Highlights of Union Budget 2024-25
2024-07-25 | Rituraj

On July 23, 2024, Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget for the seventh consecutive time.
The monsoon session of Parliament was started on July 22 with the tabling of Economic Survey 2023-24.
Earlier, Morarji Desai presented the Union Budget six times consecutively. He had presented Budgets for a record 10 times.
The Union Budget 2024-25 is focused on four themes- Employment, Skilling, MSMEs, and Middle Class.
The Finance Minister laid down nine priorities for the Budget:
Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture
- In the Union Budget 2024-25, the Government has allocated 1.52 lakh crore for agriculture and allied sectors.
- New 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released for cultivation.
- 1 crore farmers will be involved in natural farming, supported by certification and branding, within two years.
- For natural farming, 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres will be established.
- The government, in association with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture for coverage of farmers and their lands in 3 years.
- Jan Samarth-based Kisan Credit cards will be enabled in five states.
- The government will form National Cooperation Policy for the growth of the rural economy and to generate employment opportunities.

(Source: PIB)
Employment & Skilling
- The government will implement 3 schemes for ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ to be implemented. These are as follows:
- Scheme A: First Timers
- One-month salary of up to Rs 15,000 will be provided in 3 instalments to first-time employees.
- Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing
- Incentives will be provided directly to both employee and employer with respect to their EPFO contribution in the first 4 years of employment.
- Scheme C: Support to Employers
- The government will reimburse up to Rs 3,000 per month for 2 years towards the EPFO contribution of employers, for each additional employee.
- Higher participation of women in the workforce will be facilitated through setting up of working women hostels in collaboration with industry and establishing creches.

(Source: PIB)
Skill Development
- A new centrally sponsored scheme for Skilling under the Prime Minister’s Package has been announced for 20 lakh youth for a 5-year period.
- 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes will be upgraded in the hub and spoke arrangements with outcome orientation.
- Model Skill Loan Scheme will be revised to facilitate loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with a guarantee from a government-promoted Fund.
- Financial support for loans upto ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions will be provided to youth.
- E-vouchers for this purpose will be given directly to 1 lakh students every year for annual interest subvention of 3 % of the loan amount.

(Source: PIB)
Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Under the Purvodaya initiative, the government will form a plan for the all-round development of the eastern region of the country covering Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- It will cover human resource development, infrastructure, and the generation of economic opportunities.
- The Industrial node at Gaya will be developed along the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor.
- Power projects of a 2400 MW power plant will be developed at Pirpainti.
- The government will launch Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan to improve the socio-economic condition of tribal communities.
- Under this scheme, steps will be taken for complete coverage of tribal families in aspirational districts and tribal-dominated villages.
- More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be set up in the North East region to expand the banking services.
- For promoting women-led development, the Budget has allocated more than Rs 3 lakh crore for schemes benefitting women and girls.
- The government will provide funds for essential infrastructure development in the Kopparthy node on the Visakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and the Orvakal node on the Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
Manufacturing & Services
- The limit of Mudra loans under the ‘Tarun’ category will be enhanced from 10 lakhs to 20 lakhs for those who have successfully repaid previous loans.
- A credit guarantee scheme without collateral or third-party guarantee in term loans to MSMEs for purchase of machinery and equipment.
- Financial support will be provided to 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector.
- The turnover threshold of buyers for mandatory onboarding on the TReDS platform has been reduced from 500 crore to 250 crore.
- E-Commerce Export Hubs will be set up under the public-private-partnership (PPP) mode for MSMEs and traditional artisans.
- The government will launch a comprehensive scheme for providing internship opportunities in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth in 5 years.
- A self-financing guarantee fund will be constituted to provide guarantee cover up to Rs 100 crore.
- A new mechanism will be launched to facilitate the continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during their stress period.

