Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 09-11-2023
09-11-2023
 14:02 PM IST
14:02 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
The chapter discusses asexual reproduction and its types. It also explains sexual reproduction.
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is the production of new individuals from their parents. Flowers perform the function of reproduction in plants. The ways of reproduction in plants are categorized into two types given below.
Asexual reproduction
In this type of reproduction, plants can give rise to new plants without seeds. There are several methods of asexual reproduction such as fragmentation, budding, spore formation and vegetative propagation.
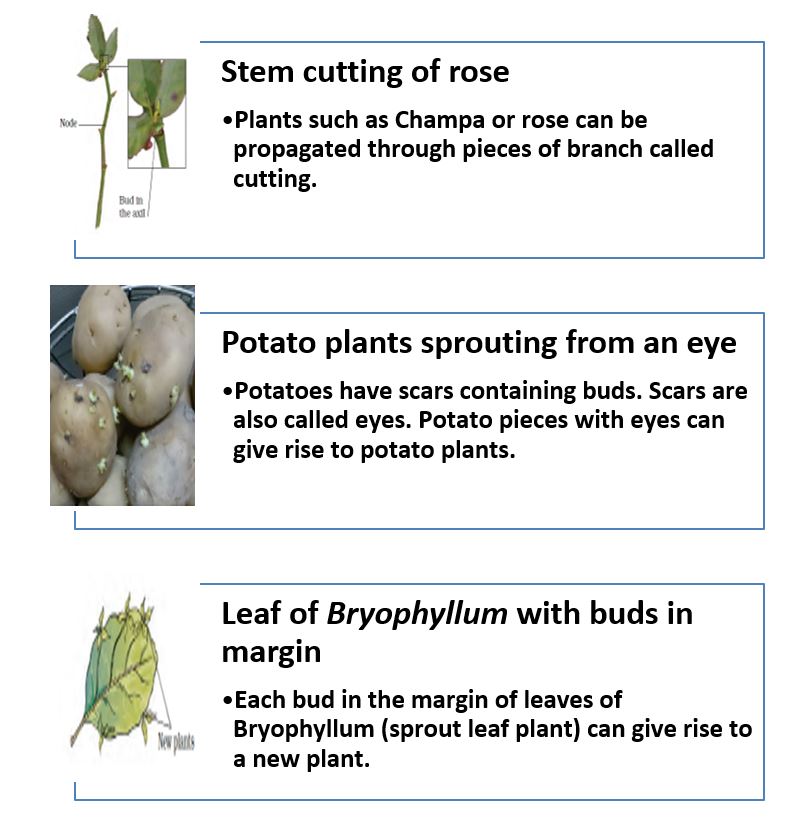
A. Vegetative propagation
It is a type of asexual reproduction. In vegetative propagation, new plants are produced from vegetative parts of plant such as roots, stems, leaves and buds. Buds (Vegetative buds) develop in the axil of leaves.
They consist of a short stem surrounded by immature overlapping leaves. They develop into shoots. They can also give rise to new plants. Roots of sweet potato and dahlia can also give rise to new plants.
Cacti produce new plants when their parts get detached from the main plant body. Some other examples and applications of vegetative propagation are given below.
Characteristics of plants produced from vegetative propagation: They take less time to grow and produce flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. They are exact copies of the parent plant because they are produced from a single parent. Plants produced by sexual reproduction have characteristics of both parents.
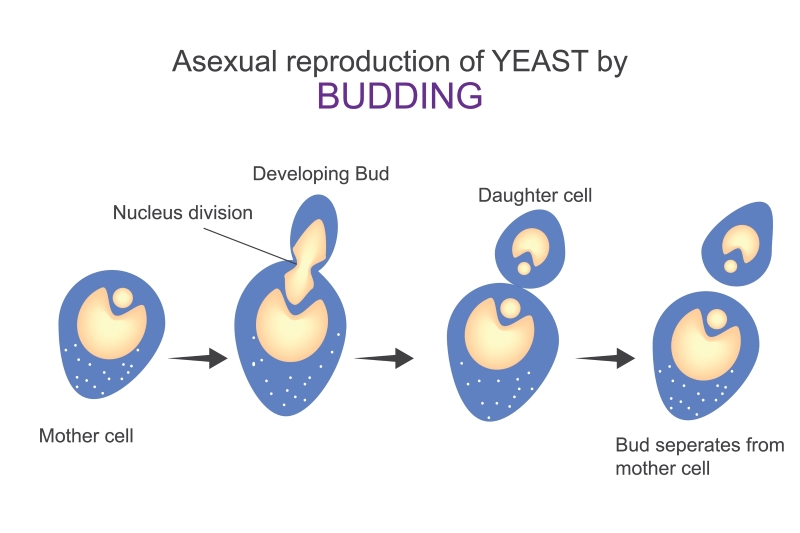
B. Budding
Yeast multiplies through budding. In budding, a small bulb-like projection comes out from the yeast cell. This projection is called a bud. The bud gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell.
