Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 09-11-2023
09-11-2023
 14:03 PM IST
14:03 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
This chapter discusses the transport of substances in plants and animals. It also discusses the function of the heart and blood vessels along with the function of vascular tissues in plants.
Circulatory system
It consists of the heart and blood vessels. They function together to transport substances and together form the circulatory system. Blood flows in blood vessels.
Blood
Blood is a fluid which flows in blood vessels. It is composed of fluid called plasma. Different types of cells are suspended in plasma. They are given below.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): RBCs contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. Haemoglobin binds with oxygen and transports it to all the parts of the body and ultimately to all the cells. They are also known as erythrocytes.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): WBCs fight against germs that may enter our body. These are also known as leukocytes.
- Platelets: Platelets are responsible for formation of blood clot. These are also known as thrombocytes.
Functions of blood:
1. It transports substances like digested food from the small intestine to the other parts of the body.
2. It carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body.
3. It also transports waste for removal from the body.
Blood vessels
Blood vessels carry blood. They are of two types:
- Arteries: Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body. Since the flow of blood is rapid and at a high pressure, arteries have thick elastic walls.
- Veins: They carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from all parts of the body back to the heart. They have thin walls. Valves are present in veins. Valves in the veins allow blood to flow only towards the heart.
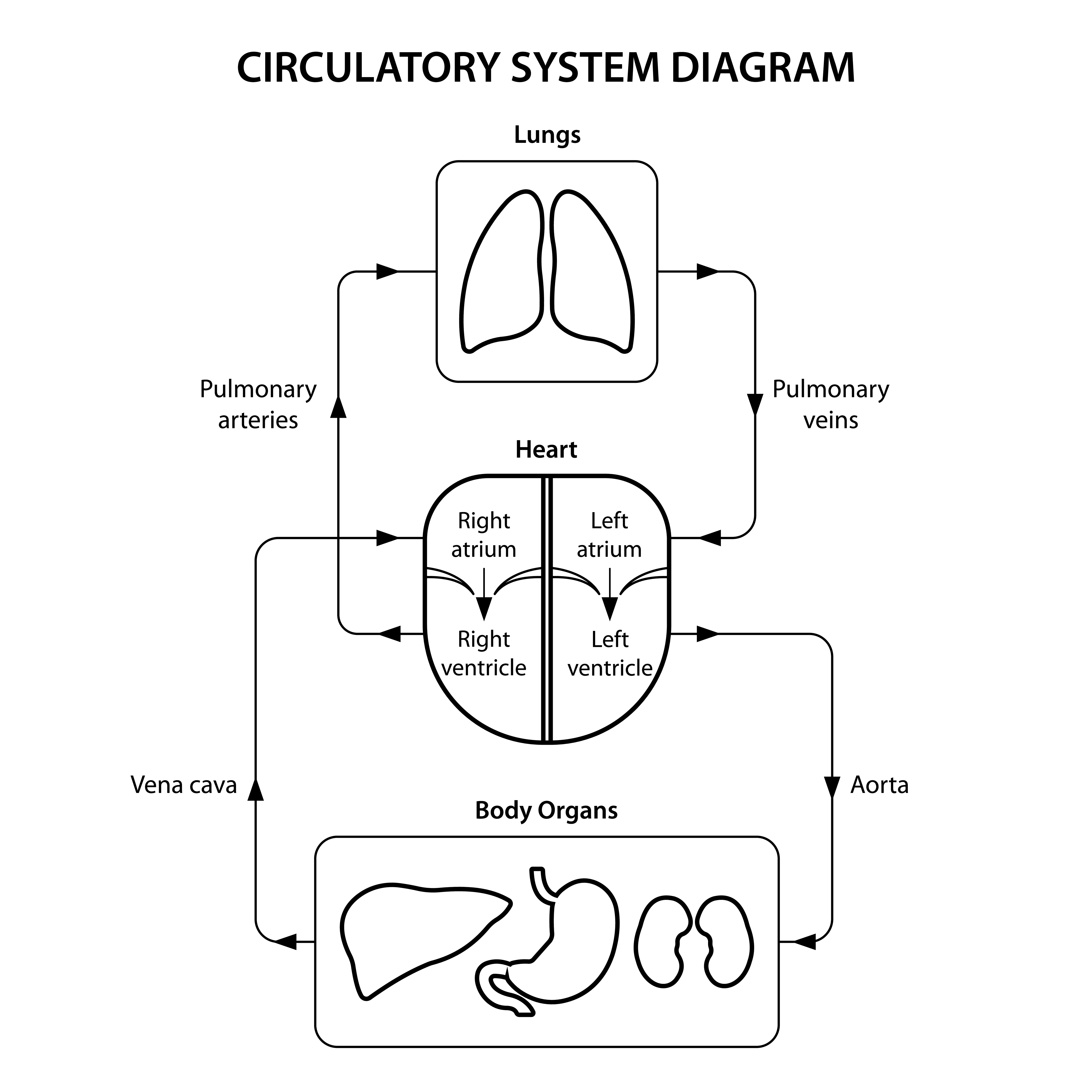
Diagram showing circulation
When arteries reach the tissues, they divide further into extremely thin tubes called capillaries. They join to form veins which empty into the heart.
