Commands of Indian Army | Values of Indian Army | Structure of Indian Army | Organization of Indian Army
The soldiers in the Indian Armed forces live for three Ns- Naam (Honour), Namak (loyalty to Nation) and Nishan (flag of the unit or Nation). The values of comradeship, team spirit and unity can be seen across all ranks of the army.
1. Values of the Indian Army
1. Espirit-de-Corps: The spirit of comradeship and brotherhood of the brave, regardless of caste, creed or religion. The motto is, "One for all and all for one"!
2. Spirit of Selfless Sacrifice
3. Valour Fearlessness in combat and in the face of the enemy
4. Non-discrimination: A soldier is a soldier first and anything else later.
5. Fairness and Honesty
6. Discipline and Integrity: Feeling of patriotism, honesty and courage under all circumstances is imparted through discipline and integrity.
7. Death to Dishonour
8. Forthrightness
2. Role of Indian Army
The Indian Army is mainly tasked to protect the territorial integrity of India and safeguard its sovereignty from external aggression. It also assists civil administration in case of a natural or man-made disaster or any other situation which requires the assistance of the Indian Army.
Indian Army also sends its troops in UN Peacekeeping missions. Indian Army leads role in United Nations Peacekeeping with presence in 8 out of 14 (current) United Nations Missions worldwide. Currently, 5,400 military personnel are deployed in challenging circumstances under the United Nations flag. Indian Army has a large presence in United Nations Missions in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Lebanon, South Sudan, Golan Heights, Syria, Western Sahara, Abyei and Cyprus. India is also deploying an infantry Battalion Group in UNISFA (Abyei).
3. Structure of Indian Army
Indian Army is headed by the Chief of the Army Staff who is 4 star-rank General. There are a total of 7 commands, out of which 6 are operational commands and one is Army Training Command. Each command is headed by General Officer Commanding in Chief (GOC-IN-C) who is a 3-star rank Lieutenant General.
The army soldiers are further grouped into a fighting force.
Section: Commanded by Section Commander with a Rank of Havildar. 10 soldiers make a section.
Platoon: Commanded by Platoon Commander with Rank of JCO (Junior Commissioned Officer). It comprises of three sections.
Rifle Company: Commanded by Company Commander with Rank of Lieutenant Colonel/ Major. It comprises of three Platoons.
Battalion/ Regiment: Commanded by Commanding Officer with a Rank of Colonel. It comprises of Four Rifle Companies. This is the main fighting unit of infantry.
Brigade: Commanded by Brigade Commander with a rank of Brigadier (1-star). It comprises of 3- Battalions and support elements.
Division: Commanded by GOC (Division Commander) with a rank of Major General (2-star). It comprises 3-4 Brigades. Currently, Indian Army has 37 divisions including Infantry, Mountain, Artillery and Re-organised Army Plains Infantry or RAPIDS.
Corps: Commanded by GOC (Corps Commander) with a rank of Lieutenant General (3-star). It comprises of 3-4 Divisions.
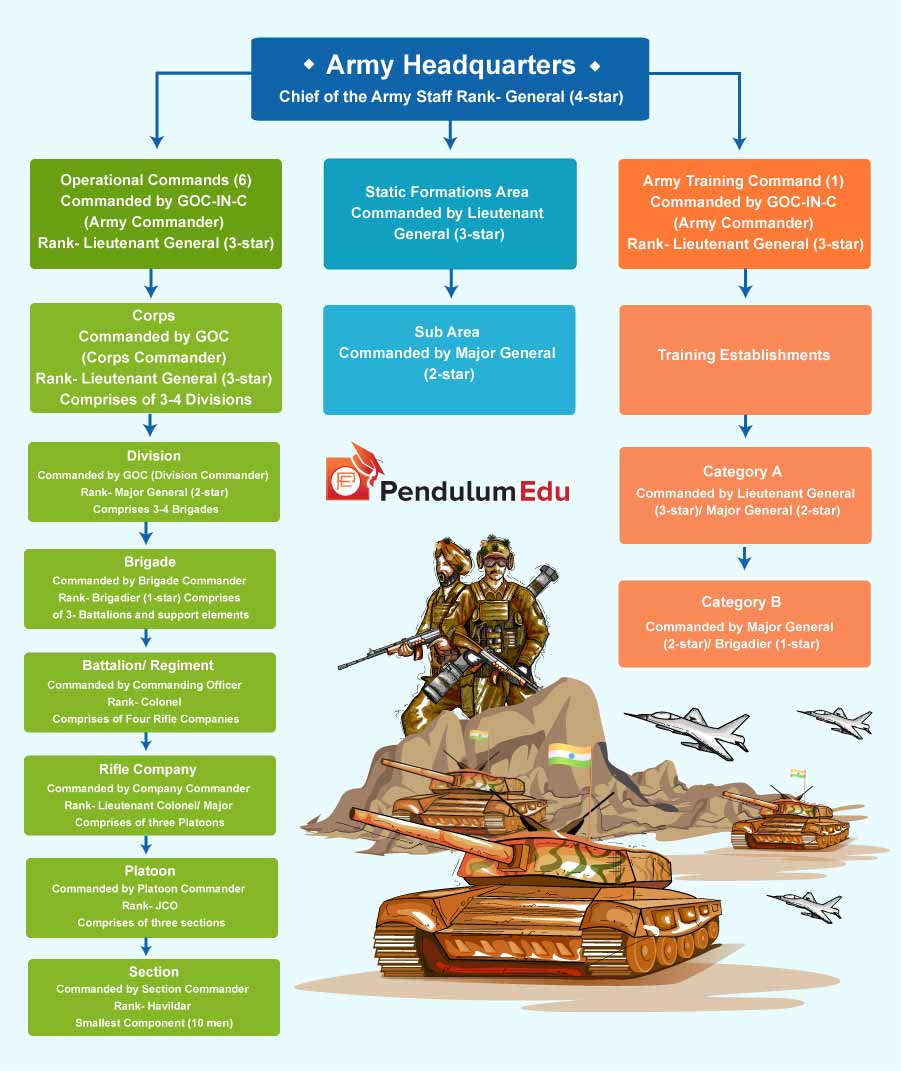
4. Commands of Indian Army
Indian Army has 7 commands- 6 operational and one training command called Army Training Command (ARTRAC).
