Topic: Reports and Indices
1. RBI’s Digital Payments Index (DPI) increased from 349.30 in March to 377.46 in September.
- According to the Economic Survey 2022-23, India has the highest fintech adoption rate of 87% among the public. Global average is 64%.
- India has achieved the third place in digital payments. It comes after US and China.
- Total digital payments transactions increased 59% y-o-y to ₹8,840 crore in FY22.
- Out of the total digital payments transactions, Unified Payment Interface (UPI) platform accounted for 52%.
- As per the Economic Survey, UPI transactions, have on average, increased 121% in terms of value and 115% in terms of volume between FY19 and FY22.
- DPI is a measure of the extent of digitization of payments across the India.
- RBI introduced DPI on January 1, 2021 to capture digitisation of payments.
>Topic: Appointments
2. V Ramachandra has been appointed as member of advisory committee of Srei NBFCs.
- RBI appointed him after the resignation of Subedar from the Advisory Committee.
- RBI has appointed Ramachandra as a member of the Advisory Committee of two Srei Group companies that are undergoing insolvency proceedings.
- The companies are Srei Infrastructure Finance and Srei Equipment Finance.
- The Advisory Committee now comprises Venkat Nageshwar Chalasani, TT Srinivasaraghavan, and V Ramachandra.
- In October 2021, RBI formed an Advisory Committee to advise the administrator of Srei NBFCs.
- R Subramaniakumar, TT Srinivasaraghavan and Farokh N Subedar were included in the original committee.
>Topic: Banking System
3. The number of payment acceptance devices deployed under PIDF Scheme increases to 1.87 crore as on December 31, 2022.
- This includes physical devices (PoS, mPoS (mobile PoS), GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), etc.
- This also includes digital devices (inter-operable QR code-based payments such as UPI QR, Bharat QR, etc.).
- The number of devices stood at 57,82,620 as on September end 2021.
- RBI operationalised Payments Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) Scheme from January 1, 2021.
- It subsidises the deployment of Points of Sale (PoS) infrastructure (physical and digital modes) in tier-3 to tier-6 centres.
- It also subsidises their deployment in northeastern states of the country.
- The scheme covered beneficiaries of PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi Scheme) in Tier-1 and Tier-2 centres from August 26, 2021.
- From June 9, 2022, J & K and Ladakh regions are included as special focus areas under the scheme.
- RBI, authorised card networks and card issuing banks make contribution to PIDF.
>Topic: Taxation
4. FM Nirmala Sitharaman made five major announcements regarding personal income tax while presenting Union Budget 2023-24.
- FM Nirmala Sitharaman proposed to raise the rebate limit to Rs. 7 lakh in the new tax regime.
- A person in the new tax regime with income up to Rs. 7 lakh will not pay any tax.
- In both old and new tax regimes, persons with income up to Rs. 5 lakh currently do not pay any income tax.
- Finance Minister also proposed a change in the tax structure in the new personal income tax regime.
- The number of slabs has been reduced to five and the tax exemption limit has been increased to Rs. 3 lakh. New tax rates are given below.
|
Total income (Rs.)
|
Rate (per cent)
|
|
Upto 0-3 lakh
|
Nil
|
|
From 3-6 lakh
|
5
|
|
From 6-9 lakh
|
10
|
|
From 9-12 lakh
|
15
|
|
From 12-15 lakh
|
20
|
|
Above 15 lakh
|
30
|
- FM Nirmala Sitharaman proposed to extend the benefit of the standard deduction to the new tax regime.
- This provides relief to the salaried class and the pensioners including family pensioners.
- Each salaried person having an income of Rs. 15.5 lakh or more will benefit by Rs. 52,500/-.
- A standard deduction of Rs. 50,000/- to salaried persons and a deduction from family pension up to Rs. 15,000/- is currently allowed only under the old regime.
- Finance Minister proposed to cut the highest surcharge rate from 37% to 25% in the new tax regime for income above Rs. 2 crore.
- This would reduce the maximum tax rate to 39% from the present 42.74%.
- Finance Minister did not propose change in the surcharge for those who choose to be under the old regime in this income group.
- An extension of the limit of tax exemption on leave encashment to Rs. 25 lakh on the retirement of non-government salaried employees has been proposed.
- The maximum amount which can be exempted presently is Rs. 3 lakh.
- The budget proposed to make the new income tax regime as the default tax regime.
- However, the citizens have the option to avail the benefit of the old tax regime.