(Source: PIB)
Urban Development
- 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will get houses under the PM AwasYojana Urban 2.0 with an investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore.
- The government will promote water supply, sewage treatment and solid waste management projects and services for 100 large cities through bankable projects.
- A new scheme will be launched to support the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs every year for the next 5 years in select cities.
- A transit-oriented development plan will be formulated for 14 large cities with a population of over 30 lakhs.
- Framework for creative brownfield redevelopment will created for existing cities.
Energy Security
- Energy security and sustainable development are pivotal elements of this budget.
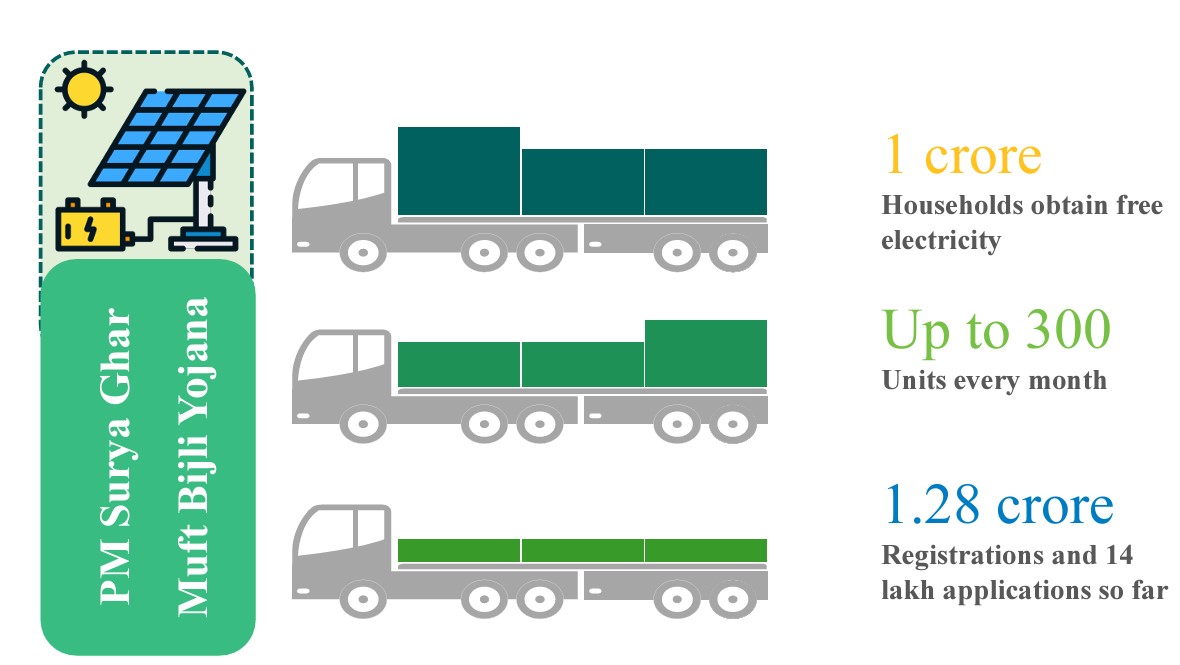
- More than 1.28 crore registrations and 14 lakh applications have been received under PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
- The government is to partner with the private sector for the R&D of Bharat Small Modular Reactor and newer technologies for nuclear energy.
- The government will set up Bharat Small Reactors.
- Policy for promoting pumped storage projects for electricity storage will be brought by the government.
- A Joint venture has been proposed between NTPC and BHEL to set up a full-scale 800 MW commercial plant using Advanced Ultra Super Critical (AUSC) technology.

(Source: PIB)
Infrastructure
- ₹11,11,111 crore has been allocated for the capital expenditure, which is 3.4% of the GDP.
- The capital expenditure of the government has increased by 2.2 times from FY21 to FY24.
- The government announced rehabilitation and irrigation projects and monetary assistance for flood-affected states.
- The financial assistance includes an allocation of Rs 11,500 crore for various projects, such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 additional schemes focused on barrages, river pollution control, and irrigation.
- A provision of ₹1.5 lakh crore for long-term interest-free loans has been made this year to assist states in their resource allocation.
- Phase IV of PMGSY will be launched to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
- The gross inflow of external commercial borrowings to infrastructure sectors also reached USD 9.05 billion in FY24.
- The Industrial node at Gaya on the Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor will be developed.
Tourism
- A comprehensive development of the Vishnupad Temple (dedicated to Lord Vishnu) Corridor and Mahabodhi Temple (dedicated to Lord Buddha) Corridor will be supported.
- The government will provide assistance to Odisha for the development of tourism.
Innovation, Research & Development
- The government will operationalize the Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development.
- The government will set up a mechanism for spurring private sector-driven research and innovation at the commercial scale with a financing pool of Rs 1 lakh crore.
- Rs 600 crore has been allocated for the Deep Ocean Mission.
- Department of Scientific and Industrial Research received an allocation of Rs 6323.41 crore.
- The budget allocation for the National Quantum Mission has been increased.
- 700 crore and ₹150 crore have been allocated for the ‘Modernisation of Forensic Capacity’ and ‘National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement’ respectively.
Space Economy
- The government announced a venture capital fund of Rs 1,000 crore for expanding the space economy.
- The government’s vision is to increase India’s share in the global commercial space economy to 10% by 2030.

