Industries Class 8 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 26-03-2024
26-03-2024
 18:53 PM IST
18:53 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
This chapter discusses different types of industries, factors responsible for industrial growth and major industrial centers of the world.
Secondary activities or manufacturing change raw materials into products of more value to people.
What is an Industry?
Industry refers to an economic activity that is concerned with production of goods, extraction of minerals or the provision of services. E.g., iron and steel industry, coal mining industry, tourism industry.
Classification of Industries
On the basis of raw materials
1. Agro-based industries – They use plant and animal-based products as their raw materials. Food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile, dairy products and leather industries are examples of agro-based industries.
2. Mineral based industries – They are primary industries that use mineral ores as their raw materials.
The products of these industries feed other industries. Iron made from iron ore is the product of mineral based industry.
This is used as raw material for the manufacture of a number of other products, such as heavy machinery, building materials and railway coaches.
3. Marine based industries – They use products from the sea and oceans as raw materials. Industries processing sea food or manufacturing fish oil are some examples.
4. Forest based industries – These industries utilise forest produce as raw materials. The industries associated with forests are pulp and paper, pharmaceuticals, furniture and buildings.
On the basis of size
The industries are classified on the basis of size i.e. the amount of capital invested, number of people employed and volume of production.
1. Small scale industries: In this industry, the products are manufactured by hand, by the artisans. Cottage or household industries are a type of small-scale industry.
Basket weaving, pottery and other handicrafts are examples of cottage industry.
Small scale industries use lesser amount of capital and technology as compared to large scale industries that produce large volumes of products.
2. Large scale industries: Investment of capital is higher and the technology used is superior in large scale industries.
Production of automobiles and heavy machinery are large scale industries.
On the basis of ownership
1. Private sector industries: These industries are owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals.
2. Public sector industries: These are owned and operated by the government, such as Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and Steel Authority of India Limited.
3. Joint sector industries: These are owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. Maruti Udyog Limited is an example.
4. Co-operative sector industries: These industries are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both. Anand Milk Union Limited and Sudha Dairy are successful co-operative ventures.
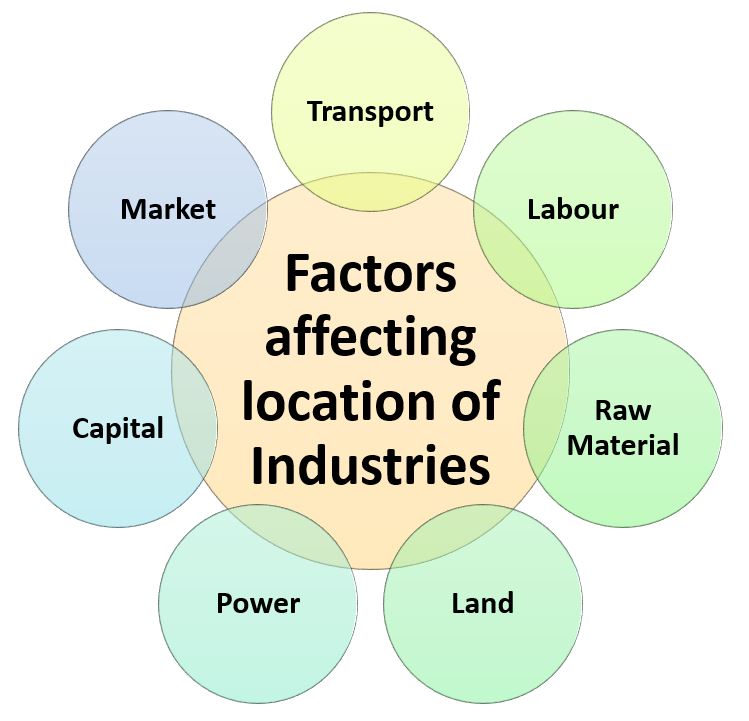
Factors affecting location of Industries
Factors which affect the location of industries are:
- Availability of Transport
- Availability of Labour
- Availability of Raw Material
- Availability of Power
- Availability of Land
- Availability of Capital
- Availability of Market
Industrial Regions of the world
Industrial regions emerge when a number of industries locate close to each other and share the benefits of their closeness.
