Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 23-08-2023
23-08-2023
 17:13 PM IST
17:13 PM IST
 Yadvendra Singh
Yadvendra Singh
Like other processes of digestion, circulation, respiration, excretion, etc., that take place in an organism, reproduction is also an important process to study. This chapter discusses modes of reproduction, human reproductive organs and the process of reproduction in humans.
Reproduction
Reproduction is essential for the continuation of species. It ensures the continuation of similar kinds of individuals, generation after generation. There are two modes by which animals reproduce. These are asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction
The type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction.
- Budding: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new individuals develop from buds. Hydra shows budding. In hydra, new individuals develop from bulges called buds.
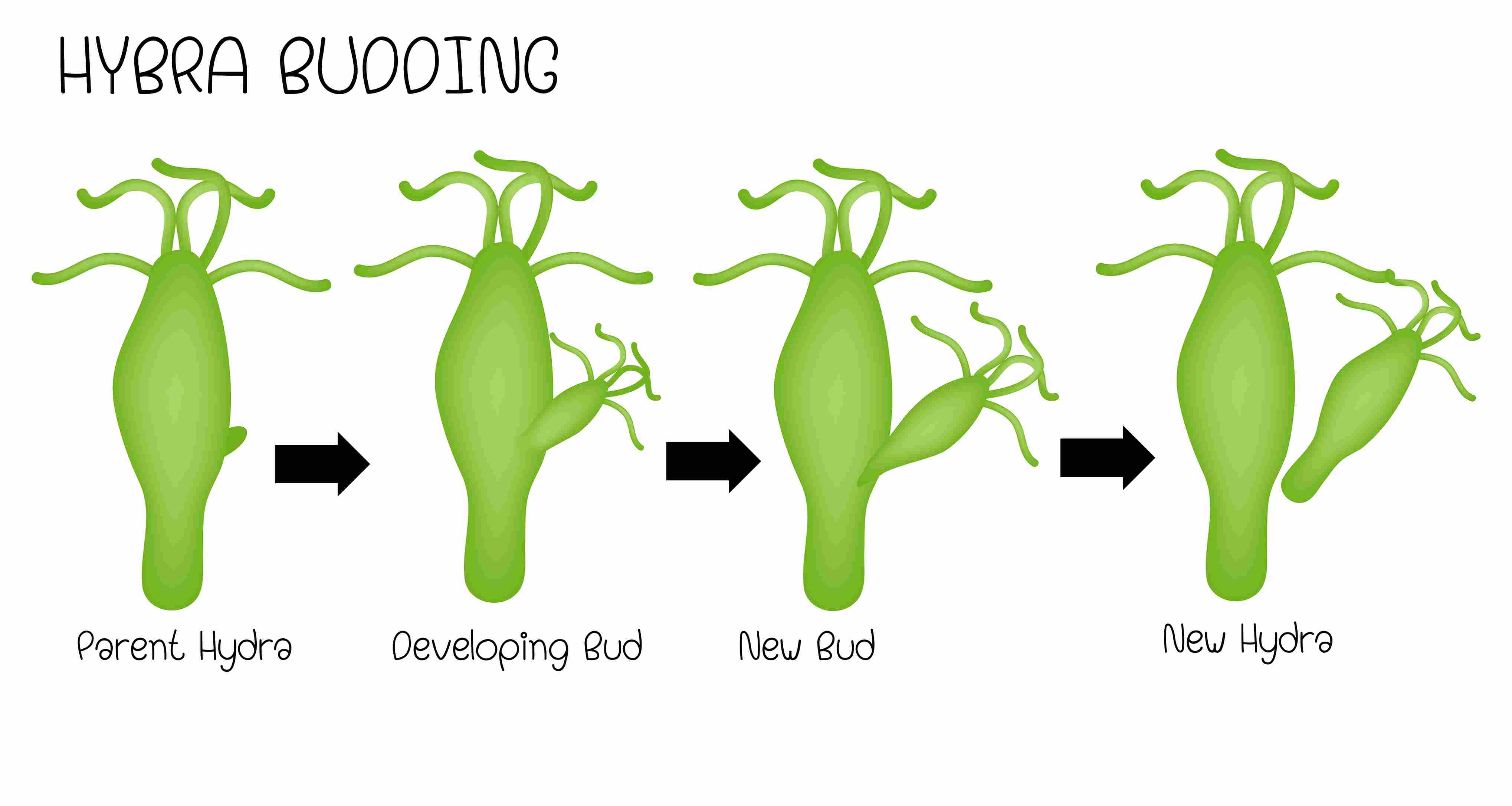
Fig.1: Budding in Hydra
- Binary fission: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals. Amoeba shows binary fission. It reproduces by dividing itself into two. First, its nucleus divides into two. Then, its body (single-cell) divides into two.