(Source: PIB)


Topic: Reports and Indices
5. The seasonally adjusted S&P Global India Services PMI Business Activity Index declined to 57.2 in January from 58.5 in December.
- However, it remained above its long-run average (53.5). It was above neutral value 50 for the 18th straight month.
- According to PMI survey, the overall level of positive sentiment fell to a six-month low.
- 80% of panelists forecast no change in activity from current levels.
- S&P Global India Composite PMI Output Index declined from December’s near 11-year high of 59.4 to 57.5 in January.
- It remained above its long-run average (54.1). Composite PMI Output Index measures combined services and manufacturing output.
- PMI value above 50 means expansion. PMI score below 50 means contraction.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
6. The output of eight core industries increased to a three month high level of 7.4% in December 2022.
- This increase was higher than growth recorded in December 2021. In December 2021, 4.1% output growth was recorded.
- The increase in output of eight core industries in December 2022 was also higher than revised 5.7% growth in November 2022.
- Coal, fertilizers, steel, cement, electricity, crude oil, natural gas and refinery products are eight core industries.
- Seven of the eight core sectors have shown positive growth in December 2022.
- Only crude oil sector has shown a contraction of 1.2%. Coal sector recorded output growth at 11.5%. Fertilizers and steel sectors have shown 7.3% and 9.2% output growth, respectively.
- Cement sector has shown output growth at 9.1% and electricity sector has shown output growth at 10%.
- Natural gas sector saw an output growth of 2.6%. Refinery products output grew 3.7%.
- Output of eight core industries grew 8% for April-December 2022. 12.6% was recorded in the same period last year.
- Final growth rate of eight core industries for September 2022 has been revised from 7.9% earlier to 8.3%.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
7. Union Budget for 2023-24 presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in Parliament on 1 February.
- Presenting the last full budget of the second term of the Narendra Modi government, Sitharaman said that this is the first budget of Amrit Kaal.
- The vision of Amrit Kaal includes strong public finances and a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with a strong financial sector.
- She said that this year's budget fulfills the vision of a prosperous and inclusive India.
- She stated that the economic growth rate is estimated to be 7% in the current year.
- Capital investment outlay will be increased by 33% to Rs 10 lakh crore, which will be 3.3% of GDP.
- The Government has decided to continue the 50-year interest free loan to state governments for one more year to spur investment in infrastructure, with a significantly enhanced outlay of Rs 1.3 lakh crore.
- The Agriculture Accelerator Fund will be set-up to encourage agri-startups by young entrepreneurs in rural areas to focus on the agriculture sector.
- Agriculture credit target will be increased to Rs 20 lakh crore with focus on animal husbandry, dairy and fisheries.
- Under the PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY), the government will bear an expenditure of about Rs 2 lakh crore for the supply of free food grains to all Antyodaya and priority households for the next one year.
- The outlay for the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana would be increased by 66% to over Rs 79,000 crore, furthering the government's target of Housing for All.
- Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission will be launched with an aim to improve socio-economic conditions of the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- For the implementation of this mission, an amount of Rs 15,000 crore has been earmarked over the next three years.
- The Upper Bhadra Project in the "drought-prone" central region of Karnataka will be given central assistance of Rs 5,300 crore to provide sustainable micro irrigation and filling up of surface tanks for drinking water.
- In the new tax regime, the exemption limit has been raised to Rs 7 lakh from the existing Rs 5 lakh per annum.
- In the new tax regime, the highest surcharge on personal income tax has been reduced from 37% to 25%.
- Under the Citizen Savings Scheme, a provision has been made to increase the maximum deposit amount from Rs 15 lakh to Rs 30 lakh.
- In the Monthly Income Scheme, the maximum deposit limit on single account will be increased from Rs.4.5 lakh to Rs.9 lakh and for joint account this limit will be increased from Rs.9 lakh to Rs.15 lakh.
- To boost manufacturing of mobile phones in the country, customs duty relief has been given on the import of some parts and inputs like camera lenses, and the concessional duty on lithium-ion cells for batteries has been extended for another year.
- The basic customs duty on open sale parts of TV panels has been reduced to 2.5% to promote value addition in the manufacture of televisions.
- The import duty on silver dore, bars and articles has been increased to align them with that on gold and platinum.
- The rate of basic customs duty on compound rubber has been increased from 10 per cent to 25 per cent or Rs 30 per kg, whichever is less, to prevent duty rigging.
