Ramsar sites of India 2025 - Updated List with Map | Ramsar Convention
As of July 2025, India has a total of 91 Ramsar sites, with addition of two new sites-Khichan (Phalodi) and Menar (Udaipur) from Rajasthan.With this latest addition, India has the largest number of wetlands in South Asia.
As of August 2024, India had a total of 85 Ramsar sites, including Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary and Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu, Tawa Reservoir of Madhya Pradesh, two wetlands of Bihar- Nagi and Nakti bird sanctuaries.
UK (176) and Mexico (144) are the countries with a maximum number of Ramsar sites.
On 13 August 2022, the Environment Ministry announced the addition of 11 more sites to the Ramsar List. As of 6 March 2023, there were a total of 75 Ramsar sites in India. It is important to go through the list of Ramsar Sites in India as there have been questions related to Ramsar Sites in the competitive exams.
Ramsar sites in India added in 2024:
1. Aghanashini Estuary in Karnataka
2. Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve in Karnataka
3. Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve in Karnataka
4. Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
5. Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu
Nagi Bird Sanctuary and Nakti Bird Sanctuary located in Bihar were added to the Ramsar List in October 2023.
21 new sites added in August 2022 are:
1. Koothankulam Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
2. Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve, Tamil Nadu
3. Vembannur Wetland Complex, Tamil Nadu
4. Vellode Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
5. Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
6. Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
7. Satkosia Gorge in Odisha
8. Nanda Lake in Goa
9. Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary in Karnataka
10. Sirpur Wetland in Madhya Pradesh
11. Hirakud Reservoir in Odisha
12. Tampara Lake in Odisha
13. Ansupa Lake in Odisha
14. Yashwant Sagar in Madhya Pradesh
15. Thane Creek in Maharashtra
16. Vaduvur Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
17. Chitrangudi Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
18. Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
19. Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex in Tamil Nadu
20. Hygam Wetlands Conservation Reserve in Jammu and Kashmir.
21. Shallbugh Wetlands Conservation Reserve in Jammu & Kashmir.
5 sites added in July 2022:
1. Karikili Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
2. Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu
3. Pichavaram Mangrove in Tamil Nadu
4. Pala wetland in Mizoram
5. Sakhya Sagar in Madhya Pradesh
How many Ramsar sites in India are there?
As of February 2025, India has a total of 89 Ramsar sites. In this topic - Ramsar sites of India, we are going to know about everything related to Ramsar sites, but firstly let's start with what are Ramsar Sites?
A Ramsar Site is a wetland site that has been designated as being of international importance by the Ramsar Convention.
Wetland is an area of land that is either covered with water or saturated with water.
1. What is the Ramsar convention?
It is an intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for national action and international cooperation for the conservation of wetlands. It was signed on 2 February 1971 in Ramsar, Iran, for the protection of wetland sites in the world. It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. Therefore, every year on 2nd February World Wetlands Day is observed.
The convention came into force on 21 December 1975. At present, 172 countries have signed the convention and there is a total of 2,532 Ramsar sites in the world.
Its main aim is to halt the worldwide loss of wetlands and conserve them through wise use and management. India signed the Ramsar Convention on 1 February 1982.
Important Facts:
The Cobourg Peninsula in Australia was the first designated Ramsar site in 1974.
The United Kingdom (175) has the world’s largest number of Ramsar Sites followed by Mexico.
Bolivia has the largest area with 148,000 square km under the Convention protection.
2. What are Wetlands?
- Article 1 of the Ramsar Convention defines a wetland as areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six meters.
- The Union Ministry of Environment excludes river channels, paddy fields, and other areas where the commercial activity takes place in its definition of wetlands.
- Wetlands cover 6.4% of the world's land surface while it covers 4.63 percent of the total geographical area of India. India has 19 types of wetlands. Gujarat with 34,700 sq km has the highest area under wetland.

Fig.1: Deepor Beel (Ramsar site in India)
3. Facts about Ramsar Sites in India
- Chilika lake (Odisha) and Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) were the first Indian wetland added to the Ramsar sites of India list in 1981.
- Now, India has a network of 91 Ramsar sites (as of July 2025).
- India has the highest number of Ramsar sites in South Asia.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest number of Ramsar Sites in India with 20 Indian Wetlands, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 wetlands on the list (as of August 2025).
- Renuka Wetland is the smallest wetland Ramsar site in India.
- Sundarbans is the largest Ramsar Site in India.
