Styles of Temple Architecture in India
This article is important for the candidates preparing for various government exams as one will definitely find two-three questions or even more than that from the topic ‘Art and Culture’. Characteristics of different styles along with examples are covered so as to clear the concepts. This article is also important for those preparing for State PCS Prelims as well as Mains.
Introduction
Different styles of temple architecture are famous in different parts of India. The development of the distinctive architectural style of these temples is a result of geographical, ethnic and historical diversity.
The two major styles of temple architecture in the country are known as Nagara in the north and Dravidian in the south. The third style, Vesara Style, is fusion of Nagara and Dravidian style of architecture.
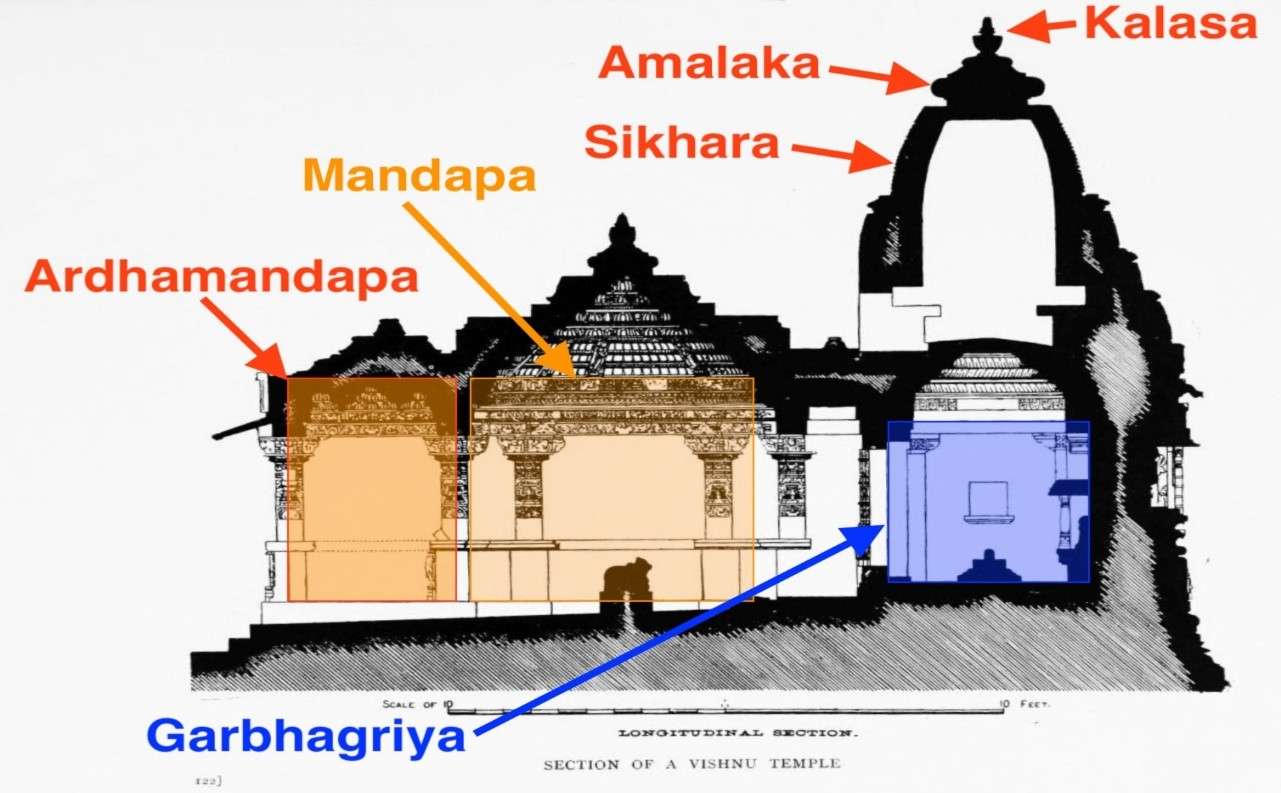
Nagara style
Nagara style features are as follows-
- In North India, an entire temple is built on a high stone platform.
- It generally did not have large enclosures and entrances.
- Initially, the temples had only one peak or shikhara, below which is located Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum). In later temples, many other peaks were also built along with the main shikhara.
- The main deity was installed in the sanctum sanctorum.
- The sanctum was always located under the tallest tower.
- Amalakh or Kalash which is installed on the shikhara of the temple is another feature of this style.
- Kandariya Mahadev Temple in Madhya Pradesh is a classic example of Nagara style of temple architecture. It was also included in the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1986.
- Other examples are Sun Temple at Modhera, Lakshman Temple of Khajuraho, Sun Temple at Konark, Jagannath Temple at Puri, etc.
Dravidian style
The characteristics of the Dravidian style are as follows:
- Large walls surround the Dravidian temple. There is a huge gate for entry inside which is called Gopuram.
- The main temple has a geometric shaped pyramid-like tower known as Vimana.
- There was a large water reservoir within the boundary of the temple.
- Ancillary temples were also built in it. Ancillary temples were either included within the tower of the main temple, or are located as small temples next to the main temple.
- The Brihadishsvara temple at Thanjavur in Tamil Nadu is a unique example of Dravidian architecture.
- Other examples are Shore Temple at Mahabalipuram, Kailashnath Temple at Ellora,

Vesara style
The characteristics of the Vesara style are as follows:
- It is a hybridized style that became popular after mid-7th century in the Deccan architecture.
- The shape of the superstructure over the sanctum is usually pyramidal and is shorter than northern shikara tower.
- The Hoysaleshvara Temple at Halebid, Karnataka is an example of this type of architecture. The temple is dedicated to Shiva as Nataraja.
- Other examples are Kedareshvara Temple at Balligavi, Chennakeshava Temple at Belur, Chalukyan Temple at Pattadakal, etc.





 Latest
Latest 



Comments