Stars and The Solar System Class 8 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 24-09-2023
24-09-2023
 18:22 PM IST
18:22 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
The chapter discusses about the solar system and its planets along with other celestial bodies.
Celestial Objects
The stars, the planets, the moon and many other objects in the sky are called celestial objects. Objects that do not twinkle are planets. The moon is the brightest object in the night sky.
Let us discuss about some of the celestial objects:
The Moon
The moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. The moon does not produce its own light; it reflects the sunlight falling on it and hence, we can see the moon. The shape of the moon keeps on changing as we see only that part of the moon from which the light of the Sun is reflected towards us.
The various shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called phases of the moon.
- Full Moon Day: The day on which the whole disc of the moon can be seen clearly. After this day, the size of the bright part of the moon (sunlit part) appears to become thinner and thinner.
- New Moon Day: On the 15th day from the full moon day, the moon is not visible. This day is called New Moon Day. The next day, only a small portion of the moon is visible. This is called crescent moon. The size of the illuminated part of the moon visible from the Earth increases each day after the new moon day.
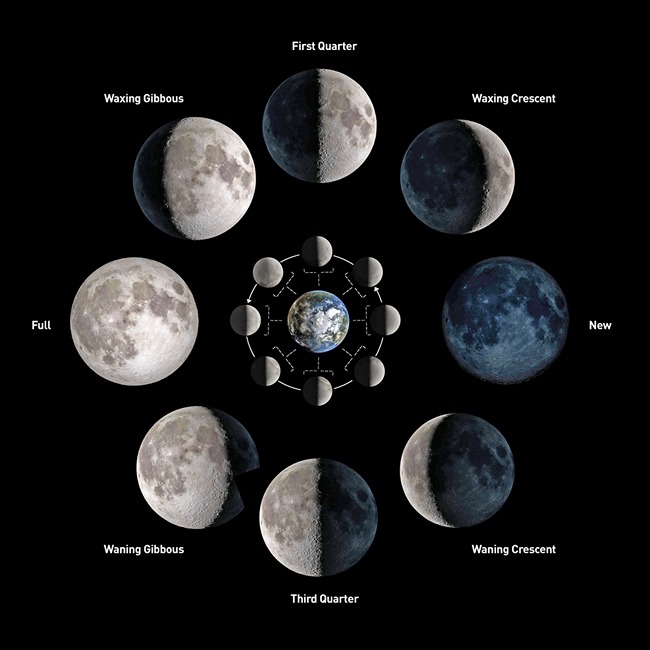

Fig.1: Phases of Moon
NOTE: The time period between one full moon and the next full moon is slightly longer than 29 days. In many calendars, this time period is called one month.
It revolves around the Earth, which along with the moon revolves around the Sun. The moon completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the Earth.
The Moon and the Earth while rotating and revolving come in a position where the given two conditions occur:
(a) Moon is between the Earth and the Sun- Moon’s shadow crosses the Earth’s surface. It blocks the sunlight from reaching the Earth. This causes a Solar Eclipse.
(b) Earth is between the Moon and the Sun- The Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the moon. Shadow of the Earth is cast over the Moon. This is called the Lunar eclipse. It occurs only when the Moon is full.
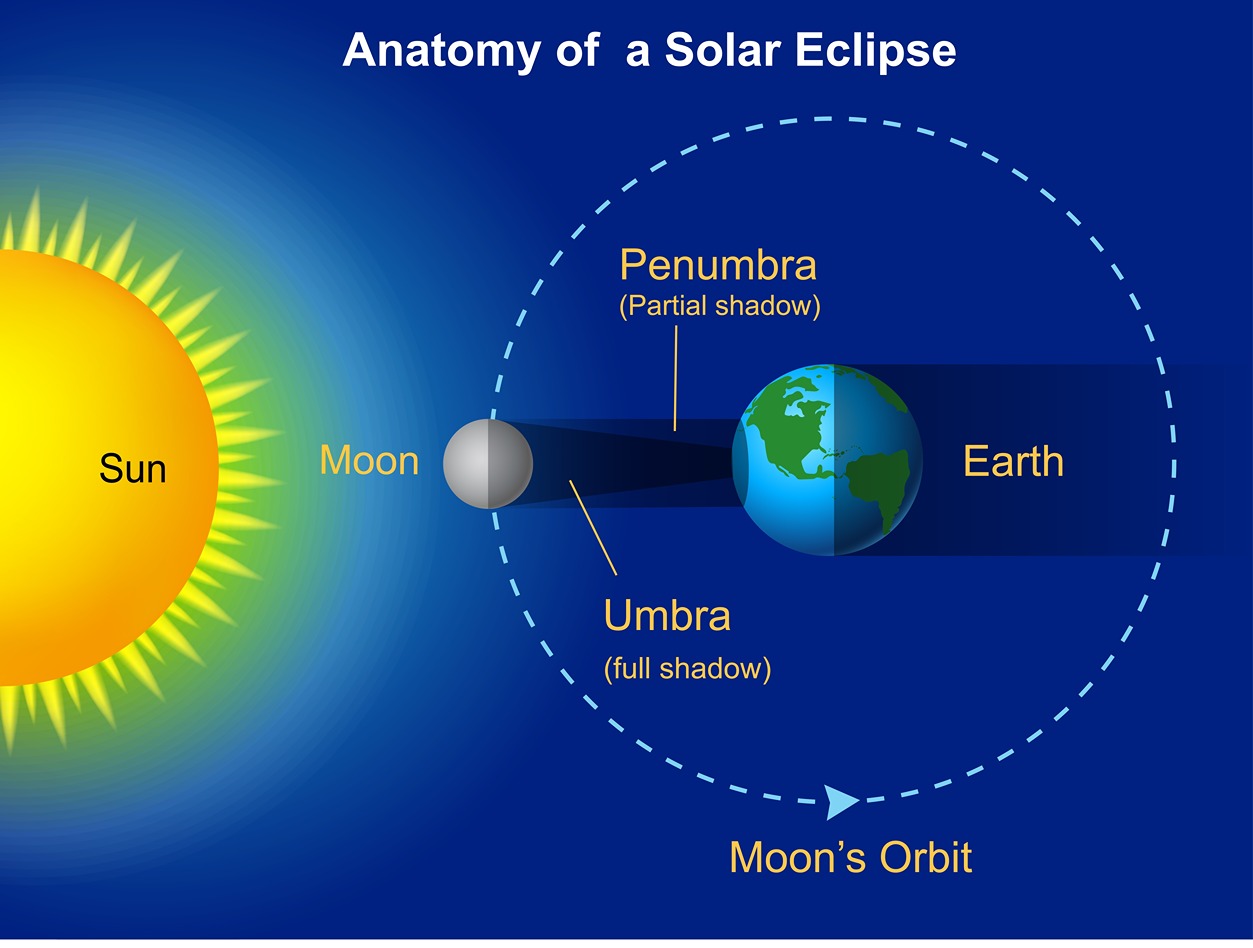
Fig.2: Solar Eclipse
The surface of the moon is dusty and barren. There are many craters of various sizes. There are also many steep and high mountains, some of which are as high as the highest mountains on the Earth. It has no atmosphere and water. (NOTE: NASA has recently announced that for the first time they have confirmed the water molecule in the sunlit areas of the moon)