(Source: PIB)
Next Generation Reforms
- Economic Policy Framework: The government will form an Economic Policy Framework to delineate the overarching approach to economic development and set the scope of the next generation of reforms.
- Rural Land Related Actions:
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands will be developed.
- A Land registry will be established and farmers will be linked to the registry.
- Labour related reforms:
- The e-shram portal will be integrated with other portals to facilitate a one-stop solution.
- Shram Suvidha and Samadhan portals will be revamped to enhance ease of compliance for industry and trade.
- Mechanism will be developed to connect job aspirants with potential employers and skill providers.
- Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investment:
- Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investments will be simplified to promote FDI.
- Indian Rupee as a currency for overseas investments will be also promoted.
- NPS Vatsalya: This scheme will allow parents and guardians to invest on behalf of children. It will facilitate long-term savings for minors.

(Source: PIB)
Sector-wise allocation from Budget 2024
|
Ministry |
Amount Allocated |
|
Defence |
Rs 6,21,940 cr |
|
Rural |
Rs 2,65,808 cr |
|
Agriculture |
Rs 1,51,851 cr |
|
Home Affairs |
Rs 1,50,983 cr |
|
Education |
Rs 1,25,638 cr |
|
IT & Telecom |
Rs 1,16,342 cr |
|
Health |
Rs 89,287 cr |
|
Energy |
Rs 68,769 cr |
|
Social welfare |
Rs 56,501 cr |
|
Commerce & Industry |
Rs 47,559 cr |
Budget Estimates 2024-25
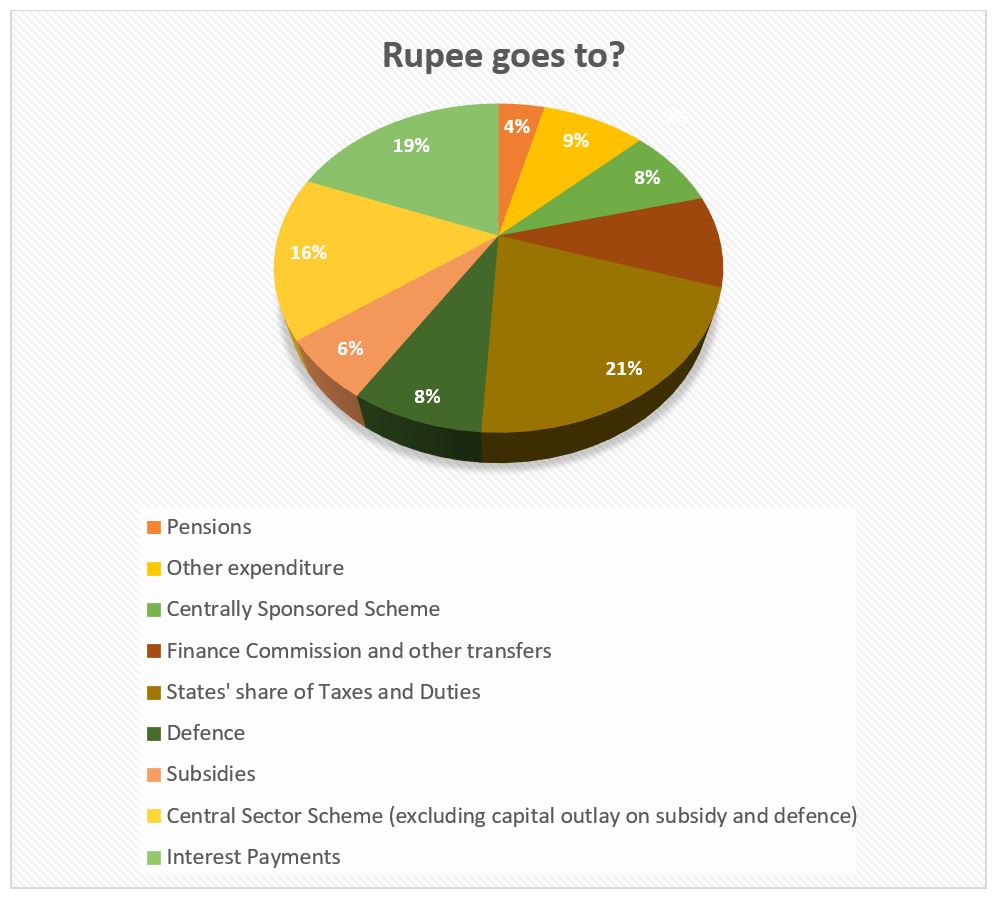