NOTE:
1. Pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide rich blood from the heart to the lungs.
2. Pulmonary vein carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart.
3. Aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body which originates from the left ventricle and carries oxygenated blood.
4. Superior and Inferior Vena cava are very large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to right atrium.
Pulse and Pulse rate: Throbbing movement on the inner side of left wrist is due to the blood flowing in the arteries and is called pulse. The number of pulse beats per minute is called the pulse rate. A resting person usually has a pulse rate between 72 and 80 beats per minute.
Heart
The heart acts as a pump for the transport of blood. It is located in the chest cavity with its lower tip slightly tilted towards the left.
It has four chambers. The two upper chambers are called the atria (singular: atrium) and the two lower chambers are called the ventricles.
The partition between atria and ventricles prevents mixing up of blood rich in oxygen with blood rich in carbon dioxide.
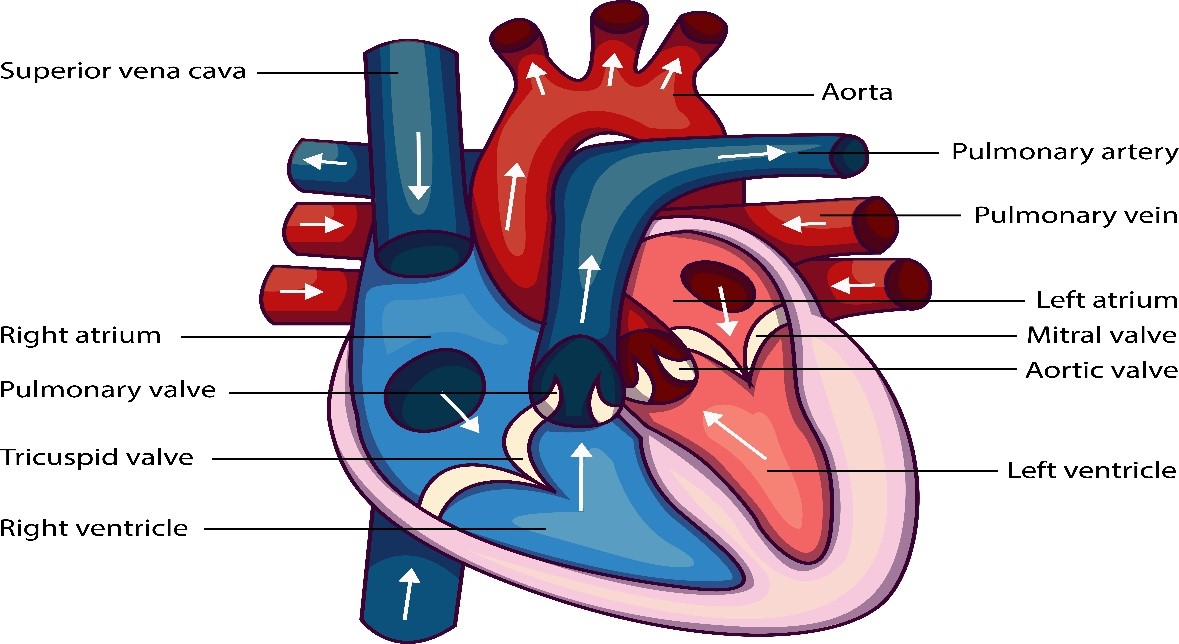
Heartbeat
Rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the walls of the chambers of the heart form heartbeat.