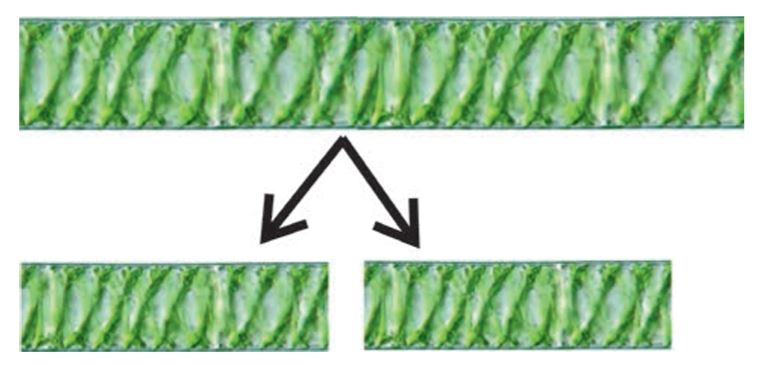
C. Fragmentation
Algae such as Spirogyra multiply rapidly through fragmentation. In fragmentation, an alga breaks up into two or more fragments. These fragments or pieces grow into new individuals.
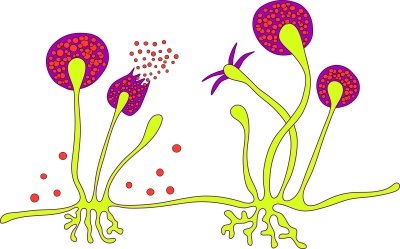
D. Spore formation
Spores are asexual reproductive bodies covered by a hard protective coat to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. Spores can survive for a long time. Fungi and plants such as moss and ferns reproduce through spores.
Sexual reproduction
In this type of reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds.
It involves the fusion of male and female gametes. The fusion of male and female gamete produces zygote.
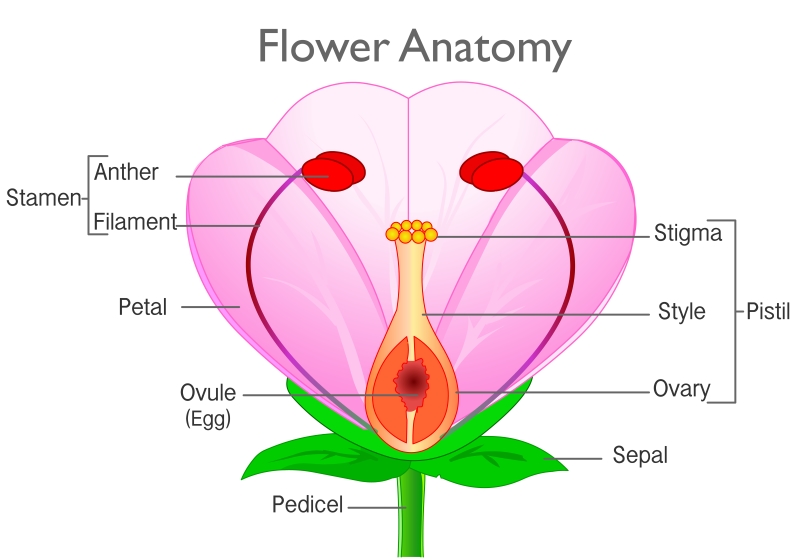
Flower and its structure
Flower is the reproductive part of a plant. It consists of stamens, the male reproductive part and pistil, the female reproductive part.
- Stamens (male reproductive part): Stamen consists of anther and filament. Anther contains pollen grains. Pollen grains produce male gametes. Tough protective coat of pollen grains prevents them from drying up.
- Pistil (female reproductive part): A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. Ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule.
Types of flowers
Based on the male and female reproductive parts, flowers are of two types.
