Human Resources Class 8 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 26-03-2024
26-03-2024
 18:57 PM IST
18:57 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
This chapter discusses the human resources and basics of studying population.
People are the most important resources of a country and are known as human resources. They can be developed through health, education and skilling.
The Government of India has a Ministry of Human Resource Development. The Ministry was created in 1985 with an aim to improve people’s skills.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojna (PKVY) was started in 2015 aiming to train one crore Indian youth from 2016 to 2020. The objective of this scheme is to encourage aptitude towards employable skills by giving quality training to probable and existing wage earners.
Population distribution
- The way in which people are spread across the earth surface is known as the pattern of population distribution.
- The distribution of population in the world is extremely uneven. The crowded areas are south and south east Asia, Europe and north eastern North America.
- Very few people live in high latitude areas, tropical deserts, high mountains and areas of equatorial forests.
- Many more people live north of the Equator than south of the Equator. Almost three-quarters of the world’s people live in two continents Asia and Africa.
- 60% of the world’s people stay in just 10 countries. All of them have more than a 100 million people.
Population density
- Population density is the number of people living in a unit area of the earth’s surface. It is normally expressed as per square km.
- The average density of population in the whole world is 51 persons per square km.
- Average density of population in India is 382 persons per square km.
- South Central Asia has the highest density of population followed by East and South East Asia.
Factors Affecting Population Distribution
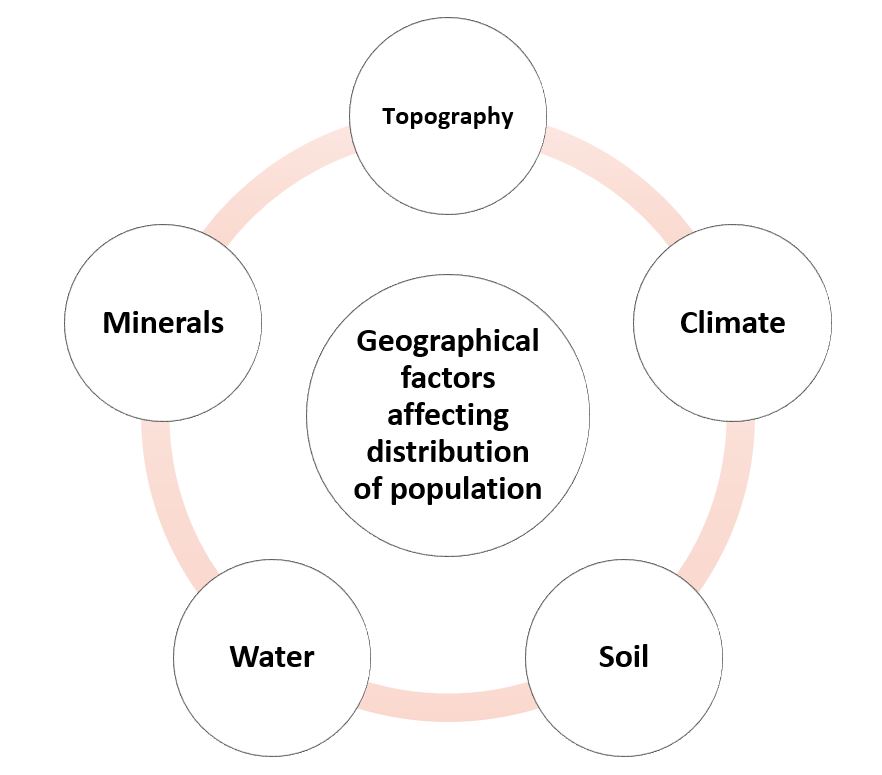
Geographical Factors
- Topography: People always prefer to live on plains rather than mountains and plateaus because these areas are suitable for farming, manufacturing and service activities.
- Climate: People usually avoid extreme climates that are very hot or very cold like Sahara Desert, polar regions of Russia, Canada and Antarctica.
- Soil: Fertile soils provide suitable land for agriculture hence fertile plains are densely populated.
- Water: People prefer to live in the areas where fresh water is easily available. The river valleys of the world are densely populated while deserts have spare population.