Neil Armstrong, an American astronaut, was the first person to land on the moon on 21 July 1969. He was followed by Edwin Aldrin.
The Stars
The Stars emit light of their own. Sun is also a star. There are numerous stars in the sky and these are millions of times farther away than the Sun. Therefore, these stars appear to be smaller than the Sun. The stars are present in the sky every time but they can’t be seen during the day time due to the bright sunlight. Stars appear to move from east to west. A star that rises in the east in the evening, sets in the west in the early morning.
NOTE: The Pole Star is situated in the direction of the Earth’s axis therefore it appears to be stationary. It is not visible from the Southern Hemisphere. All the stars appear to revolve around the Pole Star as they do not lie exactly above the Earth’s axis and therefore when the Earth rotates from West to East, the constellation appears to move from West to East around the pole star.
Constellation
The group of stars forming a recognizable shape is called a constellation.
Some of the constellations are:
The most noted constellation during the summer night is Ursa Major also called Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. Constellation also appears to move in the sky from east to west.
Orion is also a famous constellation. It can be seen during the winters. It has 7 or 8 bright stars. It is also called the Hunter. Sirius, the brightest star in the sky, is located close to Orion.
Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky. It appears like a distorted letter W or M.
Note: All the stars which make up a constellation are not at the same distance. They are just in the same line of sight in the sky.
The Solar System
The Sun and the celestial bodies revolving around it form the solar system. There are numerous bodies in our solar system which include planets, comets, asteroids, and meteors. The gravitational attraction between the Sun and the celestial bodies keeps them revolving around it.
There are 8 planets in our solar system which are listed in the increasing order of their distance from the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The first four planets are called inner planets and the last four are called outer planets.
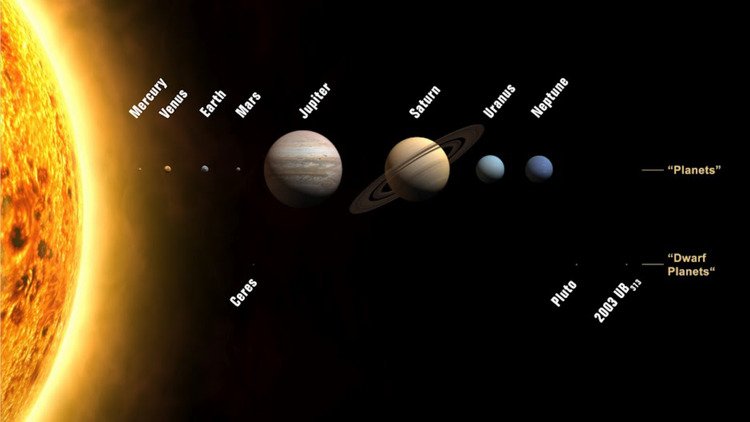
Fig.3: Solar System
The Sun
It is the nearest star to the Earth. The Sun is nearly 150,000,000 kilometres (150 million km) away from the Earth. It emits heat and light. It is the source of energy on Earth.