- Unisexual flowers: Unisexual flowers contain either only pistil (female reproductive part) or only stamens (male reproductive part). Flowers of corn, papaya and cucumber are unisexual.
- Bisexual flowers: Bisexual flowers contain both stamens (male reproductive part) and pistil (female reproductive part). Flowers of mustard, rose and petunia are bisexual.
Pollination
Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of the same or another flower. It takes place in plants with the help of wind, water and insects. It is of two types.
- Self-pollination: In self-pollination, pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower.
- Cross-pollination: In cross-pollination, pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind.
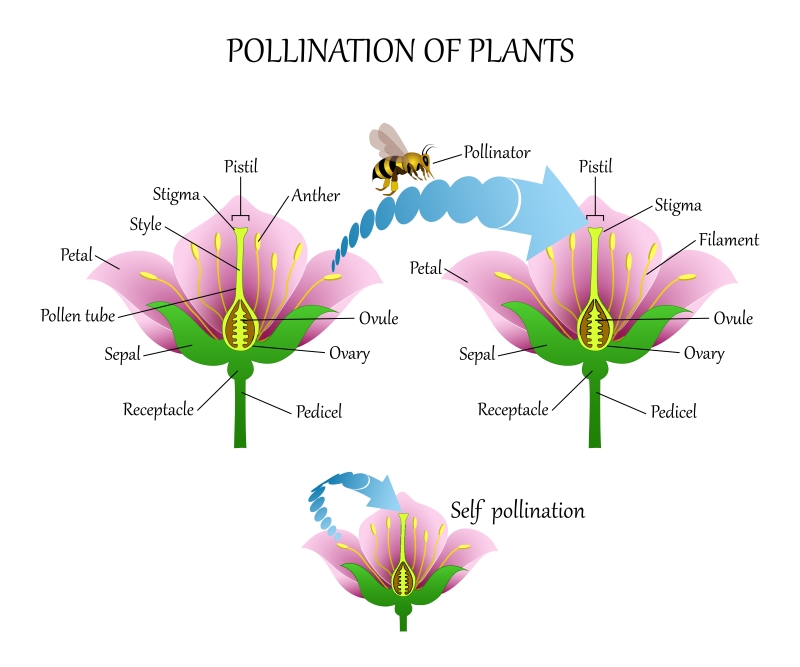
Diagram showing self-pollination and cross-pollination
Fertlisation
The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation. As a result of fertilization, zygote is formed.
Formation of fruits and seeds: Fertilised egg is called zygote. Zygote develops into an embryo. Fruit is the mature (ripened) ovary whereas ovule develops into a seed, which contains the developing embryo.
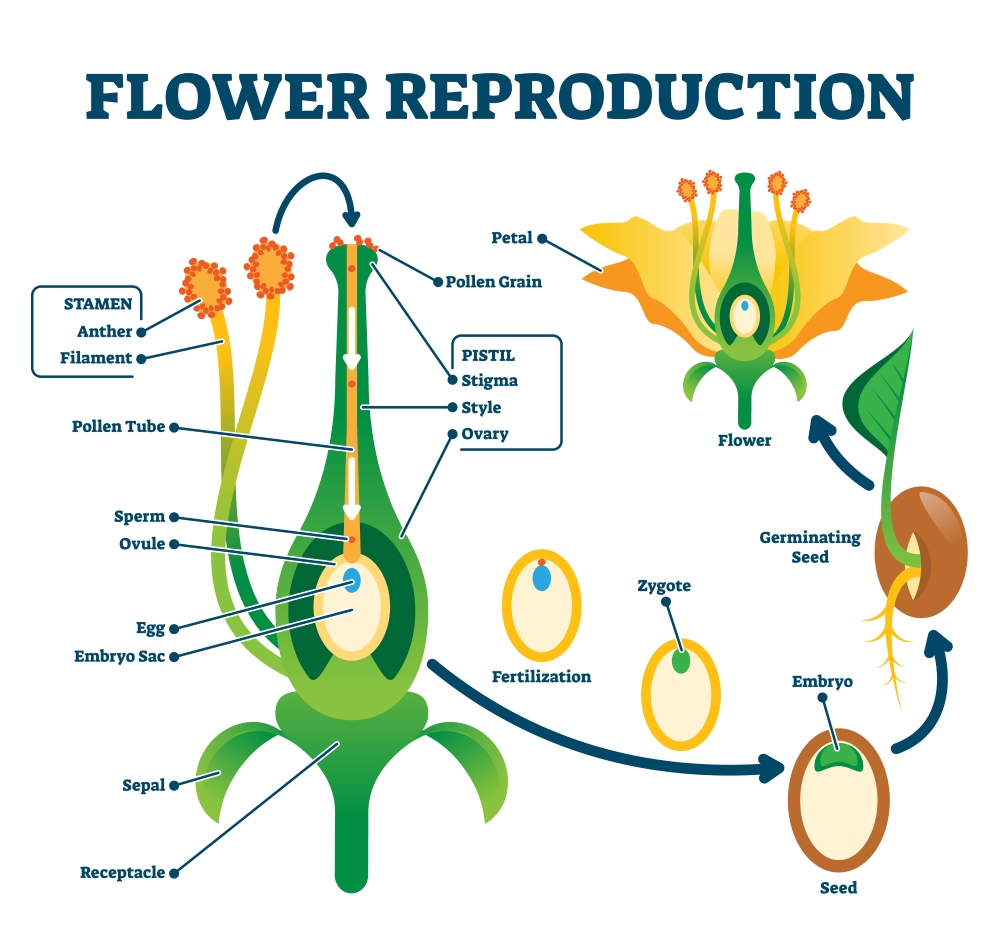
Figure showing fertilization
Seed dispersal and its benefits
It is aided by wind, water and animals. Seed dispersal benefits plants in
(i) Preventing overcrowding
(ii) Avoiding competition for sunlight, water and minerals
(iii) Invading new habitats for wider distribution
Examples of seeds and fruits dispersed by wind: Winged seeds such as those of drumstick and maple, light seeds of grasses or hairy seeds of aak (Madar) and hairy fruit of sunflower.
Example of seed dispersed by water: Coconut (has floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coat).
Examples of seeds dispersed by animals: Xanthium and Urena (Such seeds are spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals).
Examples of seeds that are dispersed when their fruits burst with sudden jerks: Castor and Balsam
MCQs based on NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12: Reproduction in Plants
1. In which of the following methods of reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds?
a. Fragmentation
b. Budding
c. Sexual reproduction
c. Vegetative propagation
Ans. c
Explanation:
