Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 23-08-2023
23-08-2023
 17:12 PM IST
17:12 PM IST
 PendulumEdu
PendulumEdu
This chapter - Microorganisms Class 8 discusses microorganisms, their benefits and their harms. It also discusses other important topics such as antibiotics, vaccines, food preservation and the nitrogen cycle.
Microorganisms (microbes)
Microorganisms are so small in size that they are not visible to the unaided eye. Some key points of microorganisms are given below.
- Some microorganisms such as fungus can be seen with a magnifying glass. Others cannot be seen without the help of a microscope.
- Microorganisms can live in all kinds of environments, ranging from ice cold climates to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands.
- Microorganisms may be unicellular (single-celled) or multicellular. Bacteria, some algae and protozoa are unicellular (single-celled). Many algae and fungi are multicellular.
- Microorganisms are found in air, water and in the bodies of plants and animals.
Major groups of microorganisms
There are four major groups of microorganisms. These are bacteria, fungi, protozoa and some algae. Viruses, though different from bacteria, fungi, protozoa and algae, are considered microbes.
Viruses
Viruses are also microscopic but are different from other microorganisms. They reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism. A bacterium, plant or animal may be the host organism for viruses. They cause common ailments like cold, influenza (flu) and most coughs. They also cause serious diseases like polio and chickenpox.
Benefits and uses of microorganisms
- Making of food items:
- Curd: Curd contains several microorganisms. Of these, the bacterium, Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd from milk.
- Cheese and pickles: Bacteria are also involved in the making of cheese and pickles.
- Idlis and dosa batter: Bacteria and yeast are also helpful for the fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
- Baking industry: Yeast is used in the baking industry for making breads, pastries and cakes. It reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of the gas fill the dough and increase its volume.
- Commercial uses: Microorganisms are used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar). Commercial production of alcohol and wine is done by growing yeast on natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice, crushed fruit juices, etc.
- Medicinal uses: Microorganisms are sources of antibiotics. Vaccines are made on a large scale from microorganisms to protect humans and other animals from several diseases.
- Increasing soil fertility: Cyanobacteria (blue green algae) are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich the soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility.
- Cleaning environment: Some microorganisms decompose the organic waste and dead plants and animals into simple substances and clean up the environment.
Harmful microorganisms
Disease causing microorganisms in humans
Microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, food or physical contact are called communicable diseases. Cholera, common cold, chickenpox and tuberculosis are examples of communicable diseases. Protozoans cause serious diseases like dysentery and malaria.
Click here to read in detail about Human Diseases.
Some common human diseases are given below.
- Tuberculosis: It is caused by a bacterium and transmitted through the air. Its general preventive measures are following.
- Keep the patient in complete isolation
- Keep the personal belongings of the patient away from those of the others
- Vaccination at a suitable age
- Measles, Chickenpox and Polio: All three are caused by viruses. Preventive measures of measles, chickenpox and polio are the same as those for tuberculosis. Their modes of transmission are given below.
- Measles is transmitted through the air.
- Chickenpox is transmitted through air or contact.
- Polio is transmitted through air or water.
- Cholera and Typhoid: They are caused by bacteria. Cholera can be transmitted through water or food. Typhoid is transmitted through water. Their general preventive measures are following.
- Maintain personal hygiene and good sanitary habits
- Consume properly cooked food and boiled drinking water
- Vaccination
- Hepatitis A: It is caused by viruses and transmitted through water. Its general preventive measures include drinking boiled drinking water and vaccination.
- Malaria: It is caused by protozoa and transmitted through mosquitoes. Its general preventive measures are given below.
- Use mosquito net and repellents.
- Spray insecticides and control the breeding of mosquitoes by not allowing water to collect in the surroundings.
Carriers of microbial diseases
Some insects and animals act as carriers of disease causing microbes. The housefly, female Anopheles mosquito and female Aedes mosquito act as carriers of disease. Female Anopheles mosquito carries the parasite of malaria (Plasmodium). The Female Aedes mosquito acts as a carrier of the dengue virus. All mosquitoes breed in water.
Disease causing microorganisms in animals
Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium. Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
Disease causing microorganisms in plants
Some common plant diseases are given in the table.
| Plant diseases | Microorganisms | Mode of transmission |
| Citrus canker | Bacteria | Air |
| Rust of wheat | Fungi | Air, seeds |
| Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi (Okra) | Virus | Insect |
Click here to read in detail about Plant Diseases.