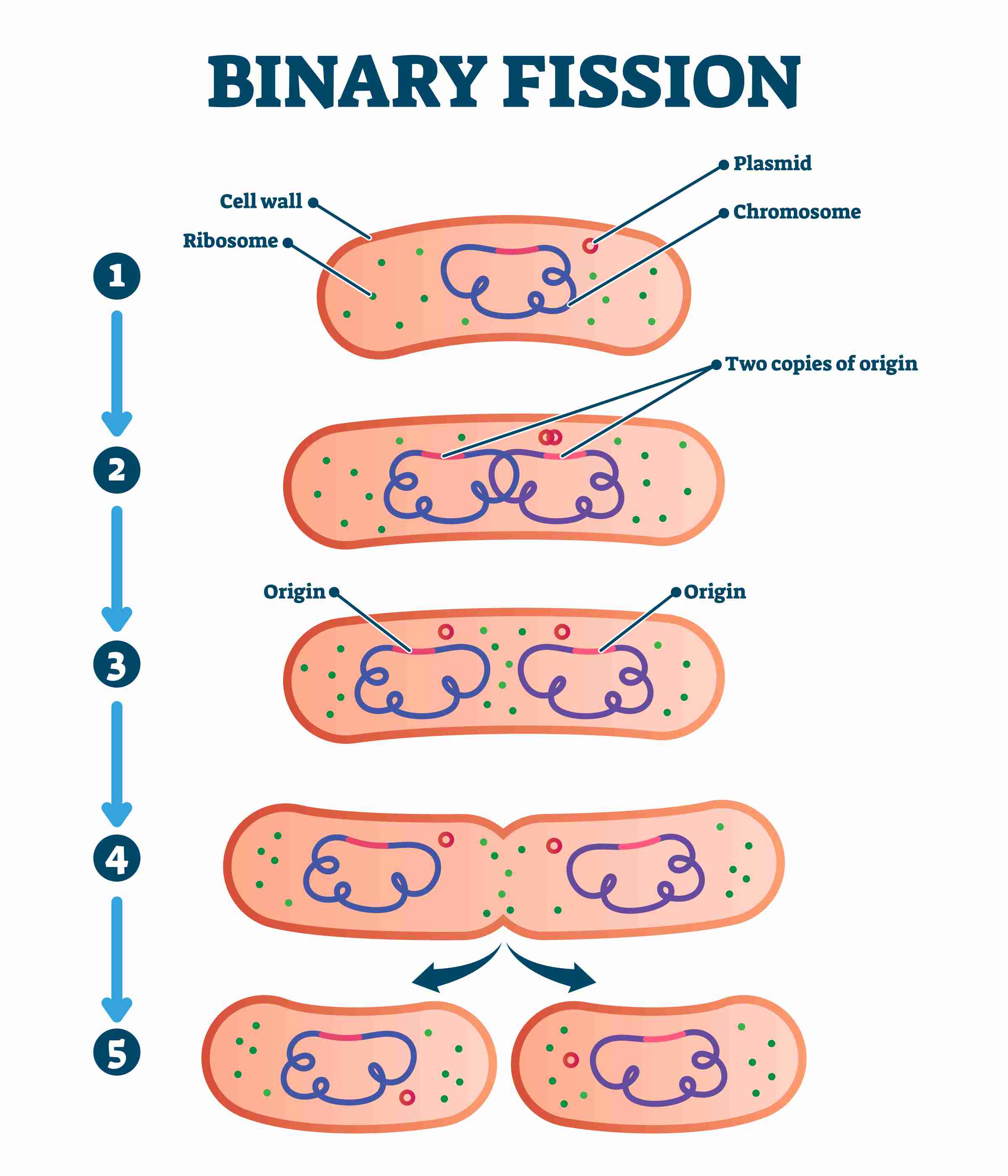
Fig.2: Binary Fission in Amoeba
Sexual reproduction
Reproduction resulting from the fusion of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction. There are different reproductive organs in males and females. The reproductive part in animals produces gametes that fuse to form a zygote similar to the plants. This zygote then develops into a new individual.