Fragmentation, budding, spore formation and vegetative propagation are methods of asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, plants can give rise to new plants without seeds. In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds.
2. Which of the following plants produces bisexual flowers?
a. Corn
b. Rose
c. Papaya
d. Cucumber
Ans. b
Explanation: Bisexual flowers contain both stamens (male reproductive part) and pistil (female reproductive part). Flowers of mustard, rose and petunia are bisexual.
3. Fruit develops from which part of a flower?
a. stamen
b. stigma
c. ovule
d. ovary
Ans d
Explanation:
Fruit is the mature (ripened) ovary whereas ovule develops into a seed, which contains the developing embryo.
4. Which of the following fruits gets dispersed by water?
a. Maple
b. Coconut
c. Castor
d. Sunflower
Explanation:
Example of seed dispersed by water: Coconut (has floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coat).
5. The reproductive part of a plant is the
a.leaf
b. stem
c. root
d. flower
Ans. d
Explanation: Flower is the reproductive part of a plant. Stamen and Pistil are the male and female reproductive parts respectively.
6. The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
a. fertilisation
b. pollination
c. reproduction
d. seed formation
Ans. a
Explanation: The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called fertilisation.
7. Mature ovary forms the
a. seed
b. stamen
c. pistil
d. fruit
Ans. d
Explanation: Fruit is the mature (ripened) ovary whereas ovule develops into a seed, which contains the developing embryo.
8. A spore producing organism is
a. rose
b. bread mould
c. potato
d. ginger
Ans. b
Explanation: Fungi and plants such as moss and ferns reproduce through spores. Bread mould is also a spore producing organism.
9. Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
a. stem
b. leaves
c. roots
d. flower
Ans. b
Explanation: Bryophyllum can reproduce by its leaves through vegetative reproduction.
10. Seed dispersal can be caused by-
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Animals
d. All
Ans. d
Explanation: Seed dispersal is aided by wind, water and animals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Reproduction in Plants
What is pollination?
Yeast is reproduced by which mode of reproduction?
What is zygote?
What is a unisexual flower?
What is fragmentation?
Share Blog
 Latest
Latest 
Comments