Respiration in Organisms Class 7 Notes NCERT and MCQs
 09-11-2023
09-11-2023
 14:03 PM IST
14:03 PM IST
 Priyanka Chaudhary
Priyanka Chaudhary
The chapter discusses respiration and its types as well as the mechanism of breathing in humans and other organisms.
What is Respiration?
Respiration is the process in which there is movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within tissues and removal of carbon dioxide in the outside environment.
Respiration releases energy from the food. Therefore, all living organisms respire to get energy from food. A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Each cell of an organism performs functions like nutrition, transport, excretion and reproduction. To perform these functions, the cell needs energy.
The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
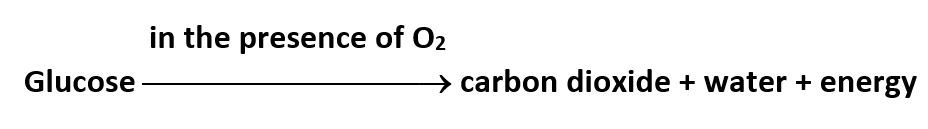
Aerobic respiration: In the cell, the food (glucose) is broken down into carbon dioxide and water using oxygen. When breakdown of glucose occurs with the use of oxygen, it is called aerobic respiration. The equation of aerobic respiration is given below.
Anaerobic respiration: Food can also be broken down, without using oxygen. This is called anaerobic respiration. Organisms that can survive in the absence of air are called anaerobes. Yeast (single-celled organisms) is an anaerobe. It respires anaerobically and produces alcohol. So, it is used to make wine and beer. Anaerobes get energy through anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, glucose breaks down into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The equation of anaerobic respiration is given below.
Our muscle cells can also respire anaerobically, but only for a short time, when there is a temporary deficiency of oxygen. This happens during heavy exercise, fast running, cycling, and walking for many hours or heavy weight lifting, when the demand for energy is high and supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. The purpose of anaerobic respiration in the muscle cells to fulfil the demand of energy. The equation of anaerobic respiration in muscles is given below.
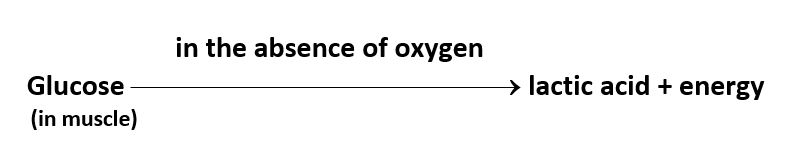
What is Breathing?
Breathing is a part of the process of respiration during which an organism takes in the oxygen-rich air and gives out air rich in carbon dioxide with the help of respiratory organs. Breathing is a continuous process which goes on all the time and throughout the life of an organism.
The number of times a person breathes in a minute is termed as the breathing rate.
NOTE: On an average, an adult human being at rest breathes in and out 15ñ18 times in a minute. During heavy exercise, the breathing rate can increase upto 25 times per minute.
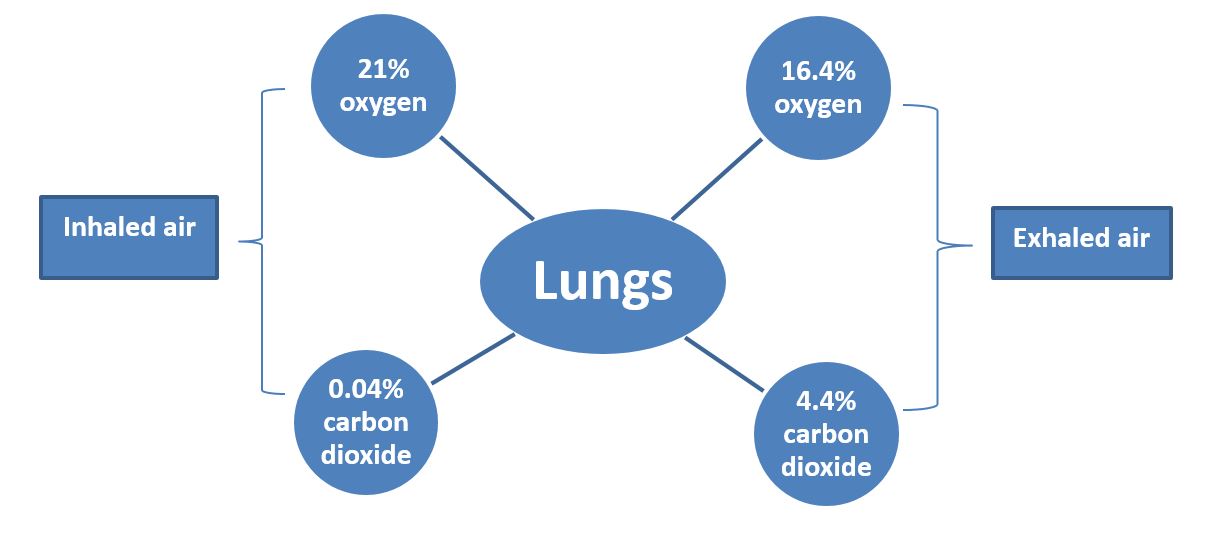
Figure showing percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in inhaled and exhaled air
Mechanism of breathing
When we inhale or take in air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe. Lungs are present in the chest cavity.