Stethoscope is a device used to amplify the sound of the heart and hear the heartbeat. Each heart beat generates one pulse in the arteries and the pulse rate per minute indicates the rate of heart beat. The human heart beats about 70–80 times per minute in an adult person. This is called heart rate.
Figure showing a stethoscope
NOTE: William Harvey discovered the circulation of blood.
Transportation in sponges and Hydra
Animals like sponges and Hydra lack circulatory system and circulatory fluid like blood. They are surrounded by water. The water brings food and oxygen as it enters their bodies and carries away waste materials and carbon dioxide as it moves out.
Excretory System
Removal of waste products from the body is called excretion. The removal of waste products from the body of the animal depends on the availability of water.
Fishes excrete waste substances such as ammonia which directly dissolve in water. Birds, insects and lizard excrete uric acid in semi-solid form.
Urea is the major excretory product in humans.
Excretory system of humans consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and urethra. Kidneys filter waste products from the blood and remove wastes as urine. Urine passes from the kidneys into urinary bladder through the two ureters. It is stored in urinary bladder. Urine goes out of the body through urinary opening at the end of a muscular tube called urethra.
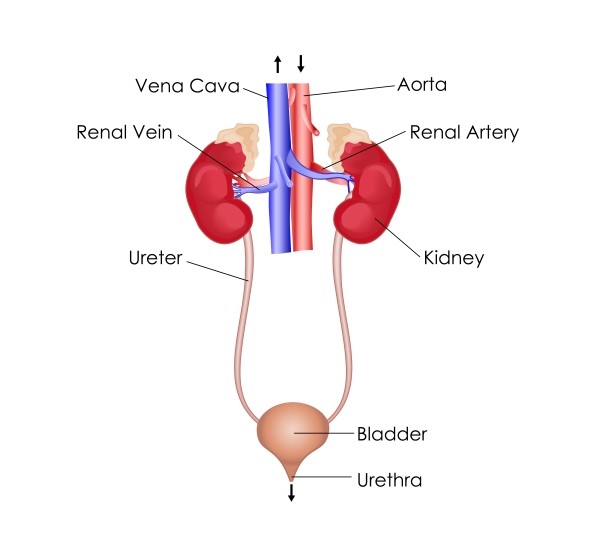
Figure showing the human excretory system
Urine: 1–1.8 L of urine is normally passed by an adult human being in 24 hours. It consists of 95% water, 2.5% urea and 2.5% other waste products.
Sweat: Salts and urea are removed along with water as sweat. When we sweat, it helps to cool our body. Sometimes in summer, white patches are formed on our clothes, especially in areas like underarms. These marks are left by salts present in the sweat.
What is Dialysis?
It is the process of filtering of blood through an artificial kidney. This process prevents accumulation of waste products in the blood of persons with kidney failure due to injury or infection and ensures their survival.
Transportation in plants
Water and mineral nutrients are absorbed by roots from the soil. For this purpose, roots have root hairs. Root hairs increase surface area of the root. Nutrients are transported along with water to the entire plant via the vascular tissue called xylem. The vascular tissue for the transport of food to the various parts of the plant is phloem.
Transpiration: Plants do not use all water absorbed by roots from the soil. A lot of water is lost by plants in the form of vapour through stomata during transpiration.
Significance of transpiration: The process of transpiration generates a force (suction pull) which pulls up water absorbed by the roots from the soil, to reach the stem and leaves and to great heights in the tall trees. It also cools the plant.