Microbes causing food poisoning
Some of the microorganisms grow on our food and cause food poisoning. Salmonella, Clostridium perfringens, Campylobacter, Staphylococcus aureus, E.coli, Norovirus are some of the microorganisms that cause food poisoning. The bacterium Campylobacter jejuni is a common cause of food poisoning
Food preservation
Salts and edible oils are the common chemicals generally used to check the growth of microorganisms. They are called preservatives. Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are common preservatives. Some common methods of food preservation are given below.
| Method | Use/ Key points |
| Preservation by Common Salt | Used to preserve meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes, tamarind |
| Preservation by Sugar | Used to preserve Jams, jellies and squashes |
| Preservation by Oil and Vinegar | Used to preserve pickles, Vegetables, fruits, fish and meat |
| Heat and Cold Treatments | Boiling kills the growth of microbes and keeping food in the refrigerator inhibits their growth |
| Pasteurisation | Milk is heated to about 70o C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored |
Antibiotics
Medicines that kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotics. Some important points about antibiotics are given below.
- A large number of antibiotics, such as Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin are made from fungi and bacteria.
- Antibiotics are also used to control microbial infections in animals, including livestock and poultry and to control plant diseases.
- Antibiotics taken unnecessarily may kill the beneficial bacteria in the body.
- Antibiotics are not effective against cold and flu as these are caused by viruses.
Vaccines
Several diseases, including cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination. Polio drops given to children are actually a vaccine. A worldwide campaign against smallpox has finally led to its eradication from most parts of the world. Vaccines are dead or weakened microbes. When dead or weakened microbes in the form of a vaccine are introduced into a healthy body, the body fights and kills the invading bacteria by producing antibodies. The antibodies remain in the body. As a result, the body is protected from the disease-causing microbes forever.
Fermentation
Yeast converts sugar into alcohol through the process known as fermentation. Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation in 1857.
Nitrogen fixation
Some microorganisms reside in the root nodules of leguminous plants. They can fix nitrogen from the air into the soil and increase the soil fertility. Bacterium Rhizobium lives in the root nodules of leguminous plants such as beans and peas. It has a symbiotic relationship with these plants. Sometimes nitrogen gets fixed through lightning.