Diaphragm is a large, muscular sheet that forms the floor of the chest cavity. The chest cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides.
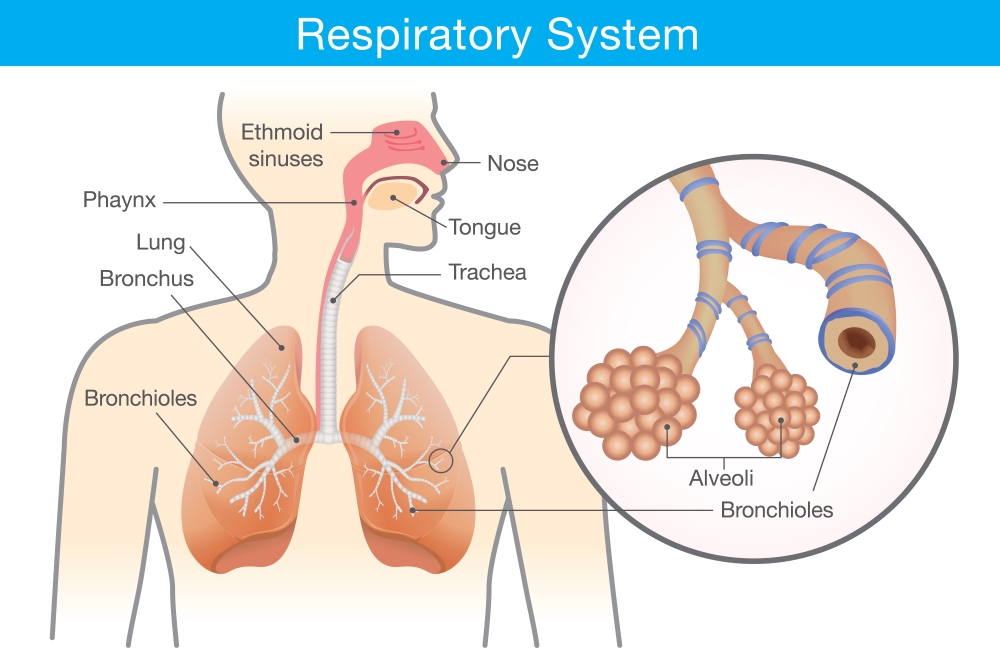
Figure showing human respiratory system
During inhalation, ribs move up and outwards and the diaphragm moves down. This causes the movement of air into the lungs. During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position. This causes movement of air out of the lungs. During inhalation, our lungs expand and then come back to the original state as the air moves out during exhalation.
