Cell — Structure and Functions Class 8 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 23-08-2023
23-08-2023
 17:13 PM IST
17:13 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
The chapter discusses cells, their shapes, size, and types of organisms based on the number of cells. It also discusses the structure of the cell and the difference between plant cells and animal cells.
What is a Cell?
All organisms are made of smaller parts called organs. Organs are made of still smaller parts. Cells were first observed in cork by Robert Hooke in 1665. The smallest living part of an organism is a ‘cell’. Some cells are big enough to be seen with the unaided eye. Hen’s egg is an example.
Shapes of cells
Cells exhibit a variety of shapes. Amoeba, a unicellular organism has no definite shape. A white blood cell (WBC) in human blood is an example of a single cell that can change its shape and size. Generally, cells are round, spherical or elongated. They may be spindle-shaped (long and pointed at both ends). Some cells are branched like the nerve cell or a neuron.
Size of cells
The smallest cell is 0.1 to 0.5 micrometre in bacteria. The largest cell is the egg of an ostrich. The size of the cells has no relation with the size of the body of an organism. The size of the cell is related to its function.
Unicellular and multicellular organisms
Organisms made of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms. Single-celled organisms (Organisms made up of a single cell) are called unicellular. They perform all the necessary functions that multicellular organisms perform. In Multicellular organisms, the functions are performed by groups of specialised cells forming different tissues. Tissues form organs.
Structure of the cell
The cell in a living organism is the basic structural unit. It has three main parts. They are cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus.
1. Cell membrane
It encloses components of a cell and provides shape to the cells of plants and animals. It is also called the plasma membrane. It is porous and substances or materials can move inward and outward through it.
2. Cytoplasm
It contains smaller components called organelles. They are mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc.
3. Nucleus
It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell. It is separated from cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane. It contains nucleolus and thread-like structures called chromosomes. It has following functions.
- It plays a role in inheritance as it contains chromosomes, which carry genes and help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
- It is the control centre of the activities of the cell.
NOTE: Gene is a unit of inheritance in living organisms. It controls the transfer of a hereditary characteristic from parents to offspring.
4. Protoplasm
It is known as living substance of the cell. It includes cytoplasm and the nucleus.
5. Plastids
These are small colored bodies present in the cytoplasm of leaf cells. They are of different colors. Some of the plastids contain green pigment (chlorophyll- important for photosynthesis); these are called chloroplasts.
Types of cells
Cells can be of two types based on their internal structure. They are given below.
Prokaryotic cells
- The cells having nuclear material without a nuclear membrane are termed prokaryotic cells.
- The organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes.
- Examples: bacteria and blue-green algae
Eukaryotic cells
- The cells, like onion cells and cheek cells having well-organized nucleus with a nuclear membrane, are termed eukaryotic cells.
- The organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes.
- Examples: All organisms other than bacteria and blue-green algae
Difference between Plant cells and Animal cells
Coloured bodies called plastids are found in plant cells only. Plant cell has a big central vacuole unlike a number of small vacuoles in animal cells.
In plants, the cell membrane is surrounded by an outer thick layer called cell wall. The cell wall protects plants against variations in temperature, high wind speed, atmospheric moisture, etc. A cell wall is absent in animal cells while it is present in a plant cell.
Centrioles are found in animal cells while they are absent in plant cells.
