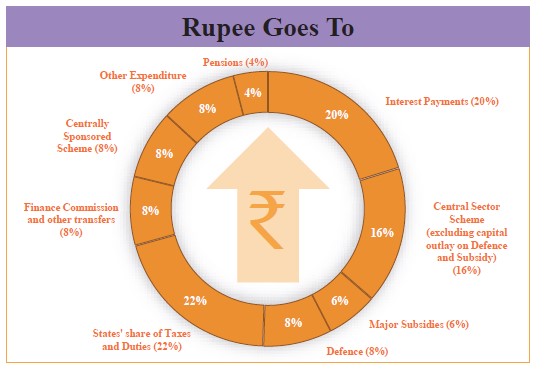
- Deficits:
- Revenue deficit in 2025-26 is estimated to be 1.5% of GDP. It is lower than the revised estimate of 4.8% of GDP in 2024-25.
- Fiscal deficit in 2025-26 is targeted at 4.4% of GDP. It is less than the revised estimate of 4.8% of GDP in 2024-25.
- Debt: In 2025-26, outstanding liabilities are estimated to be 56.1% of the GDP.
- Transfer to states: The central government will transfer Rs 25,59,764 crore to states in 2025-26, an increase of 12.5% over the revised estimate of 2024-25.
- Disinvestment: The government is estimated to meet 66% of its disinvestment target in 2024-25. The disinvestment target for 2025-26 is Rs 47,000 crore.

(Source: PIB)
Expenditure by Ministries
- The Ministry of Defence has got the highest allocation in 2025-26 of Rs 6,81,210 crore. It got 13.4% of the total budgeted expenditure of the central government.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has been allocated Rs 2.87 lakh crore.
- The Ministry of Railways received Rs 2.55 lakh crore.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has been allocated Rs 2.33 lakh crore.
- The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution received Rs 2.15 lakh crore.
- The Ministry of Rural Development received Rs 1.90 lakh crore.
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare has received Rs 1.38 lakh crore.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare received Rs 1.00 lakh crore.
- The Ministry of Education has been allocated 1,28,650 crores in the budget 2025-26.
List of Major Custom Duty exemptions
- 36 lifesaving drugs and medicines have been fully exempted from Basic Customs Duty (BCD).
- BCD on Wet Blue leather has been fully exempted and Crust leather has been exempted from 20% export duty.
- Cobalt powder and waste, the scrap of the lithium-ion battery, Lead, Zinc and 12 more critical minerals are fully exempted from BCD.
- In the shipping sector, the exemption of BCD on raw materials, components, consumables or parts for the manufacture of ships extended for another ten years.
- BCD on Frozen Fish Paste (Surimi) for the manufacture and export of its analogue products has been reduced from 30% to 5%.
Other major points of Budget 2025
- In the next five years, 10,000 additional seats will be added in medical colleges and hospitals with a goal of adding 75,000 seats.
- Under the PM Research Fellowship scheme, 10,000 fellowships will be provided for technological research in IITs and IISc.
- The Atomic Energy Act and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act will be amended to allow private-sector partnerships for the development of nuclear energy.
- A National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship and Management to be set up in Bihar.
- A plant with an annual capacity of 12.7 lakh metric tons is to be set up at Namrup, Assam.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Union Budget 2025-26
What is the theme of Union Budget 2025-26?
Finance Minister presented the Union Budget 2025-26 with the theme “Sabka Vikas”.
What is the fiscal deficit target of government as per Budget 2025?
In the budget 2025–26, the government has kept the budget deficit target to 4.4 percent of GDP.
As per the Union Budget 2025, what is the income limit upto which no income tax will be payable?
As per the Union Budget 2025-2026 announced on February 1, the income limit upto which no income tax will be payable is Rs. 12 lakh.




 Latest
Latest 



Comments