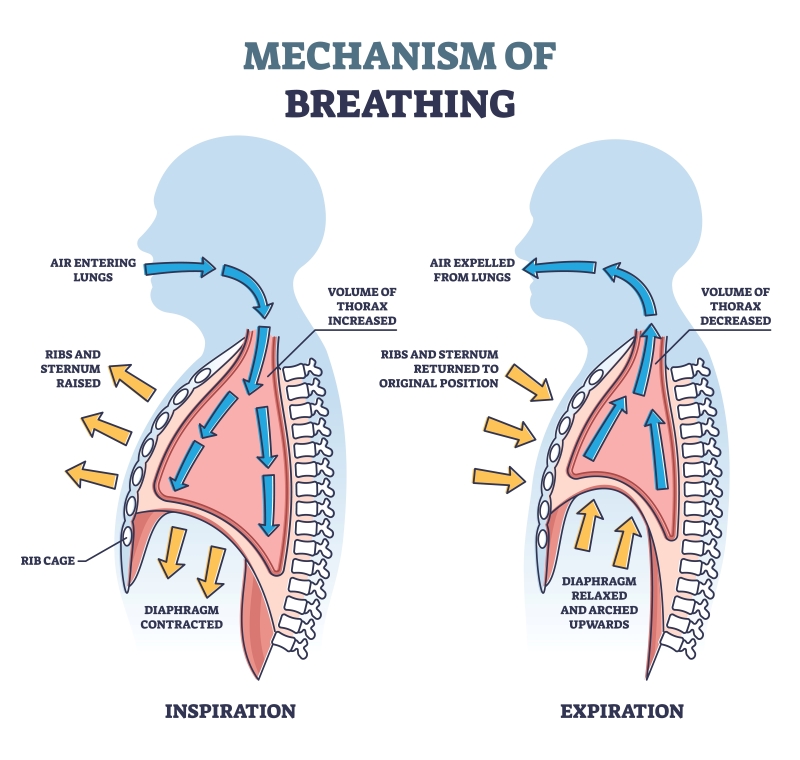
Figure showing mechanism of breathing in human beings
Breathing in other animals
- In animals like cow, buffalo, dog and cat the respiratory organs and the process of breathing are similar to those in humans.
- Insects have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Cockroaches and other insects have small openings on the side of their body. These openings are called spiracles. Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles.
- In earthworms, the exchange of gases occurs through the moist skin.
- In fishes, it takes place through the gills. Gills are well supplied with blood vessels.
- Frogs breathe through their skin and lungs.
- In a plant, the roots take in air present in the soil. Leaves have tiny pores called stomata through which they exchange gases.
MCQs based on NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 10: Respiration in Organisms
1. Which of the following is responsible for the exchange of gases in insects?
a. Tracheae
b. Spiracles
c. Skin
d. Gills
Ans. a
Explanation: Insects have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Cockroach and other insects have small openings on the side of their body. These openings are called spiracles. In earthworm, the exchange of gases occurs through the moist skin. In fishes it takes place through gills. Gills are well supplied with blood vessels. Frogs breathe through their skin and lungs.
2. Which of the following shows the correct sequence of passage of air during breathing?
a. Nostrils, windpipe, nasal cavity, lungs
b. Nostrils, nasal cavity, windpipe, lungs
c. Nasal cavity, nostrils, windpipe, lungs
d. Windpipe, nostrils, nasal cavity, lungs
Ans. b
Explanation: When we inhale or take in air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe.
3. Which of the following is a product of anaerobic respiration in our muscles?
a. Alcohol
b. Water
c. Lactic acid
d. Methane
Ans. c
Explanation: Our muscle cells can also respire anaerobically, but only for a short time, when there is a temporary deficiency of oxygen. Lactic acid is a product of anaerobic respiration in our muscles.
4. In cockroaches, air enters the body through
a. lungs
b. gills
c. spiracles
d. skin
Ans. c
Explanation: In cockroaches, air enters the body through small openings on the side of their body called spiracles.
5. Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is:
a. 9ñ12
b. 15ñ18
c. 21ñ24
d. 30ñ33
Ans. b
On an average, an adult human being at rest breathes in and out 15ñ18 times in a minute. During heavy exercise, the breathing rate can increase upto 25 times per minute.
6. During exhalation, the ribs
a. move outwards
b. move downwards
c. move upwards
d. do not move at all
Ans. b
Explanation: During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position.
7. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because:
a. At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air.
b. The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
c. The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground.
d. The pressure of air is higher than that on the ground.
Ans. b
Explanation: The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because the amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Respiration in Organisms
Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden particles?
What is diaphragm?
Share Blog
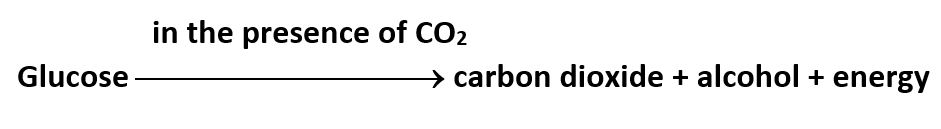
 Latest
Latest 
Comments