4. List of Ramsar sites in India
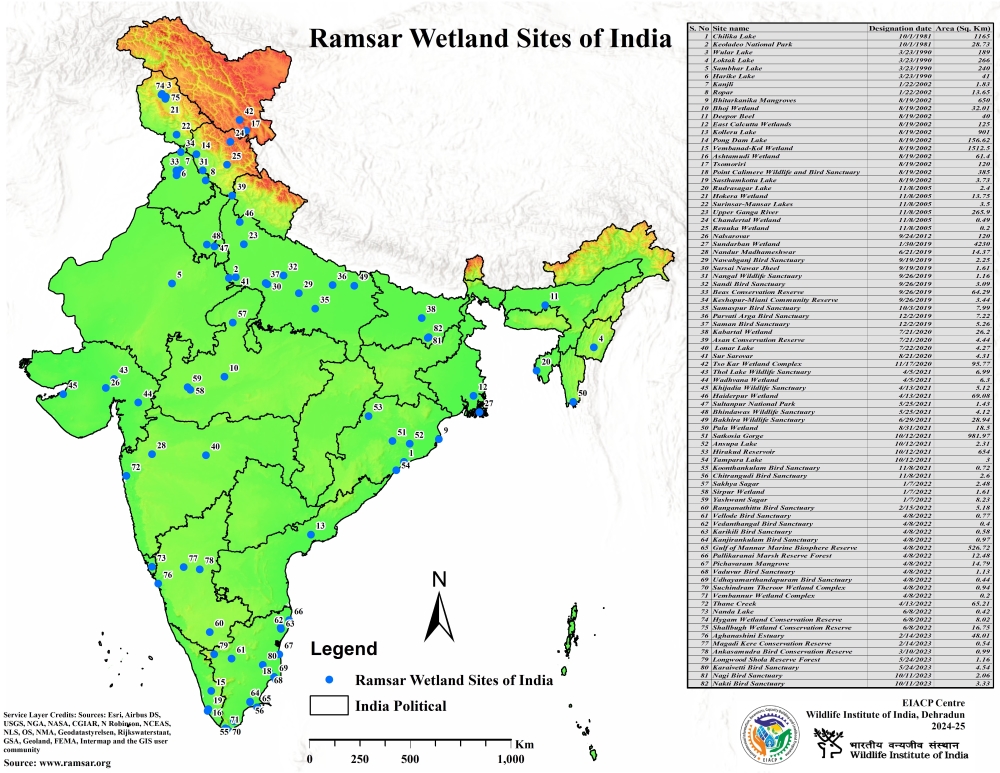
Fig.2: Location on Map for Ramsar Sites in India (Source: ENVIS)
State-wise List of All 82 Ramsar Sites in India
| Ramsar site | State/UT -No. of sites | Important Facts about Ramsar site |
| Bakhira Wildlife Sanctuary | Ramsar sites in UP - 10 | It is the largest natural flood plain wetland of India in Sant Kabir Nagar district of Eastern Uttar Pradesh. |
| Haiderpur Wetland | It is the largest human-made wetland. It is located within the boundaries of Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary. | |
| Saman Bird Sanctuary | It is a seasonal oxbow lake on the Ganges floodplain. | |
| Samaspur Bird Sanctuary | It is a perennial lowland marsh typical of the Indo-Gangetic Plains. | |
| Sandi Bird Sanctuary | It is also known by its ancient name as “Dahar Jheel”. It is famous for migratory birds. | |
| Sarsai Nawar Jheel | It is an example of cohabitation of humans and wildlife. | |
| Upper Ganga river | It is the habitat of Ganges River Dolphin, Gharial, Crocodile, 6 species of turtles, otters. | |
| Sur Sarovar | It is a human-made reservoir. It is also known as Keetham lake. Spotted eagle (Clanga clanga), sarus crane (Grus antigone) and catfish Wallago attu are found at this lake. | |
| Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary | It is a bird sanctuary located in Unnao district. It provides protection to more than 250 species of migratory birds. | |
| Parvati Agra Bird Sanctuary | It is located in the Gonda district. It has two oxbow lakes- Parvati Tal and Arga Tal.
