Haryana at a Glance- Culture, Economy, Symbols, Geography, Tourism, Politics and Demography of Haryana
1. GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT HARYANA
- 1 November is celebrated as Haryana Day because Haryana was separated from Punjab on 1st Nov 1966.
- `Haryana' word meaning is inscribed on a stone found during the reign of Sultan Mohammad-bin-Tughlaq. Dharanidhar in his work Akhand Prakash says that “this word comes from Haribanka, connected with the worship of Hari, Lord Indra. Since the tract is a dry one, its people worshipped Indra (Hari) for rain”.
- Haryana ranks 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% (44,212 km2 or 17,070 sq mi) of India's land area.
- It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 November 1966 on a linguistic basis.
- Haryana’s most populous city is Faridabad, which is a part of the National Capital Region.
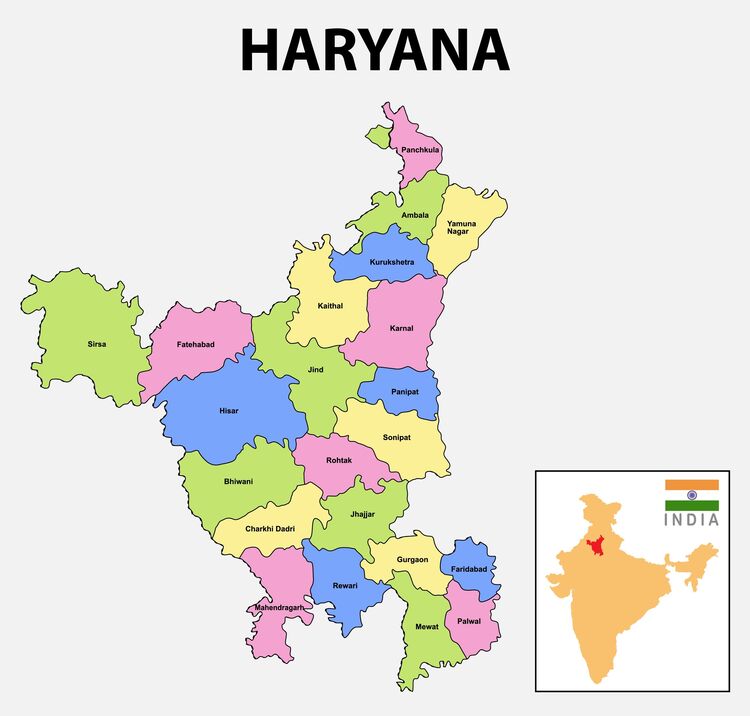
- Haryana has 6 administrative divisions, 22 districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 community development blocks, 154 cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 villages panchayats.
- Chandigarh is the capital city of Haryana & the language Punjabi is the official language.
STATE SYMBOLS OF HARYANA
| Haryana State Symbol | Name of Haryana State Symbol | Image of Haryana State Symbol |
| Haryana State Mammal | Black buck |
|
| Haryana State Bird | Black francolin |
|
| Haryana State Flower | Lotus |
|
| Haryana State Tree | Peepal |
|
| Haryana State Emblem |
|
|
2. HISTORY OF HARYANA
- Haryana’s ancient name is Hariyana.
- Haryana region was known as Brahmavarta, Aryavarta and Brahomoupdesa. These names are based on the emergence of Brahama-Lord on the land of Haryana; the abode of Aryas and home of preachings of vedic cultures.
- The history of Haryana finds its origin in the Vedic Age. This region is the land where the Bharata dynasty flourished and gave the name “Bharat” to India.
- Haryana finds mention in the writings which date back to 12th Century A.D.
- The Tomara Rajputs ruled over `Hariyana’ from Delhi when the Ghaznavids invaded India from north –west.
- Tomaras were overpowered by the Chahamanas who defeated Mahummad Ghuri in the First Battle of Tarain. While in Second Battle of Tarain, Chahamanas under Prthvi Raj, were defeated by Ghori and Prithvi Raj was captured and executed in 1192.
- The region was significantly less developed due to the repressive policy of the British government. It remained socially, educationally, economically and politically backward throughout the 19th century.
- It got further isolated after the change of capital from Calcutta to Delhi on 12 December 1911.
- In 1928, all parties conference at Delhi demanded for extension of boundaries of Delhi.