Reproductive organs in human
- The reproductive organs in males include a pair of testes, two sperm ducts and penis. Testes produce millions of male gametes called sperms. They are very small in size. Each sperm is a single cell having all cell components and a head, a middle piece and a tail.
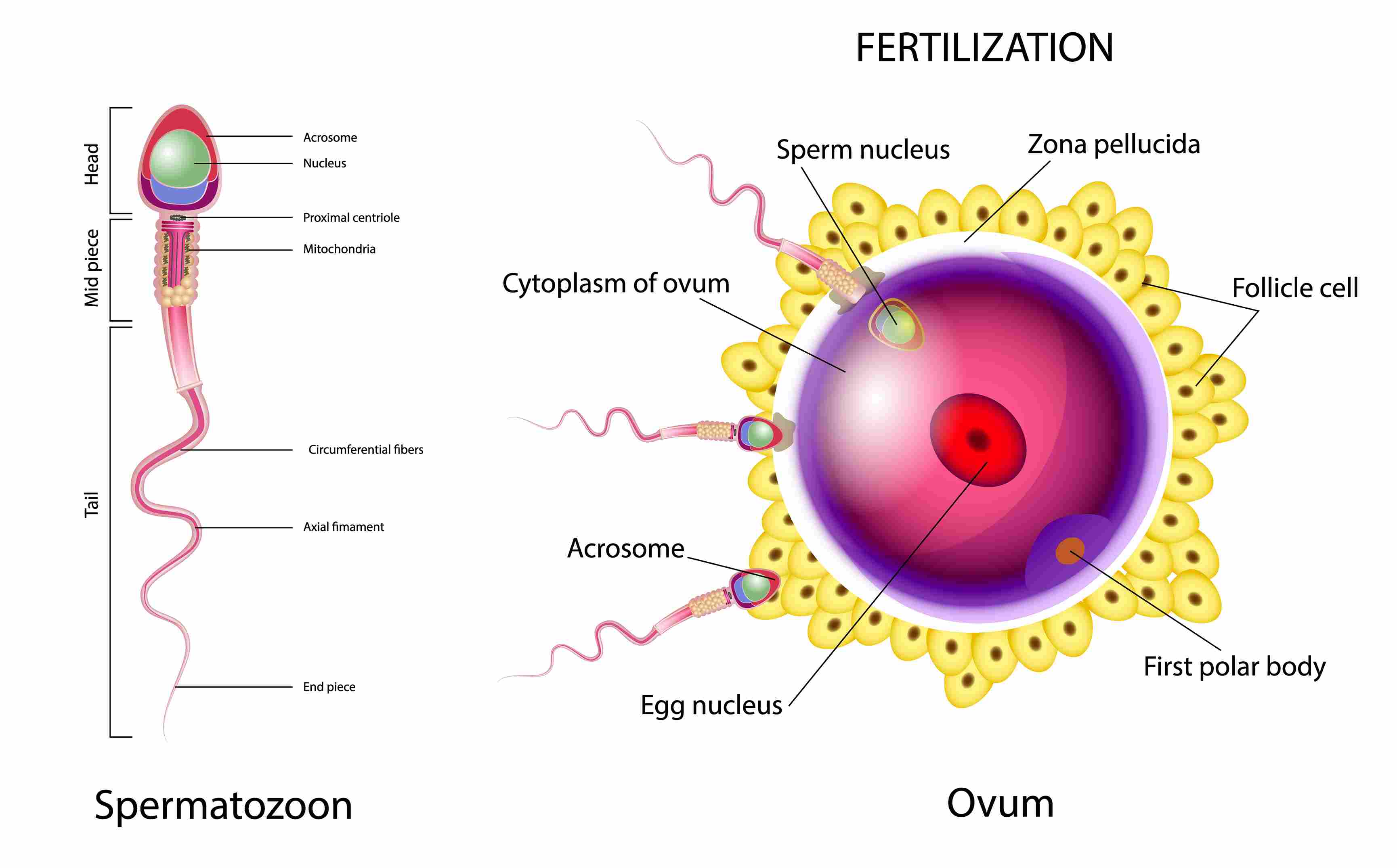
Fig. 3: Human Sperm and Ovum
- The reproductive organs in the female include a pair of ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes) and uterus. Female gametes called ova (eggs) are produced by ovaries. An egg is a single cell and a single matured egg is released every month into the oviduct. Development of the baby takes place in the uterus.