- Minerals: Areas with mineral deposits are more populated. Diamond mines of South Africa and the discovery of oil in the Middle east led to settling of people in these areas.
Social, Cultural and Economic Factors
- Social: Areas of better housing, education and health facilities are more densely populated e.g., Pune.
- Cultural: Places with religion or cultural significance attract people. Varanasi, Jerusalem and Vatican City are some examples.
- Economic: Industrial areas provide employment opportunities due to which large number of people are attracted to these areas. Osaka in Japan and Mumbai in India are two densely populated areas.
Population change
- The population change refers to the change in the number of people during a specific time.
- Until the 1800s, the world’s population grew steadily but slowly. Large numbers of babies were born, but they died early too as there were no proper health facilities.
- Sufficient food was not available for all the people.
- As a result, the total increase in population was very low.
- In 1959, the world’s population reached 3 billion while in 1999, 40 years later, the population doubled to 6 billion. This is often called population explosion.
- The main reason for this growth was that with better food supplies and medicine, deaths were reducing, while the number of births still remained fairly high.
Important Terms related to Population growth
- Births are usually measured using the birth rate i.e., the number of live births per 1,000 people.
- Deaths are usually measured using the death rate i.e., the number of deaths per 1,000 people.
- Life expectancy is the number of years that an average person can expect to live.
- The difference between the birth rate and the death rate of a country is called the natural growth rate.
- Migration is another way by which population size changes. It is the movement of people in and out of an area.
- Emigrants are people who leave a country; immigrants are those who arrive in a country.
- The general trend of international migrations is from the less developed nations to the more developed nations in search of better employment opportunities.
- Within countries large number of people may move from rural to urban areas in search of employment, education and health facilities.
Population Composition
It refers to the structure of the population.
Population composition of a country can be studied through the population pyramid, also called an age-sex pyramid.
A population pyramid shows
- The total population divided into various age groups, e.g., 5 to 9 years, 10 to 14 years.
- The percentage of the total population, subdivided into males and females, in each of those groups.
- The numbers of children (below 15 years) are shown at the bottom and reflect the level of births. The size of the top shows the numbers of aged people (above 65 years) and reflects the number of deaths.
- Number of dependents in a country. There are two groups of dependents — young dependents (aged below 15 years) and elderly dependents (aged over 65 years). Those of the working age are the economically active.
The population pyramid of a country in which birth and death rates both are high is broad at the base and rapidly narrows towards the top. This is because although, many children are born, a large percentage of them die in their infancy, relatively few become adults and there are very few old people.
In countries where death rates (especially amongst the very young) are decreasing, the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, because more infants survive to adulthood.
Such populations contain a relatively large number of young people and which means a strong and expanding labour force.
Low birth rates make the pyramid narrow at the base and decreased death rates allow numbers of people to reach old age.
MCQs based on NCERT Class 8 Geography Chapter 6: Human Resources
1. What does the term population distribution refer to?
(a) How population in a specified area changes over time.
(b) The number of people who die in relation to the number of people born in a specified area.
(c) The way in which people are spread across a given area.
(d) Number of dependents in a country.
Ans. a
2. Which are three main factors that cause population change?
(a) Births, deaths and marriage
(b) Births, deaths and migration
(c) Births, deaths and life expectancy
(d) Births, deaths and immigration
Ans. b
3. In 1999, the world population reached
(a) 1 billion
(b) 3 billion
(c) 6 billion
(d) 8 billion
Ans. c
4. What is a population pyramid?
(a) A graphical presentation of the age, sex composition of a population.
(b) When the population density of an area is so high that people live in tall buildings.
(c) Pattern of population distribution in large urban areas.
(d) None of the above
Ans. a
5. Which of the following is one of the factors affecting distribution of population?
(a) Climate
(b) Soil
(c) Water
(d) All of the above
Ans. d
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Human Resources
What is birth rate?
What is death rate?
What is Migration?
What are the causes for the uneven distribution of population in the world?
What is meant by population composition?
Share Blog
 Latest
Latest 
Comments