- In 1931, at the Second Round Table Conference, Financial Commissioner of the then Punjab Government suggested reorganization of the Punjab boundaries and the separation of Ambala division from Punjab.
- Rakhigarhi is an archaeological site belonging to the Indus Valley civilisation in Hisar District of Haryana.
3. GEOGRAPHY OF HARYANA
- Haryana is a landlocked state in northern India (between 27°39' to 30°35' N latitude and between 74°28' and 77°36' E longitude). Haryana has 4 states and 2 union territories on its border – Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, and Chandigarh.
- The total geographical area of the state is 44,212 sq km.
- Haryana is geographically divided into five divisions – The Bagar and undulating sandy plains, The Alluvial Plain, The Shiwaliks, Aravali Range and The Foot Hill zone. The plains form the largest part.
- The Forest and Tree Cover of the Haryana state is 6.49% of its geographical area.
CLIMATE AND SOIL
Haryana state is a vast ground of moist land. The climate of Haryana varies from moist sub- tropical in north bordering Himachal Pradesh to arid in southern part bordering Rajasthan. The summers are extremely hot and winters are quite cool. Occasional showers can be experienced during December-January.
Seasons
Haryana has three distinct seasons as given below:
- Summer Season - April to June
- Rainy Season - June to October
- Winter Season - December to February
Average annual rainfall range– 200 mm to 1400 mm
Average Annual Temperature range- 1 °C to 45 °C
Soils
- Haryana falls in the Agro Climatic Zone-VI, which is called “Trans-Gangetic Plains Region”.
- The type of soil commonly found in Haryana is alluvial. The alluvium is of the old type which consists of sand, silt, clay, and kankars in the whole region except for the floodplains of Ghaggar and Yamuna.
- Soil degradation problem is due to soil compaction, soil salinity, sodicity, water logging, and pesticide residue, and multiple nutrient deficiency. The agricultural land for non-agricultural use is an emerging big problem.
- Saline - Sodic Soils occur in different parts of India these soils are classified under ' Aridisols', ' Entisols' and ' Vertisols'. Saline soils are found in Jhajjar and Panipat districts of Haryana.
Haryana is often called the “Food Mine” of India. Majority of population is dependent on Agriculture.
Major Crops Grown in Haryana: Rice, jowar, bajra, maize, wheat, barley, gram, mustard (including rapeseed), cotton (both American and Desi) and sugarcane. The crops account for 88 per cent of total cropped area in the state in 2008-09.
The main kharif crops in the state include sugarcane, groundnut, maize and paddy etc. The minor kharif crops are chillies, bajra, jawar, pulses and vegetables.
Major Crops Fruits in Haryana: Additional area of 1570 hectare is under fruit cultivation in Haryana. The farming of fruits like mango, lichi, guava, ber, chiku, amla and citrus are under the horticulture department.
RIVERS, LAKES AND WATERFALLS
Important Lakes of Haryana:
- Badkal Lake - Faridabad
- Surajkund - Faridabad
- Blue Bird Lake – Hisar
- Damdama Lake - Gurugram district
- Hathni Kund – Yamunanagar district
- Karna Lake – Karnal
- Tilyar Lake – Rohtak
- Brahma Sarovar – Kurukshetra
Rivers of Haryana:
There are 4 river basins in Haryana. The state has no perennial river of its own. River Yamuna defines the eastern border of Haryana. The important rivers of Haryana are Ghaggar, Saraswati, Yamuna, Markanda, Sahibi, Indori, Somb, Dohan, Chautang, Krishnavati, etc.
NATIONAL PARK AND WILDLIFE SANCTUARY IN HARYANA
Haryana has two national parks, eight wildlife sanctuaries, two wildlife conservation areas, four animal and bird breeding centers, one deer park and three zoos, all of which are managed by the Haryana Forest Department.
| Name of National Park/ Wildlife Sanctuary | Year of Notification | Total Area (km²) |
| Kalesar National Park | 2003 | 46.82 |
| Sultanpur National Park | 1989 | 1.43 |
| Abubshehar Wildlife Sanctuary | 1987 | 115.3 |
| Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary | 1986 | 4.12 |
| Chhilchila Wildlife Sanctuary | 1986 | 0.29 |
| Bir Shikargarh Wildlife Sanctuary | 1987 | 7.67 |
| Kalesar Wildlife Sanctuary | 1996 | 54.06 |
| Morni Hills Wildlife Sanctuary | 2004 | 48.83 |
| Kharparwas Wildlife Sanctuary | 1991 | 0.83 |
| Nahar Wildlife Sanctuary | 1987 | 2.11 |
4. ECONOMY OF HARYANA
- Haryana is majorly an agricultural state with 80% of the total geographical area under agriculture.