- The National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) has been increased on specified cigarettes by about 16%.
- The government has increased the limit for cash deposits and loans in cash to Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies (PACS) and Primary Cooperative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (PCARDBs) to 2 lakh per member.
- Payments received by Agniveers from Agniveer Corpus Fund has been exempted from taxes.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
8. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman tabled the Economic Survey 2022-2023 in both the Houses of Parliament.
- The Economic Survey reviews how the economy performed in this financial year and the way forward for the next year.
- Chief Economic Adviser V. Anantha Nageswaran has prepared the Economic Survey.
- The Economic Survey is released one day before the Union Budget for the next fiscal year, which begins on April 1.
- Annual Pre-Budget Economic Survey of India projects GDP growth rate of 6-6.8% for 2023-24.
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 projects a baseline GDP growth of 6.5 percent in real terms for 2023-24.
- According to the survey, the Indian economy is expected to grow at 7% in real terms during the current fiscal year.
- According to the survey, India has become the fifth largest economy in the world and the nominal GDP of India in March this year will be around US$ 3.5 trillion.
- According to the survey, the annual rate of inflation is below 6 percent and wholesale prices are rising at a rate below 5 percent.
- In the first nine months of the current financial year, exports of goods and services have increased by 16 percent as compared to the same period of 2021-22.
- The Economic Survey of India is an annual document released by the Ministry of Finance.
- For the first time the Economic Survey of the country was presented in the financial year 1950-51.
- After this, since 1964, the Ministry of Finance has been releasing the Economic Survey a day before the budget.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
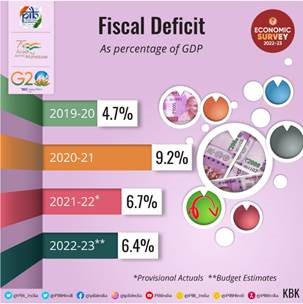
9. Fiscal deficit is expected to be at 6.4 per cent of GDP in the financial year 2022-2023.
- Government is on the track to achieve the fiscal deficit target for FY 23.
- As per the survey, India’s economic growth has been mainly led by private consumption and capital formation.
- According to the survey, Gross Tax Revenue registered a year-on- year growth of 15.5% from April to November last year.
- The Union government emphasised on capital expenditure (Capex) despite higher revenue expenditure requirements.
- The government has increased spending in the social sector. Budgeted expenditure on health sector touched to 2.1% of GDP in FY23 (BE) and 2.2% in FY22 (RE).
- As per the survey, Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), Under Five mortality rate (U5MR) and neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) have shown a steady decline.
- Since January 2022, Credit to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) has grown by an average of around 30%.
- India has become the second-largest mobile phone manufacturer globally
- The services sector is expected to grow at 9.1% in FY23. India is one of the top ten services exporting countries in 2021.
- Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio reached to a seven- year low of 5%.
(Source: PIB)
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
10. The revamped credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs is to be effective from 01st April 2023.
- While presenting the Union Budget 2023-24, FM Nirmala Sitharaman announced that this scheme would be effective from 01st April 2023 through the infusion of ₹ 9000 crore in the corpus.
- She said that this will enable additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of ₹ 2 lakh crore.
- She said that the cost of credit will come down by about 1%.
- She proposed that if MSMEs failed to execute contracts during the Covid period, 95% of the forfeited amount relating to the bid will be returned to them by government and government undertakings.
- She proposed that a voluntary settlement scheme with standardized terms will be introduced to settle contractual disputes of government and government undertakings.
- This proposal will apply to disputes, wherein an arbitral award is under challenge in a court.
- Finance Minister proposed that micro-enterprises with turnover up to ₹2 crore can avail the benefit of presumptive taxation.
- Certain professionals with turnover of up to ₹50 lakh can also avail the benefit of presumptive taxation.
- She also proposed to provide enhanced limits of ₹3 crore and ₹75 lakh to the tax payers whose cash receipts are no more than 5%.
- She proposed to extend the date of incorporation for income tax benefits to start-ups from 31 March 2023 to 31 March 2024.
- She proposed to provide the benefit of carry forward of losses on change of shareholding of start-ups from 7 years of incorporation to 10 years.
- Budget 2023-24 also proposed establishing a subsidiary of EXIM Bank for trade re-financing and recognizing offshore derivative instruments as valid contracts.
.jpg)
(Source: PIB)


.jpg)


 Previous
Previous 
 Latest
Latest 








Comments