Process of reproduction in humans
1. Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the first step in the process of reproduction. The fusion of an egg cell from the mother and a sperm cell from the father is called fertilisation. During fertilisation, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus. Fertilization can be of two types.
- Internal fertilization: Fertilisation that takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. This is observed in human beings and other animals such as hens, cows and dogs.
- External fertilization: Fertilisation that takes place outside the female body is called external fertilisation. This is observed in frogs, fish, starfish, etc. These organisms produce a large number of eggs and sperms. This is necessary to ensure fertilization of at least a few of them. Not all eggs get fertilized as the eggs and sperms are exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. In frogs, the female lays hundreds of eggs that are not covered by a shell and are comparatively very delicate. Sperms of frog swim randomly in water and come in contact with egg.
2. Development of embryo
As a result of fertilisation, fertilised egg or zygote is formed. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts are identifiable is called foetus.
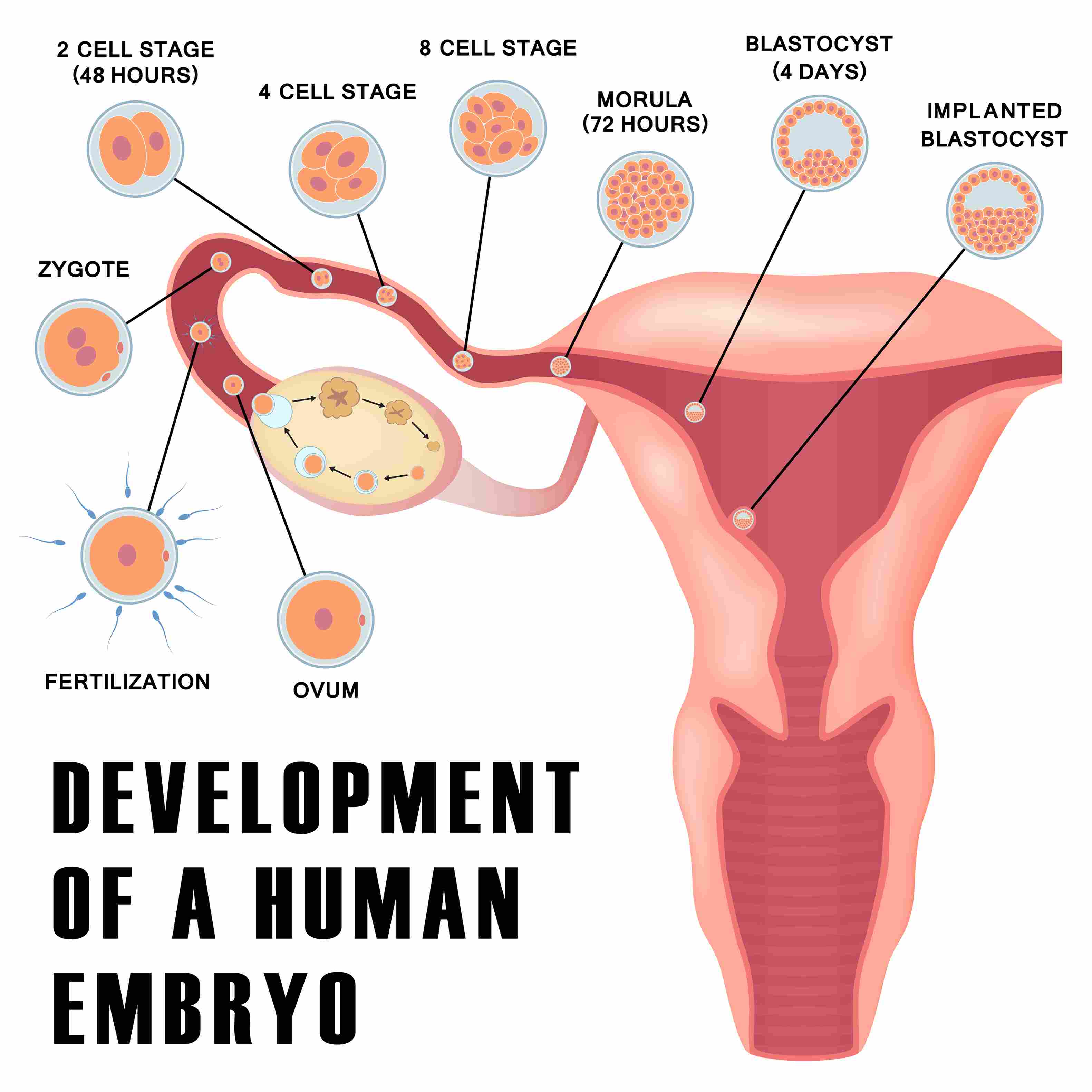
Fig.4: Development of Embryo in humans
Viviparous animals and Oviparous animals
Animals such as human beings, cows and dogs which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals.
The animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. Animals such as hens, frogs, lizards and butterflies are examples of oviparous animals.
Metamorphosis
The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis. The examples of metamorphosis are the development of adults in silkworms and frogs. In a silkworm, egg develops into larva or caterpillar. Larva or caterpillar forms pupa. Pupa develops into an adult silkworm. In frog, the egg develops into a tadpole (larva). Tadpole develops into an adult.
In vitro fertilization and test tube babies
The term test tube baby is misleading because babies cannot grow in test tubes. Test tube babies are produced through the technique of IVF or in vitro fertilisation (fertilisation outside the body). The technique is usually adopted in cases where women are unable to bear babies as their oviducts are blocked and sperms cannot reach the egg for fertilization. Complete development of a baby in IVF or in vitro fertilization takes place in the uterus and the baby is born like any other baby. The technique of IVF or in vitro fertilization involves following steps.