- The economy of Haryana is the 13th largest in India, with a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of 7.65 trillion (US$100 billion). As per the advance estimates for 2021-22, the state’s GSDP at current prices has been estimated at Rs. 8,95,671.25 crore (US$ 120.11 billion). At current prices, Haryana’s GDP growth was projected at 18.1% for FY22.
- Though Haryana is geographically a small State, the contribution of the State to the National Gross Domestic Product at constant (2011-12) prices has been estimated as 3.8 percent as per Quick Estimates of 2018-19.
- The contribution of Agriculture and allied sectors was the largest (60.7%) at the beginning of 4th Five year plan (1969-70). Since the 11th five year plan, the contribution of the services sector is the highest (more than 50%).
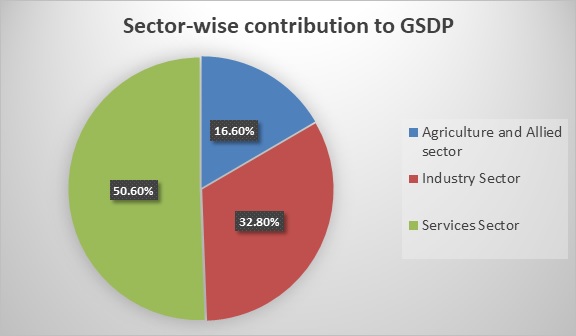
- The industries sector is split across 69% manufacturing, 28% construction, 2% utilities and 1% mining. Haryana produces India's 67% of passenger cars, 60% of motorcycles, 50% of tractors and 50% of the refrigerators making it one of India’s largest automobile hubs.
- Readymade cotton garments are one of the major exports from Haryana.
- Services sector is split across 45% in real estate and financial and professional services, 26% trade and hospitality, 15% state and central govt employees, and 14% transport and logistics & warehousing. It is the third largest exporter of software in India.
- Agriculture sector is split across 93% crops and livestock, 4% commercial forestry and logging, and 2% fisheries.
- More than 60 percent export of Basmati Rice is taking place from Haryana State.
- Haryana is traditionally an agrarian society of zamindars. The Green Revolution in Haryana of the 1960s and Western Yamuna Command Network canal system in 1970s resulted in significantly increased food grain production.
- As per Economic Survey of Haryana 2019-20, the area under Paddy crop was 14.47 lakh hectare in 2018-19. The area under commercial crops i.e. sugarcane, cotton and oilseeds has shown fluctuating trends. Haryana is fast emerging as one of the leading State in the field of Horticulture in India.
MINERALS
Mahendragarh is the richest district amongst others in Haryana in association with mineral resources. Minerals such as Limestone, Dolomite, Quartz, Slate, Barytes, Calcite, Felspar, Marble, Copper, etc are found in this district.
Haryana state is the principal holder of country's resources of tin (64%), quartz-silica sand (52%) and quartzite (49%). The value of mineral production in Haryana was Rs. 149 crore from minor minerals during 2011-12.
List of minerals found in Haryana
- China Clay - Faridabad, Gurgaon and Rewari Districts
- Limestone - Ambala, Bhiwani, Mahendragarh and Panchkula Districts
- Dolomite- Ambala and Mahendragarh Districts
- Quartz/ Silica Sand - Bhiwani, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Mahendragarh Districts
- Quartzite- Faridabad and Gurgaon Districts
- Slate - Mahendragarh and Gurgaon Districts
- Copper - Bhiwani and Mahendragarh Districts
- Tin and Tungsten - Bhiwani District
- Granite - Bhiwani District
5. KEY STATISTICS OF HARYANA –CENSUS 2011
There are 22 Districts in Haryana with 140 blocks and 7356 villages. A large area of Haryana is included in the NCR region. As per Haryana census data, 88.36% houses are owned while 9.55% were rented. It is the 17th most populated state in India. With an area of around 44000 sq. km, it is 20th largest state in India.