The next nearest star is Alpha Centauri. It is around three times as far as the Sun from the Earth. Large distances are expressed in another unit known as light year. It is the distance travelled by light in one year. The speed of light is about 3x108 m/s. Therefore, the distance of the Sun from the Earth is about 8 light minutes. The distance of Alpha Centauri is about 4.3 light years.
The Planets
The planets do not have the light of their own; they reflect the sunlight falling on them. Planets unlike stars do not twinkle and keep changing their positions with respect to the stars.
Orbit: The planets revolve around the Sun in a definite path called orbit.
Period of Revolution: The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution. It increases with the increase in distance from the Sun.
Period of Rotation: The time taken by a plant to complete one rotation on its own axis.
Satellite: Any celestial body revolving around another celestial body is called its satellite. The man-made satellites revolving around the Earth are called artificial satellites.
1. Mercury (Budh)
- Mercury is nearest to the Sun and is the smallest planet. It can be observed just before sunrise or just after sunset, near the horizon.
- Mercury has no satellite of its own.
2. Venus (Shukra)
- Venus is Earth’s nearest planetary neighbour. It is the brightest planet in the night sky.
- It is called morning or an evening star as it sometimes appears in the eastern sky before sunrise and sometimes in the western sky just after sunset.
- Venus has no moon or satellite of its own.
- It rotates from east to west while the Earth rotates from west to east.
3. The Earth (Prithvi)
- The Earth is the only planet in the solar system on which life is known to exist. Some favourable conditions like the right distance from the Sun, the right temperature range, the presence of water and suitable atmosphere and a blanket of ozone are responsible for the existence of life on the Earth.
- It is also called Blue Planet as it appears blue due to the reflection of light from water and landmass on its surface.
- The axis of rotation of the Earth is not perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. It is somewhat tilted. The plane of the equator is called the equatorial plane. The plane in which the Earth revolves around the Sun is called the orbital plane of the Earth. These two planes are inclined to each other at an angle of 23.5°. The change of seasons on the Earth is due to the tilt of the axis of the Earth.
- The Earth has only one moon.
4. Mars (Mangal)
It is called the Red planet as it appears slightly reddish. It has two small natural satellites.
5. Jupiter (Brihaspati)
It is the largest planet in our solar system. The mass of Jupiter is about 318 times that of our Earth. It has a large number of satellites and has rings around it.
6. Saturn (Shani)
It appears yellowish in color. It has rings around it. It also has a large number of satellites. It is the least dense among all the planets. Its density is in fact less than that of water.
7. Uranus and Neptune
These are the outermost planets in the Solar System. Uranus rotates from East to West. It has a highly tilted rotational axis due to which its orbital motion appears to roll on its side. The outer planets have a large number of moons.
Other celestial bodies in our solar system
1. Asteroids: The gap in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the Sun. These are called asteroids. They can only be seen through large telescopes.
2. Comets: They revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. It generally appears as a bright head with a long tail that grows in size as it approaches the Sun. The tail is directed away from the Sun. Halley’s Comet appears after nearly 76 years. It appeared last in 1986.
3. Meteors and Meteorites: Meteors are commonly called shooting stars. These are generally small objects that occasionally enter the Earth’s atmosphere. Due to the atmospheric friction, it heats up, glows and evaporates quickly. Large meteors that reach the Earth are called meteorites. When the Earth crosses the tail of a comet, swarms of meteors are seen. These are known as meteor showers.
4. Artificial Satellites: These are man-made satellites launched from the Earth. Aryabhatta was the first Indian satellite. Other Indian satellites are INSAT, IRS, Kalpana-I, EDUSAT, etc. These satellites can be used for forecasting weather, transmitting television and radio signals, telecommunication and remote sensing.
MCQs based on NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 17:Stars and The Solar System
1. Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
a. An asteroid
b. A satellite
c. A constellation
d. A comet
Ans. c
Explanation:
Sun and other celestial bodies revolving around it including planets, asteroids, comets, satellite, meteors, etc. form the solar system.
2. Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
a. Sirius
b. Mercury
c. Saturn
d. Earth
Ans. a
Explanation:
There are 8 planets in our solar system which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
3. Phases of the moon occur because
a. we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
b. our distance from the moon keeps changing.
c. the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon’s surface.
d. the thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Ans. a
Explanation:
Phases of the moon occur because we can see only that part of the moon that reflects light towards us.
4. Name the star that appears stationary from the Earth.
a. Pole Star
b. Ursa Major
c. Ursa Minor
d. Orion
Ans. a
Explanation:
Pole Star lies directly above the axis of rotation of the Earth, therefore, it appears to be stationary from the Earth.
5. Which planet is called a morning star or an evening star?
a. Mercury
b. Venus
c. Earth
d. Mars
Ans. b
Explanation:
Venus is called morning or an evening star as it sometimes appears in the eastern sky before sunrise and sometimes in the western sky just after sunset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Sun and the Solar System
Why can’t we see the stars during day time?
Why the Sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west?
Why do all constellations appear to revolve around the pole star?
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Share Blog
 Latest
Latest 
Comments