- Doctors collect freshly released egg and sperms and keep them together for a few hours for IVF or in vitro fertilization, which is fertilisation outside the body).
- In case fertilisation occurs, the zygote is allowed to develop for about a week and then it is placed in the mother’s uterus.
Cloning
It is the production of an exact copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organism. Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland for the first time successfully cloned an animal. It was a sheep named Dolly. Born on 5th July 1996, Dolly was the first mammal to be cloned. It died on 14th February 2003 due to certain lung disease.
MCQs based on NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 9- Reproduction in Animals
1. Which of the following shows budding mode of asexual reproduction?
a. Amoeba
b. Hydra
c. Pupa
d. Tadpole
Ans. b
Explanation:
Hydra shows budding mode of asexual reproduction. In hydra, new individuals develop from bulges called buds.
2. Which of the following is not an example of oviparous animal?
a. Human
b. Frog
c. Lizard
d. Butterfly
Ans. a
Explanation:
The animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. Animals such as hen, frog, lizard and butterfly are examples of oviparous animals.
3. Internal fertilization occurs-
a. in female body
b. outside female body
c. in male body
d. outside male body
Ans. a
Explanation:
Fertilisation that takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation.
4. A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of -
a. Fertilisation
b. Metamorphosis
c. Embedding
d. Budding
Ans. b
Explanation:
The transformation of the larva into adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis. In frog, egg develops into tadpole (larva). Tadpole develops into adult.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Reproduction in Animals
How many nuclei are present in a zygote?
In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
What is the term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra?
What is metamorphosis?
Share Blog
 Latest
Latest 
Comments