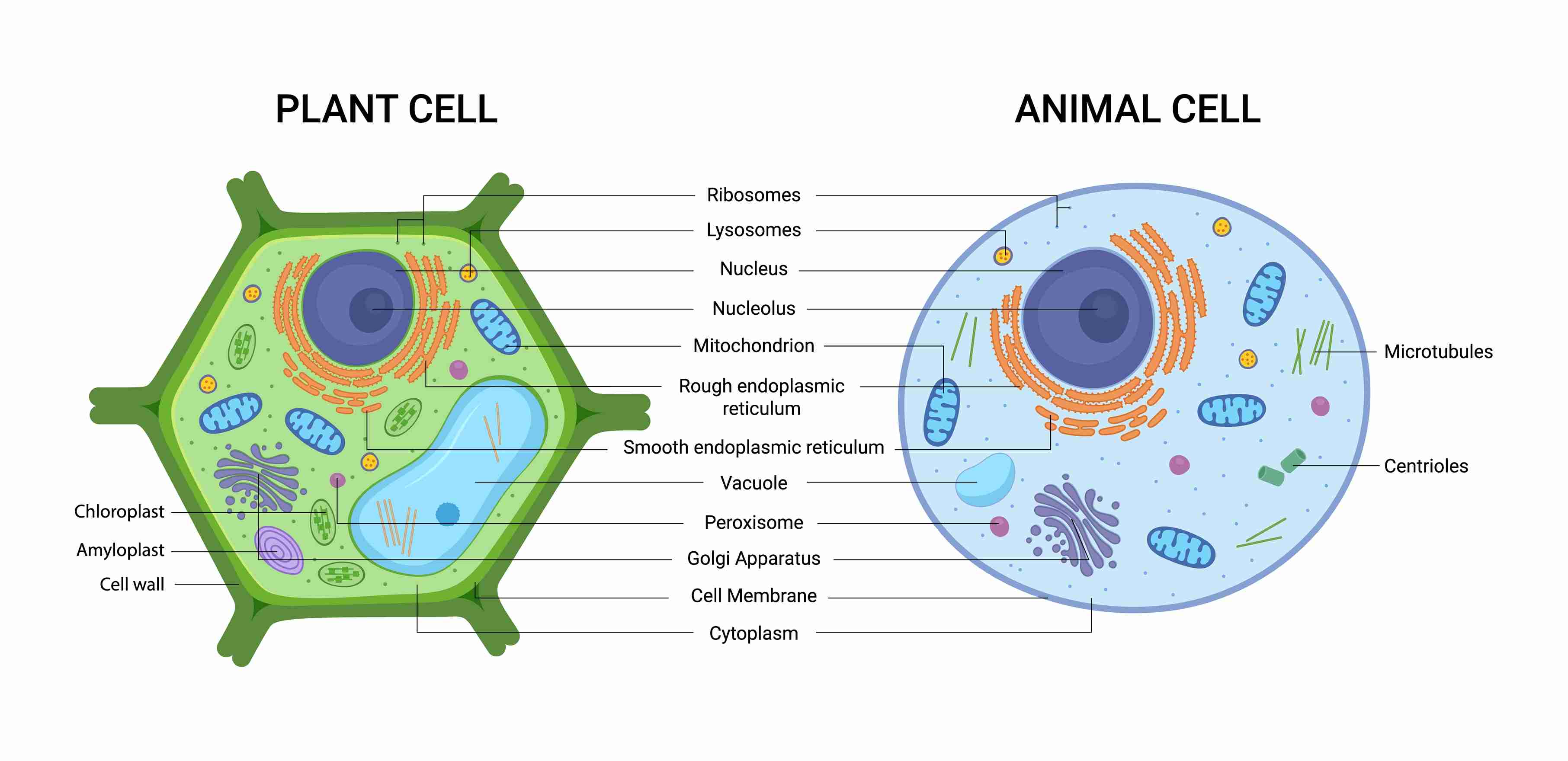
Fig.1: Animal and Plant Cell
MCQs based on NCERT Class 8 Chapter 8- Cell- Structure and Functions
1. Which of the following is not a characteristics feature of plant cells?
a. Cell wall
b. Plastids
c. Small vacuoles
d. Both a and b
Ans. c
Explanation:
Coloured bodies called plastids are found in plant cells only. In plants, cell membrane is surrounded by an outer thick layer called cell wall. Plant cell has a big central vacuole unlike a number of small vacuoles in animal cells. So, characteristic features of plant cells are the cell wall, a large central vacuole and plastids.
2. Which of the following is known as the living substance of the cell?
a. Cytoplasm
b. Protoplasm
c. Nucleus
d. Cell membrane
Ans. b
Explanation:
Protoplasm is known as the living substance of the cell. It includes the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The cell membrane encloses components of cell and provides shape to the cells. It is also called the plasma membrane.
3. Which of the following is the control centre of activities of cell?
a. Cytoplasm
b. Nucleus
c. Cell membrane
d. Cell wall
Ans. b
Explanation:
Nucleus is the control centre of the activities of the cell. It also plays a role in inheritance as it contains chromosomes, which carry genes and help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
4. Green plastids are known as ________.
a. Leucoplast
b. Chromoplast
c. Chloroplast
d. Amyloplast
Ans. c
Explanation:
Plastids are colored bodies found in plant cells only. The green color plastid is called chloroplast. It is green due to the presence of chlorophyll.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Cell-Structure and Functions
Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Where are chromosomes found in a cell?
What is the living substance in the cell called?
Share Blog
 Latest
Latest 
Comments