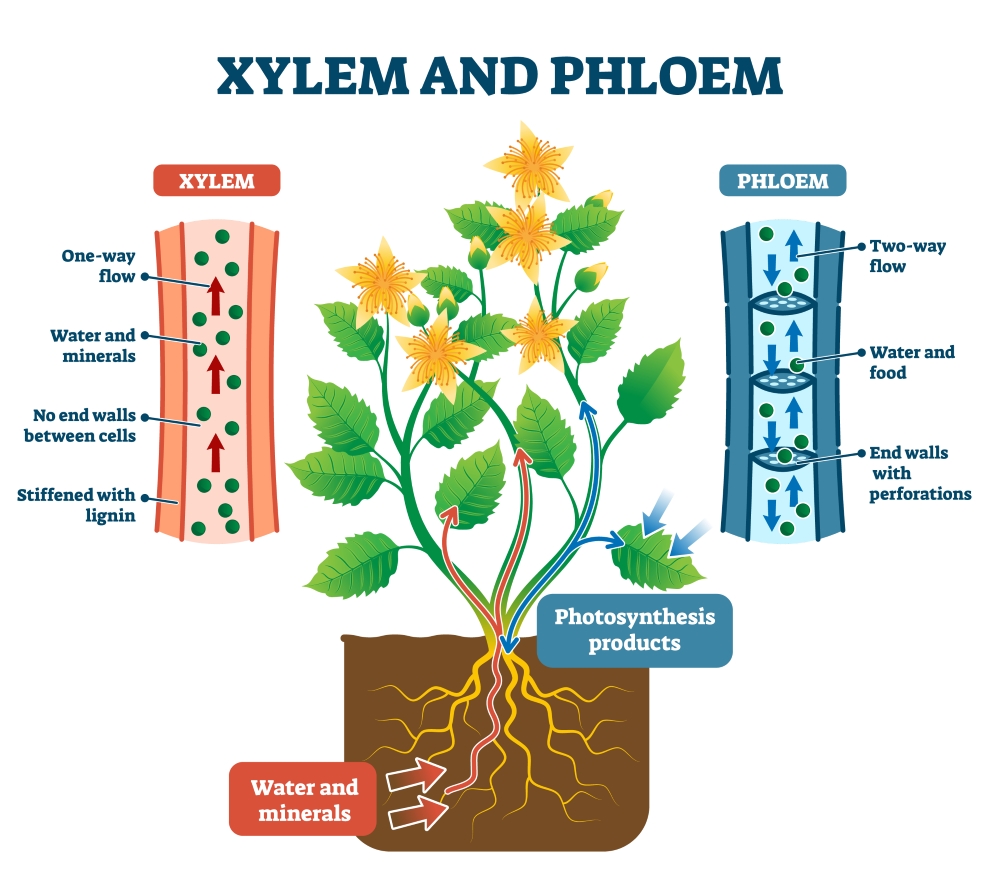
Figure showing vascular tissues-Xylem and Phloem
MCQs based on NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 11: Transportation in Plants and Animals
1. Which of the following blood cells is/are responsible for blood clotting?
a. White Blood Cells
b. Red Blood Cells
c. Platelets
d. Both a and c
Ans. c
Explanation:
Platelets are responsible for the formation of blood clots.
2. Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of arteries?
a. They carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body.
b. They have thick elastic walls.
c. They divide further into extremely thin tubes called capillaries.
d. Valves are present in them.
Ans. d
Explanation:
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body. They have thick elastic walls. When arteries reach the tissues, they divide further into extremely thin tubes called capillaries. Valves are present in veins.
3. Which of the following organisms excrete waste substances such as ammonia?
a. Birds
b. Fishes
c. Insects
d. Lizards
Ans. b
Explanation:
Fishes excrete waste substances such as ammonia which directly dissolve in water. Birds, insects and lizard excrete uric acid in semi-solid form.
4. How much percentage of urine is water?
a.70%
b.75%
c.85%
d. 95%
Ans. d
Explanation: Kidneys filter waste products from the blood and remove wastes as urine. 1–1.8 L of urine is normally passed by an adult human being in 24 hours. It consists of 95% water, 2.5% urea and 2.5% other waste products.
5. In plants, water is transported through
a. xylem
b. phloem
c. stomata
d. root hair
Ans. a
Explanation: Nutrients are transported along with water to the entire plant via the vascular tissue called xylem.
6. Water absorption through roots can be increased by keeping the plants
a. in the shade
b. in dim light
c. under the fan
d. covered with a polythene bag
Ans. c
Explanation: Water absorption through roots can be increased by keeping the plants under the fan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Transportation in Animals and Plants
In which blood cells is haemoglobin present?
What are the components of blood?
Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood?
Share Blog
 Latest
Latest 
Comments