Nitrogen cycle
The atmospheric nitrogen cannot be taken directly by plants and animals. Some bacteria present in the soil fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into nitrogenous compounds. Certain bacteria convert compounds of nitrogen present in the soil into nitrogen gas which is released to the atmosphere.
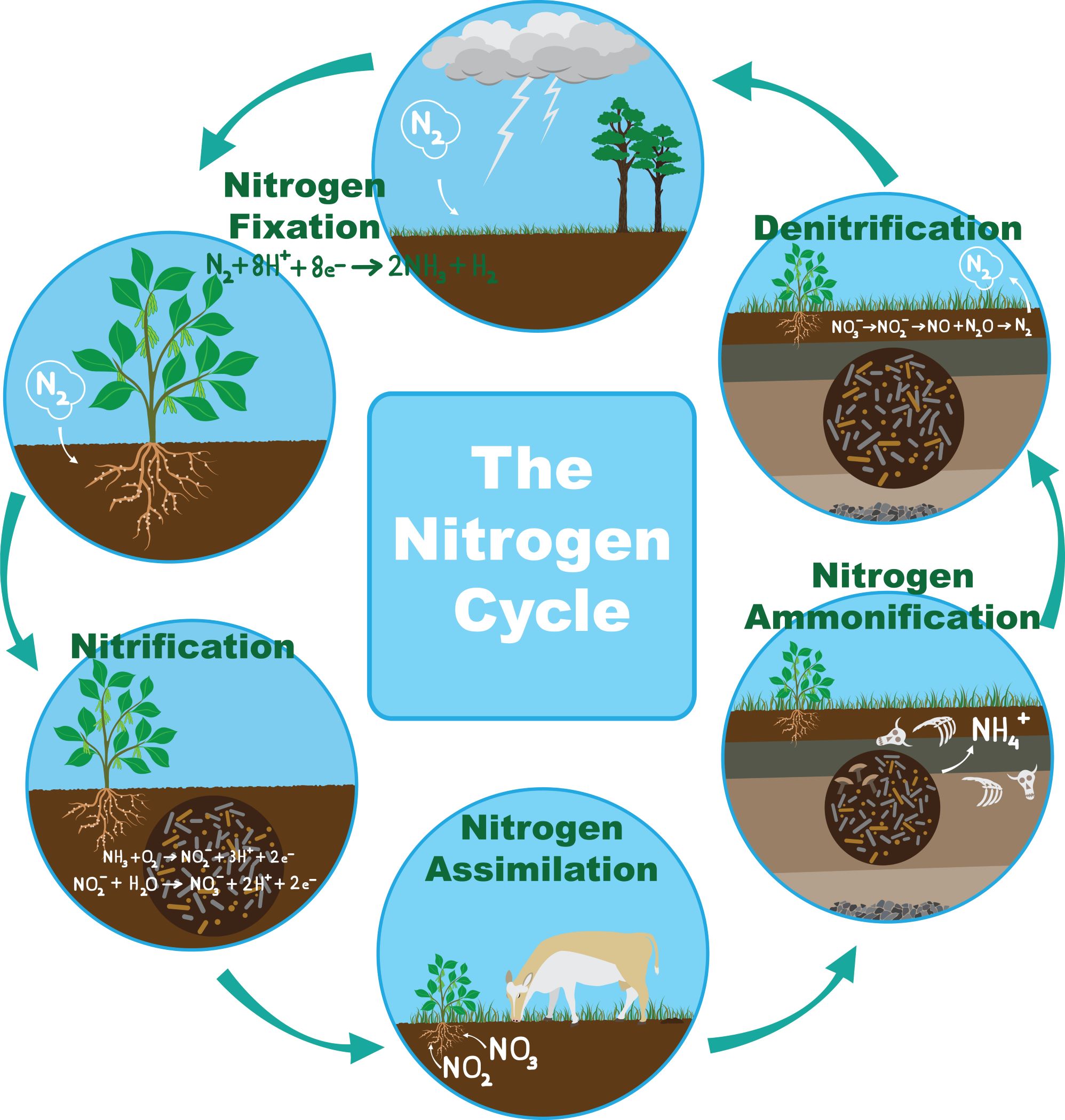
Fig.1: Nitrogen Cycle
NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Question and Answers
1. Yeast is used commonly in the baking industry. It comes under which of the following category of microorganisms?
a. Bacteria
b. Protozoa
c. Algae
d. Fungi
Ans. d
Explanation: There are four major groups of microorganisms. These are bacteria, fungi, protozoa and some algae. Yeast comes under fungi. Yeast is used in the baking industry for making bread, pastries and cakes. It reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of the gas fill the dough and increase its volume.
2. Which of the following is used to preserve Jams, jellies and squashes?
a. Common salt
b. Sugar
c. Oil and vinegar
d. Heat and cold treatment
Ans. b
Explanation:
Sugar is used to preserve Jams, jellies and squashes while common salt is used to preserve meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes, tamarind.
3. Antibiotics are used to control microbial infections and diseases in-
a. Humans
b. Animals
c. Plants
d. All of the above
Ans.d
Explanation:
Medicines that kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotics. They are also used to control microbial infections and diseases in humans, animals, including livestock and poultry and plants.
4. Which of the following diseases is not caused by a virus?
a. Tuberculosis
b. Measles
c. Chickenpox
d. Polio
Ans a
Explanation:
Tuberculosis is not caused by a virus. It is caused by a bacterium (Mycobacterium). Measles, chickenpox and polio are caused by viruses. The modes of transmission of these diseases are given in the following table.
5. Which of the following is not a communicable disease?
a. Cholera
b. Diabetes
c. Common cold
d. Chickenpox
Ans b
Explanation:
Diabetes is not a communicable disease. Microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, food or physical contact are called communicable diseases. Cholera, common cold, chickenpox and tuberculosis are examples of communicable diseases.
6. Malaria is caused by
a. Bacteria
b. Virus
c. Protozoa
d. Algae
Ans. c
Explanation:
Malaria is caused by protozoa (Plasmodium) and transmitted through mosquitoes. Female Anopheles mosquito carries the parasite of malaria (Plasmodium). The Female Aedes mosquito acts as a carrier of the dengue virus.
| NCERT Class 8 Science Chapters |
Share Blog


 Latest
Latest 
Comments