Preamble of the Indian Constitution | Meaning of Terms used in Preamble
The Preamble is the mirror of the Constitution. It briefly gives a glimpse of the entire Constitution. Similarly, the Preamble to the Constitution of India is a brief introductory statement, which sets forth the principles of the Constitution. The Constitution of India was adopted by the Constituent Assembly on 26 November 1949 and came into force on 26 January 1950, which is celebrated as Republic Day in India.
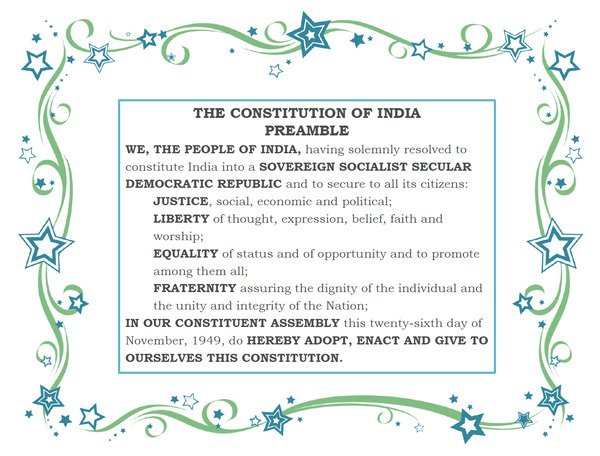
Key highlights of the Preamble:
- According to the Preamble, the Constitution gets its power from the people of India. In other words, people of India are source of power of the Constitution.
- The Preamble declares India as a sovereign, socialist, secular and democratic republic.
- According to the Preamble, the purpose of the Constitution is to promote brotherhood in order to ensure justice, freedom, equality for all citizens and unity and integrity of the nation.
Some important facts related to the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
- The Preamble is developed from Objectives Resolution. Jawaharlal Nehru drafted Objectives Resolution and put it forward for discussion on 13 December 1946. The Constituent Assembly adopted the Objectives Resolution on 22 January 1947.
- In the Berubari case (1960), the Supreme Court said that Preamble is not an integral part of the Indian Constitution.
- In Keshavanand Bharti's case (1973), the Supreme Court decided that the Preamble is an integral part of the Indian Constitution. In the Keshavanand Bharti case (1973), the Supreme Court also ruled that the Preamble can be amended under Article 368. The court held that its basic feature should not be changed.
- In Central Government v. LIC case (1995), the Supreme Court repeated its opinion of the Keshavanand Bharti case (1973) once again said that the Preamble is an integral part of the Constitution.
- The Preamble has been amended only once during the Emergency on 18 December 1976.
- In 1976, the 42nd amendment to the Constitution added two words (socialist and secular) between the words, sovereign and democratic. It replaced the phrase, unity of the nation, with another phrase, unity, and integrity of the nation.
Meaning of keywords used in the Preamble:
-
Sovereign:
Sovereign means the independent power of a state. In other words, a sovereign state is not subject to the control of any other state or external power, and that state has the power to legislate on any subject.
-
Socialist:
It was added to the Preamble by the 42nd Amendment in 1976. Though the word socialist was not part of the Preamble, the Constitution contained socialistic principles as part of Directive Principles of State Policy in the Constitution. Socialism in India is democratic socialism. India has a mixed economy with the coexistence of both private and public sectors.
-
Secular:
It was also added into the Preamble by the 42nd Amendment in 1976. Secular means that relations between government and religious groups are determined according to the Constitution and the law. Secularism separates the power of state and religion. In Indian secularism, all religions receive the same support from the state.
-
Democratic:
The term democratic means that the Constitution of India provides for a form of government that derives its authority from the will of the people expressed in an election.
-
Republic:
The term republic means that the head of state is elected by the people. In India, the President of India is the elected head of state, who is indirectly elected by the citizens of India.
-
Justice:
The Constitution provides for social, economic, and political justice to ensure equality among its citizens.
-
Social justice
Social justice means the absence of privileges to certain sections in society. It means that no discrimination shall be made against any citizen on the basis of caste, creed, color, religion, sex or place of birth.
-
Economic justice
Economic justice means that there is no discrimination between people on the basis of income, wealth and economic status.
-
Political justice
Political justice means giving equal, free, and fair opportunities to people for participation in the political process.
-
Liberty:
The ideal of liberty means that rules do not limit or control the activities of individuals. The Preamble gives five different types of liberty. They are liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith, and worship.
-
Fraternity:
The word means a feeling of brotherhood and an emotional attachment to the country and all people. Fraternity helps to promote dignity and unity in the nation.






 Latest
Latest 



Comments