Faridabad is the largest city of Haryana.
| Demographic Label | 2011 | 2001 |
| Approximate Population | 2.54 Crores | 2.11 Crore |
| Total population | 25,351,462 | 21,144,564 |
| Male | 13,494,734 | 11,363,953 |
| Female | 11,856,728 | 9,780,611 |
| Total Literacy rate | 75.55% | 67.91% |
| Male Literacy | 84.06 % | 78.49 % |
| Female Literacy | 65.94 % | 55.73 |
| Sex Ratio | 879 | 861 |
| Child Sex Ratio | 834 | 819 |
6. HARYANA POLITY
- Total Number of Lok Sabha Seats of Haryana: 10
- Rajya Sabha (Council of States) seats of Haryana: 05
- Haryana has a unicameral legislature with 90 seats.
- The current Legislature Assembly of Haryana is 14th Vidhan Sabha.
- Current Speaker of Haryana Legislative Assembly: Gian Chand Gupta
- First Speaker of Haryana Legislative Assembly: Smt. Shanno Devi
- Leader of Opposition: Bhupinder Singh Hooda
- Chief Minister of Haryana: Manohar Lal Khattar
- First Chief Minister of Haryana: Bhagwat Dayal Sharma
- Longest-serving Chief Minister of Haryana: Ch. Bansi Lal (12 Yr.)
- Deputy CM of Haryana: Dushyant Chautala
- Governor of Haryana: Bandaru Dattatreya
- First Governor of Haryana: Sh. Dharm Vira
- Panchayati Raj Act was enacted in Haryana on 22 April 1994.
- President rule in the state- 3 times i.e. on 2 Nov 1967, in 1977, in 1991
- Chief Justice of Haryana & Punjab High Court: Ravi Shankar Jha
7. HARYANA CULTURE
- The people of Haryana have their own traditions. The age old customs of meditation, Yoga and chanting of Vedic Mantras, are still observed by the masses. The state is rich in folklore. Their culture and popular art are Saangs, dramas, ballads and songs which entertain them the most.
- Apart from Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu and English, various dialects are also spoken in Haryana. Sanskrit is also taught in many schools. Harayanvi, Bangaru or Jatu is the language majorly spoken by the people living in Haryana.
- People in Haryana give more importance to milk and curd. Some special varieties of rotis made in this region include Besan Masala Roti and Bajra Aloo Roti. Curd, lassi, buttermilk, and sherbet are part of everyday food.
FAIRS AND FESTIVALS OF HARYANA
Some of the important fairs and festivals observed in Haryana are Lohri (13th January), Baisakhi (13th April), Teej, Sanjhi (October), Kurukshetra Festival in Haryana (May-June), Kurukshetra Festival in Kurukshetra (Nov-Dec) and Mango Festival (May-June).
- Surajkund International Fair (February)
- Haryana Day (1 November)
- Geeta Jayanti (Shukla Ekadashi of Margashirsha month)
- Basant Panchami
- Pinjore Heritage Festival
- Gopal-Mochan Fair (Ambala)
- Masani Fair
- Gugga Naumi / Guggapir Festival (Aug-Sept)
- Bathing at Sohna
MUSIC AND DANCE
- Haryana’s famous folk song is Bara Masa, it is a song for twelve months. Folk dance and music are the representators of folk tradition and culture.
- Folk songs in Haryana are called ‘Raganis’, although this style has nothing in common with the classical traditions of Raga-Ragani system. Gharwa Gayan, Jhoolana, Patka, Rasia are the different folk singing styles in Haryana.
- In Haryana, folk singers sing the glories of their success. Fine examples are war songs of Haryana. These poems are called ‘Dohas’ and are sung by bards, known as ‘Jogis’.
- Traditional musical instruments are Harmonium, Chimta, Deru, Dhadd, Dholak, Manjeera, Khartals, Damaru, Duggi, Daf, Bansuri, Been, Ghungroo, Dhak, Gharah, Saarangi, Shehnai and Shankha.