| Command | Headquarters | GOC-in-C | Other points | Sub-ordinate units |
| Southern Command
| Pune, Maharashtra | Lt. Gen JS Nain | It is the oldest field formation of the Indian Army. | 2 Corps - XII Corps at Jodhpur, XXI Corps at Bhopal and 41st Artillery Division at Pune |
| Western Command
| Chandimandir, Haryana | Lt. Gen Nav K Khanduri | It was formed in 1920. | The Western Command has been assigned operational units: - II Corps (Ambala), IX Corps (Yol), XI Corps (Jalandhar) and 40th Artillery Division. |
| Eastern Command
| Kolkata, West Bengal | Lt Gen Rana Pratap Kalita | It was formed on 1 November 1920. | The Eastern Command has been assigned operational units under III Corps (Dimapur), IV Corps (Tezpur), XXXIII Corps (Siliguri) and a 23rd Infantry Division (Ranchi). |
| Northern Command
| Udhampur, Jammu and Kashmir | Lt Gen Upendra Dwivedi | It was originally formed in 1908 as the Northern Army of the British Indian Army. | Currently, the XIV Corps (Leh), XV Corps (Srinagar) and XVI Corps (Nagrota) control its operational units. |
| South-Western Command
| Jaipur, Rajasthan | Lt Gen Amardeep Singh Bhinder | It was established on 15 April 2005 and became fully operational on 15 August 2005. | 42nd Artillery Division (Jaipur), I Crops (Mathura), X Corps (Bhatinda) |
| Central Command
| Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh | Lt Gen Yogendra Dimri | The Command was first established in 1942 and then re-established on 1 May 1963. | I Corps (Mathura) |
| Army Training Command (ARTRAC)
| Shimla, Himachal Pradesh | Lt Gen SS Mahal | It is the only non-operational command as it has all service training institutes under it. It was established on 1 October 1991 at Mhow but then shifted to Shimla in 1993. | - |
India also has a tri-services command- Strategic Forces Command, Integrated Defense Staff and Andaman and Nicobar Command headed by Army, Navy and Air Force officers on a rotational basis.
5. Organisation of the Indian Army
Indian Army is organized in two parts - Combat Arms and Services.
A. Combat Arms: This is the fighting force of the Army. It comprises of-
1. Armoured Corps It consists of tanks as its main weapons. They also provide vital support to the Infantry (foot soldiers).
2. Mechanized Infantry - Mechanised Infantry is the latest arm of the Indian Army.
3. Infantry - These are fighting troops who attack and occupy the captured ground. It is the most important and largest branch of the fighting forces in the Indian Army. It is supported by combat support arms which are:
- Artillery
- Corps of Engineers (also known as Sappers): These are Engineers who perform operations like laying and clearing of mines, constructing bridges, and roads and handling explosives. Their motto is Sarvatra or Everywhere.
- Corps of Army Air Defence: Their motto is Akashe Shatrun Jahi (Defeat the Enemy in the Sky).
- Army Aviation Corps: Their motto is Suveg Va Sudrid. It has a helicopter which can operate in different terrains, climatic conditions and other challenges.
- Corps of Signals: They ensure connectivity to soldiers in remote locations and provide cyber security in both peacetime and in war. Their motto is Teevra Chaukas or Intense Alertness.
B. Services: The remaining army is organised under the services to provide logistical (arms, ammunition, rations etc.) material to the army. The Services include the following departments:
- Army Service Corps
- Army Medical Corps
- Army Dental Corps
- Army Ordnance Corps
- Corps of Electronics and Mechanical Engineers
- Remount and Veterinary Corps
- Military Farms Service
- Army Education Corps
- Corps of Military Police
- Pioneer Corps
- Army Postal Service Corps
- Intelligence Corps
- Judge Advocate General's Department
- Military Nursing Service











 Latest
Latest 



Comments