Major industrial regions of the world are eastern North America, western and central Europe, eastern Europe and eastern Asia.
Major industrial regions tend to be located in the temperate areas, near sea ports and especially near coal fields.
India has several industrial regions like Mumbai-Pune cluster, Bangalore-Tamil Nadu region, Hugli region, Ahmedabad-Baroda region, Chottanagpur industrial belt, Vishakhapatnam-Guntur belt, Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut region and the Kollam-Thiruvanathapuram industrial cluster.
Industrial disasters
Industries can also lead to disasters like the Bhopal Gas Tragedy, 1984 and Gao Qiao blowout in China in 2005.
Several risk reduction measures can be taken to prevent such disasters –
- Densely populated residential areas should be separated far away from the industrial areas.
- People staying in the vicinity of industries should be aware of the storage of toxins or hazardous substances and their possible effects in case if an accident occurs.
- Fire warning and fighting system should be improved.
- Storage capacity of toxic substances should be limited.
- Pollution dispersion qualities in the industries should be improved.
Iron and Steel Industry
- This is a feeder industry whose products are used as raw material for other industries.
- The inputs for the industry include raw materials such as iron ore, coal and limestone, along with labour, capital, site and other infrastructure.
- The process of converting iron ore into steel involves many stages. The raw material is put in the blast furnace where it undergoes smelting and then refined.
- The output obtained is steel which may be used by other industries as raw material.
- Steel is tough and it can easily be shaped, cut, or made into wire.
- Special alloys of steel can be made by adding small amounts of other metals such as aluminium, nickel, and copper. Alloys give steel unusual hardness, toughness, or ability to resist rust.
- Steel is often called the backbone of modern industry. Ships, trains, trucks, and autos are made largely of steel. Steel is used to build machinery for oil drilling, mining of minerals, farm machinery, build large buildings and to make pipelines for oil transportation.
- In India, all the important steel producing centres such as Bhilai, Durgapur, Burnpur, Jamshedpur, Rourkela, Bokaro are situated in a region that spreads over four states — West Bengal, Jharkhand, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
- Bhadravati and Vijay Nagar in Karnataka, Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, Salem in Tamil Nadu are other important steel centres utilising local resources.
- The Indian iron and steel industry consists of large integrated steel plants as well as mini steel mills. It also includes secondary producers, rolling mills and ancillary industries.
Major iron and steel centers are:
Jamshedpur
- Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited (TISCO) was the first iron and steel plant in the country.
- TISCO was started in 1907 at Sakchi, near the confluence of the rivers Subarnarekha and Kharkai in Jharkhand. Later on, Sakchi was renamed as Jamshedpur.
- This place was very near the Kalimati station on the Bengal-Nagpur railway line.
- It was close to the iron ore, coal and manganese deposits as well as to Kolkata, which provided a large market.
- TISCO, gets coal from Jharia coalfields, and iron ore, limestone, dolomite and manganese from Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
- The Kharkai and Subarnarekha rivers ensured sufficient water supply.
Pittsburgh
- It is an important steel city of the United States of America. The steel industry at Pittsburgh enjoys locational advantages.
- Some of the raw material such as coal is available locally, while the iron ore comes from the iron mines at Minnesota, about 1500 km from Pittsburgh.
- The Great Lakes waterway is used for shipping ore cheaply. Trains carry the ore from the Great Lakes to the Pittsburgh area.
- The Ohio, the Monogahela and Allegheny rivers provide adequate water supply.
Cotton Textile Industry
- It is one of the oldest industries in the world. In 18th century power looms facilitated the development of cotton textile industry, first in Britain and later in other parts of the world.
- Today India, China, Japan and the USA are important producers of cotton textiles.