| |
| Sultanpur National Park | Ramsar sites in Haryana - 2 | It is located in the Gurugram district of Haryana. It is part of the Central Asian Flyway route. Amur falcons, Egyptian vultures, plovers, ducks can be seen at this lake. |
| Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary | It is the largest wetland in Haryana. It supports more than ten globally threatened species. It was designated as an Eco-sensitive zone by the government in 1986. | |
| Nanda Lake | Ramsar Sites in Goa- 1 | Nanda Lake comprises intermittent freshwater marshes that lie adjacent to one of the major tributaries of the Zuari River. |
| Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary | Ramsar Sites in Karnataka- 4 | It is also referred to as Pakshi Kashi of Karnataka. It is located in the Mandya district. It is the largest bird sanctuary in Karnataka. |
| Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve | It is a human-made wetland primarily constructed to store monsoon rainwater for irrigation in a rural area of the Gadag district. | |
| Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve | The Site is found in the Vijayanagara District. It was declared as a Conservation Reserve for the protection and conservation of resident and migratory aquatic birds. | |
| Aghanashini Estuary | The Site is an estuary where the Aghanashini River flows into the Arabian Sea in Karnataka State. In addition to its estuarine and shallow marine waters, it features rocky and pebble shores, intertidal mudflats and some aquaculture ponds and rice fields. | |
| Khijadia Wildlife Sanctuary | Ramsar sites in Gujarat - 4 | It is home of more than 250 species of migratory birds. It has a unique ecosystem having both freshwater lakes, salt and freshwater marshlands. |
| Thol Lake Wildlife Sanctuary | It is on the Central Asian Flyway and more than 320 bird species can be found at this Sanctuary. | |
| Nalsarovar Bird sanctuary | It is the largest wetland bird sanctuary in Gujarat. It is a Ramsar site since 24 September 2012. | |
| Wadhvana Wetland | It is located in a semi-arid agricultural landscape. It is home of more than 80 species that migrate on the Central Asian Flyway. | |
| Ashtamudi Wetland | Ramsar sites in Kerala - 3 | It is the second-largest wetland of Kerala. It is a backish water lake. It supports a number of mangrove species as well as over 40 associated plant species.
|
| Vembanad Kol Wetland | It is the largest brackish, humid tropical wetland ecosystem. Over 90 species of resident birds and 50 species of migratory birds are found in Kol area. | |
| Sasthamkotta lake | It is the largest freshwater lake in Kerala. It is known as the Queen of Lakes. | |
| Beas Conservation Reserve | Ramsar sites in Punjab - 6 | It is the first river to be declared as a conservation reserve. The gharial reintroduction in the Beas Conservation Reserve is an ambitious programme of the Punjab government. |
| Nangal Wildlife Sanctuary | It is home of many threatened species including the endangered Indian pangolin (Manis crassicaudata) and Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus). | |
| Kanjli Wetland | It is a man-made wetland constructed across the Kali Bein river. | |
| Ropar Wetland | It is a man-made freshwater riverine and lacustrine wetland. It is home of the endangered turtle Chitra indica and the threatened snake Python molurus. | |
| Harike Wetlands | It is the largest wetland in northern India. It is particularly famous for diving ducks. | |
| Keshopur-Miani Community Reserve | It is a mosaic of natural marshes, aquaculture ponds and agricultural wetlands maintained by the annual rainfall-runoff. | |
| Bhitarkanika Mangroves | Ramsar sites in Odisha - 6 | It is a mangrove wetland in Odisha. It is famous for hosting Olive Ridley sea turtle (IUCN Status- Vulnerable). It has the highest density of saltwater crocodiles in the country. Gahirmatha Marine Wildlife Sanctuary bounds the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary to the east. |
| Chilika Lake | It is the largest brackish Water Lagoon in India. It is one of the biggest breeding places of flamingos in the world. | |
| Tampara Lake | It is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Odisha. | |
| Hirakud Reservoir | Hirakud Reservoir, the largest earthen dam in Odisha started operating in 1957. Debrigarh wildlife sanctuary is located near Hirakud dam. Hirakud Dam is built across river Mahanadi. | |
| Ansupa Lake | It is a horseshoe-shaped freshwater lake on the left bank of Mahanadi river. | |
| Satkosia Gorge | It is located within Satkosia Tiger Reserve which is a United Nations Protected Area. | |
| Bhoj Wetlands | Ramsar sites in Madhya Pradesh - 5 | It consists of two lakes located in the city of Bhopal. The two lakes are the Bhojtal & the Lower Lake. It was created by Paramara Raja Bhoj. |
| Sakhya Sagar | It is located in Shivpuri near Madhav National Park. It was created from the Manier river in 1918. | |
| Sirpur Wetland | It is a human-made wetland. It is commonly named Pakshi Vihar (bird sanctuary). It is a shallow, alkaline, nutrient-rich lake that floods during the monsoon to a maximum depth of two metres. | |