- Famous dance forms of Haryana are- Dhamaal, Ghoomar, Jhumar, Loor, Khoria, Phaag, Gugga
- Theatre in Haryana is called the Natya Plays, which is the amalgamation of music, dance, poetry and speech. The saang is the rural folk drama in Haryana, which expresses the relationship of love, depicting legendary and modern tales of valor.
- Ali Baksh of Rewari is known to be the father of traditional folk theatre in Haryana.
ART AND CRAFT OF HARYANA
- Art and craft of Haryana mainly include pottery, embroidery and weaving. Colourful Phulkari dupatta of Haryana is famous in India and abroad. Art and craft of Haryana also include sculpture and murals both of Persian and Mughal style.
- Some of the craft works for which Haryana is famous are- Woven furniture, Wooden bead making, zari and tilla jutti, lace work, bone carving, wood carving, etc. Pidhis from Sonipat and Moodas and Chairs from Farook nagar are famous in Haryana.
- Panipat is known for its handloom tradition. Pitcher made from Clay in Jhajjar is also very famous.
- Hulkari, Chope, Durries Bagh and Paintings. Most of these are essentially village handicrafts. The Villages of Haryana are most famous for their woven works.
8. TOURISM OF HARYANA
- 21 tourism hubs created by Haryana Tourism Corporation (HTC) are located in Ambala, Bhiwani Faridabad, Fatehabad, Gurgaon, Hisar, Jhajjar, Jind, Kaithal, Karnal, Kurukshetra, Panchkula, Sirsa, Sonipat, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Yamunanagar, Palwal and Mahendergarh.
- Haryana is officially part of Mahabharata and Krishna tourism development circuit.
- Famous places to visit in Haryana are:
- Kurukshetra - Bronze chariot of Lord Krishna and Arjuna at Kurukshetra, a manuscript of Mahabharata depicting the war at Kurukshetra, Sheikh Chilli's Tomb
- Hisar - Rakhigarhi Indus Valley civilization sites, Fort of Firoz Shah Tughlaq, Deer Park, Blue Bird Lake, Asigarh Fort, Kanwari Indus Valley civilization site
- Faridabad - Dried Badkhal lake, Suraj Kund, Nahar Singh Mahal, Dabua Colony
- Panchkula- Mansa Devi temple, Pinjore Gardens, Morni Hills
- Gurugram - Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary, Damdama Lake
- Panipat-City of Weavers
- Murthal
- Kalesar National Park in Yamuna Nagar
9. AWARDS OF HARYANA
- Chaudhary Devi Lal Award: It consists of 3 lakh cash prize, a citation and a plaque as an institutional award for Partnership Research for most significant contribution to agricultural productivity.
- Bhim award: It is the state's highest sports award and started in 2001.
- Sur Samman: Sur Samman award is named on the great poet `Surdas'. It is given every year by Haryana Government. The awardee gets a cash reward of 1.5 lakh.
- National Haryana Education Awards: Punjab Technical University National Punjab organized Education Summit and Awards.
- Other Awards: Rani Laxmi Bai Award, Eklavya Award, Guru Vashishth Award, Maharana Pratap Award, Vikramaditya Award, Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishan Award, Haryana Gaurav Samman, Indira Gandhi Mahila Shakti Award, Haryana Kisan Ratan Award
10. IMPORTANT PERSONALITIES FROM HARYANA
1. Manushi Chillar – Miss World in 2017
2. Kalpana Chawla – First Indian woman to travel in space.
3. Yuzvendra Chahal – Indian Cricketer
4. Sunil Grover – Indian Comedian
5. Geeta Phogat – She is the first female wrestler to win a gold medal in wrestling at the Commonwealth Games in 2010.
6. Kapil Dev – Indian Cricketer
7. Yogeshwar Dutt – Indian Wrestler
8. Randeep Hooda – Indian Actor
9. Sonu Nigam – Indian Playback Singer
10. Badshah (Aditya Prateek Singh Sisodia )– Indian Rapper
11. Baba Ramdev- Yoga Guru
12. Sushma Swaraj- Former External Affairs Minister of India
13. Virendra Sehwag- Indian Cricketer
14. Geeta Phogat and Babita Phogat- Wrestler
15. Shakshi Malik- First Indian female wrestler to win a medal at Olympics
16. Juhi Chawla- Indian Actress (1984 Miss India winner)









 Latest
Latest 



Comments