- Before the British rule, Indian hand spun and hand-woven cloth like the Muslins of Dhaka, Chintzes of Masulipatnam, Calicos of Calicut and Gold-wrought cotton of Burhanpur, Surat and Vadodara were known worldwide for their quality and design.
- However the traditional cotton textile industry could not face the competition from the new textile mills of the West, which produced cheap and good quality fabrics through mechanized industrial units.
- The first textile mill in the country was established at Fort Gloster near Kolkata in 1818 but it closed down after some time. The first successful mechanized textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
- Initially, this industry flourished in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat because of favourable humid climate. But today, this industry has spread to other parts of India.
- Coimbatore, Kanpur, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Mumbai, Kolkata, Ludhiana, Puducherry and Panipat are some of the other important centres.
- About one-third of the Indian textile industry’s total production is exported.
Major Cotton Industry centers are:
Ahmedabad
- It is located in Gujarat on the banks of the Sabarmati river.
- The first mill was established in 1859. It soon became the second largest textile city of India, after Mumbai. Ahmedabad was therefore often referred to as the ‘Manchester of India’.
- It is situated very close to cotton growing area. This ensures easy availability of raw material.
- The climate is ideal for spinning and weaving. The flat terrain and easy availability of land is suitable for the establishment of the mills.
- The densely populated states of Gujarat and Maharashtra provide both skilled and semi-skilled labour.
- Well-developed road and railway network permits easy transportation of textiles to different parts of the country, thus providing easy access to the market.
- Mumbai port nearby facilitates import of machinery and export of cotton textiles.
- In the recent years, Ahmedabad textile mills have been having some problems. Several textile mills have closed down.
- This is primarily due to the emergence of new textile centres in the country as well as non-upgradation of machines and technology in the mills.
Osaka
- It is an important textile centre of Japan, also known as the ‘Manchester of Japan’.
- The extensive plain around Osaka ensure that land was easily available for the growth of cotton mills.
- Warm humid climate is well suited to spinning and weaving. The river Yodo provides sufficient water for the mills. Labour is easily available.
- Location of port facilitates import of raw cotton and for exporting textiles.
- The textile industry at Osaka depends completely upon imported raw materials. Cotton is imported from Egypt, India, China and USA.
- The finished product is mostly exported and has a good market due to good quality and low price.
- The cotton textile industry of Osaka has been replaced by other industries, such as iron and steel, machinery, shipbuilding, automobiles, electrical equipment and cement.
Sunrise industries: Emerging industries are also known as ‘Sunrise Industries’. These include Information technology, Wellness, Hospitality and Knowledge.
Smelting: It is the process in which metals are extracted from their ores by heating beyond the melting point.
Lake Superior is the largest of the Great lakes viz., Superior, Huron, Ontario, Michigan and Erie.
MCQs based on NCERT Class 8 Geography Chapter 5: Industries
1. Which of the following is not an agro based industry?
(a) Food processing
(b) Cotton textile
(c) Leather industry
(d) Pulp and paper industry
Ans. d
2. What are the factors on the basis of which an industry can be classified as small scale or large scale industry?
(a) Capital invested, number of people employed, and volume of production
(b) Capital invested, land, and labour
(c) Entrepreneur, Market and number of people employed
(d) Market, Transport and availability of raw material
Ans. a
3. Which of the following is not one of the factors affecting location of Industries?
(a) Power
(b) Land
(c) Labour
(d) Level of urbanisation
Ans. d
4. Industrialisation often leads to-
(a) Development and growth of town and cities
(b) Increase in raw material
(c) Increase in transport cost
(d) Decrease in value of land
Ans. a
5. Emerging industries are also known as
(a) Skyrise industries
(b) Sunrise industries
(c) Moonrise industries
(d) Essential industries
Ans. b
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Industries
Which industry is often referred to as the backbone of modern industry?
Which are the main factors which influence the location of an industry?
What is meant by the term ‘industry’?
What are the examples of forest based industries?
Share Blog
.JPG)
 Latest
Latest 
Comments