| Yashwant Sagar | It is a dam reservoir on Gambhir river that supplies water to Indore. | |
| Tawa Reservoir | ||
| Deepor Beel | Ramsar sites in Assam - 1 | It is a perennial freshwater lake and the only Ramsar site in Assam. It is a staging site on migratory flyways and is home of many aquatic birds. |
| East Kolkata Wetlands | Ramsar sites in West Bengal - 2 | It hosts the largest sewage fed aquaculture in the world. |
| Sunderbans Wetland | It is the largest mangrove forest in the world. It is home of many critically endangered species including the Irrawaddy dolphin, fishing cat. | |
| Hokera Wetland | Ramsar sites in Jammu & Kashmir - 5 | It is the largest bird reserve in the Kashmir Valley. It is included in the network of Important Bird Areas and protected through National Wetlands Conservation Programme. |
| Surinsar- Mansar lakes | It is home to thousands of bats. Surinsar and Mansar Lakes are considered twin lakes. | |
| Wular lake | It is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Asia. It was formed as a result of tectonic activity and is fed by the Jhelum River. | |
| Hygam Wetlands Conservation Reserve | It is located in the Baramulla district of Jammu and Kashmir. It has a rich source of water lilies. Hygam Wetland falls within the River Jhelum basin. | |
| Shallbugh Wetlands Conservation Reserve | This site qualifies as a Key Biodiversity Area of international significance and is located near Srinagar. The marshes in the region are fed by the Sindh river and local snowmelt. The wetland is important for the recharge of aquifers. A major natural floodplain system. | |
| Keoladeo National Park | Ramsar sites in Rajasthan - 2 | It is one of the world’s most important bird breeding and feeding center. It became World Heritage Site in 1985. It is home of 370 species of birds and animals. |
| Sambhar lake | It is India's largest saline lake. It is also known as "Salt Lake of Rajasthan". It is famous for pink flamingos and other birds that migrate from northern Asia and Siberia. | |
| Kolleru lake | Ramsar sites in Andhra Pradesh - 1 | It is one of the largest freshwater lakes in India. It is located between Krishna and Godavari delta. It was an important habitat for 20 million migratory birds. |
| Loktak lake | Ramsar sites in Manipur - 1 | It is the largest natural freshwater lake and ancient supervolcanic caldera in India. Keibul Lamjao National Park, the only floating national park in the world, is an integral part of Loktak lake. |
| Nandur Madhameshwar | Ramsar sites in Maharashtra - 3 | It has been formed by shallow backwaters of the Nandur Madhmeshwar dam. It is known for the avian population. |
| Lonar Lake | It is also known as Lonar crater. It was formed due to the meteorite collision. It has been declared as the Wildlife Sanctuary for the conservation and conservation of Lonar lake. | |
| Thane Creek | It is an inlet on the shoreline of the Arabian Sea that isolates the city of Mumbai from the Konkan region of the Indian mainland. | |
| Point Calimere Wildlife and Bird Sanctuary | Ramsar sites in Tamil Nadu - 18 | It has mangroves, tropical evergreen forests, and grassland ecosystems. It was created in 1967 for the conservation of Blackbuck. |
| Karikili Bird Sanctuary | It is a protected area located in the Kancheepuram district of Tamil Nadu. It was established in 1988. This region is surrounded by open areas, paddy fields and scrub forest. The bird sanctuary along with Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary has been identified as one of the Important Bird Areas of Tamil Nadu. | |
| Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest | It is located adjacent to the Bay of Bengal. It is the only surviving wetland ecosystem in Chennai. A Ministry of Environment project on "Inland Wetlands of India" had prioritized Pallikaranai marsh as one of the most significant wetlands of India. | |
| Pichavaram Mangrove | The Pichavaram Mangrove Forest near Chidambaram is the world’s second largest mangrove forest. It is located between two prominent estuaries, the Vellar estuary in the north and the Coleroon estuary in the south. | |
| Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary | It is a protected area near Mudukulathur Ramanathapuram District, Tamil Nadu. It was declared a bird sanctuary in 1989. | |
| Chitrangudi Bird Sanctuary | It is locally known as "Chitrangudi Kanmoli". It is a protected area located close to Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary. It was declared a bird sanctuary in 1989. | |
| Vaduvur Bird Sanctuary | It is located in Vaduvoor Lake 25 kms from Thanjavur and 30 kms from Thiruvarur. It was created in the year 1999. The sanctuary attracts more than 40 species of water birds like the White Ibis, Painted stork, Grey Pelican, Pintails, Cormorants, etc. | |
| Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary | The Sanctuary consists of human-made irrigation tanks, interconnected by an ancient network of canals and fed by the Mettur dam through the Koraiyar canal. | |
| Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary | It is one of the major Water Bird Sanctuaries in India. It is located 25 Kms from Chengalpattu. Storks, Egrets, Cormorants, Darter, Flamingos, Pelicans, moor hens, etc., are some of the birds which arrive here during season. | |
| Vellode Bird Sanctuary | It is located near Erode town. It was established in 1996. It is one of the 141 prioritised wetlands in the state. | |
| Vembannur Wetland Complex | It was the first wetland declared as Ramsar site in the Kanniyakumari district. It is a man-made inland tank. It forms part of the Important Bird and Biodiversity Area and hence part of the BirdLife International Data Zone. | |
| Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve | It is located on the southeastern coastline and is a unique marine environment rich in biodiversity. This is the first Marine Biosphere Reserve in South and South-East Asia. | |
| Koothankulam Bird Sanctuary | It is a man-made wetland that is located in Nanguneri Taluk of Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu It is the largest reserve for breeding resident and migratory water birds in South India. | |
| Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex | It is part of the Suchindrum-Theroor Manakudi Conservation Reserve. It is declared an Important Bird Area and lies at the southern tip of the Central Asian flyway of migratory birds. | |
| Karaivetti Bird sanctuary | It is one of the largest inland freshwater lakes in Tamil Nadu. The gum Arabic tree (Acacia nilotica) provides roosting and nesting grounds for threatened species such as spotted eagle. | |
| Longwood Shola Reserve Forest | It is located in the Nilgiris district. This Site is the only natural shola forest remaining in the vicinity of Kothagiri and has very high species endemism. | |
| Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary | Kaluveli Bird Sanctuary or Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary is a protected area and bird sanctuary located in Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu. The sanctuary covers an area of 51.56 km² and was notified in 2021. | |
| Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary | The Nanjarayan lake a large shallow wetland situated along the north-eastern region of Uthukuli Taluk of Tiruppur District in Tamil Nadu. | |
| Pong Dam lake | Ramsar sites in Himachal Pradesh - 3 | It is also known as Maharana Pratap Sagar. It is a sanctuary for birds of numerous species including Barheaded Geese and Red-necked Grebe. |
| Renuka lake | It is the largest lake in Himachal Pradesh. It became a Ramsar site in November 2005. | |
| Chandra Taal | It is a barren but beautiful lake located at a height of 14100 feet. It is situated in the Spiti part of the Lahul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh. | |
| Rudrasagar Lake | Ramsar sites in Tripura - 1 | It is one of the wetlands of National Importance for conservation and sustainable use. |
| Asan Conservation Reserve | Ramsar sites in Uttarakhand - 1 | It is a blue-green water body. It became Uttarakhand’s first Ramsar site in 2020. |
| Kanwar Lake or Kabal Taal | Ramsar sites in Bihar - 3
| It is Asia's largest freshwater oxbow lake. It is a freshwater natural wetland. |
| Nagi Bird Sanctuary | It was designated a bird sanctuary in 1984. It is located in Jamui district of Bihar. It was formed as a result of construction of Nagi dam. | |
| Nakti Bird Sanctuary | The Site is a man-made wetland that was developed primarily for irrigation through the construction of Nakti Dam. | |
| Tso Kar Wetland Complex | Ramsar sites in Ladakh - 2 | It is a fluctuating Salt Lake known for its size and depth. It is a high altitude wetland complex found at more than 4500 metres above sea level. It consists of two main water bodies- Startsapuk Tso & the hypersaline Tso Kar. |
| Tsomoriri Lake | It is located in the Changthang Plateau. It is famous for Black-necked crane, Great Tibetan Sheep or Argali. | |
| Pala wetland | Ramsar sites in Mizoram- 1 | It is located in Siaha district of Mizoram. It is the largest natural wetland in Mizoram. The wetland has two small outlets, one named Tipo Didao, which converges with the small Pala river. It is said that the Mara tribe (immigrated from Myanmar) first settled around this wetland. |
Summary
- A Ramsar Site is a wetland site that has been designated as being of international importance by the Ramsar Convention.
- Ramsar convention is an intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for national action and international cooperation for the conservation of wetlands.
- It was signed on 2 February 1971 in Ramsar, Iran and came into force on 21 December,1975.
- India signed the Ramsar Convention on 1 February 1982.
- Gujarat with 34,700 sq km has the highest area under wetland.
- Chilika lake (Odisha) and Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) were the first Indian wetland added to the Ramsar site list in 1981.
- India has the highest number of Ramsar sites in South Asia.
- Renuka Wetland is the smallest wetland Ramsar site of India and Sundarbans is the largest Ramsar Site in India.






 Latest
Latest 



Comments