- The government is estimated to spend Rs 48,20,512 crore in 2024-25, 8.5% higher than the actual expenditure in 2023-24.
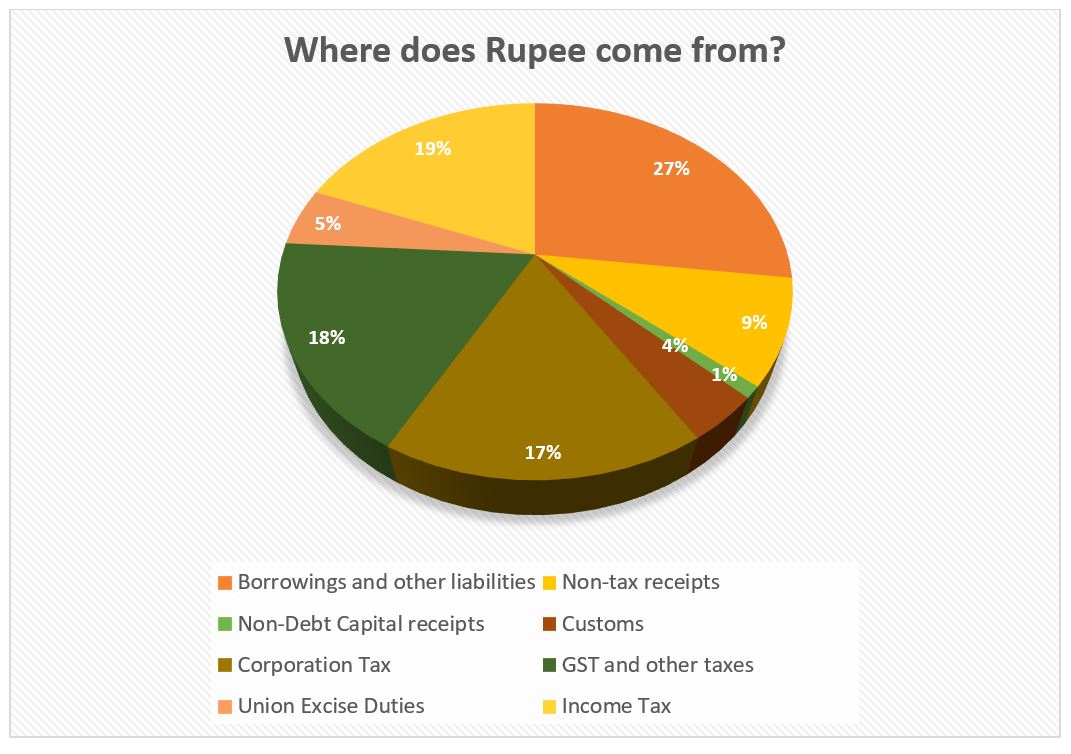
- The total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at ₹32.07 lakh crore and ₹48.21 lakh crore respectively.
- The net tax receipts are estimated at ₹25.83 lakh crore.
- The fiscal deficit target for the current financial year at 4.9% of GDP. The government will aim to reach a deficit below 4.5 % in FY25.
- The revenue deficit in 2024-25 is targeted at 1.8% of GDP.
- The government has estimated a nominal GDP growth rate of 10.5% in 2024-25 (i.e., real growth plus inflation).
- The gross and net market borrowings through dated securities during 2024-25 are estimated at ₹14.01 lakh crore and ₹11.63 lakh crore respectively.
- Rs 62,593 crore has been allocated to the Department of Economic Affairs for New Schemes.
Indirect Taxes
|
Medicines and Medical Equipment |
|
|
Mobile Phone and Related Parts |
|
|
Precious Metals |
|
|
Solar Energy |
|
|
Critical Minerals |
|
Direct Taxes
|
Simplification for Charities and of TDS |
|
|
Rationalisation of Capital Gains |
|
|
Litigation and Appeals |
|
|
Employment and Investment |
|
|
Deepening tax base |
|
Changes in Personal Income Tax under the new tax regime
- The standard deduction has been increased from 50,000 to Rs 75,000.
- The deduction on family pensions has been raised from Rs 15,000 to Rs 25,000 under the new tax regime.
- The deduction on employers' National Pension System (NPS) contribution to employees' basic salary has been raised from 10 % to 14 %.
- The new tax regime rate structure will give benefits up to ₹ 17,500/- in income tax.
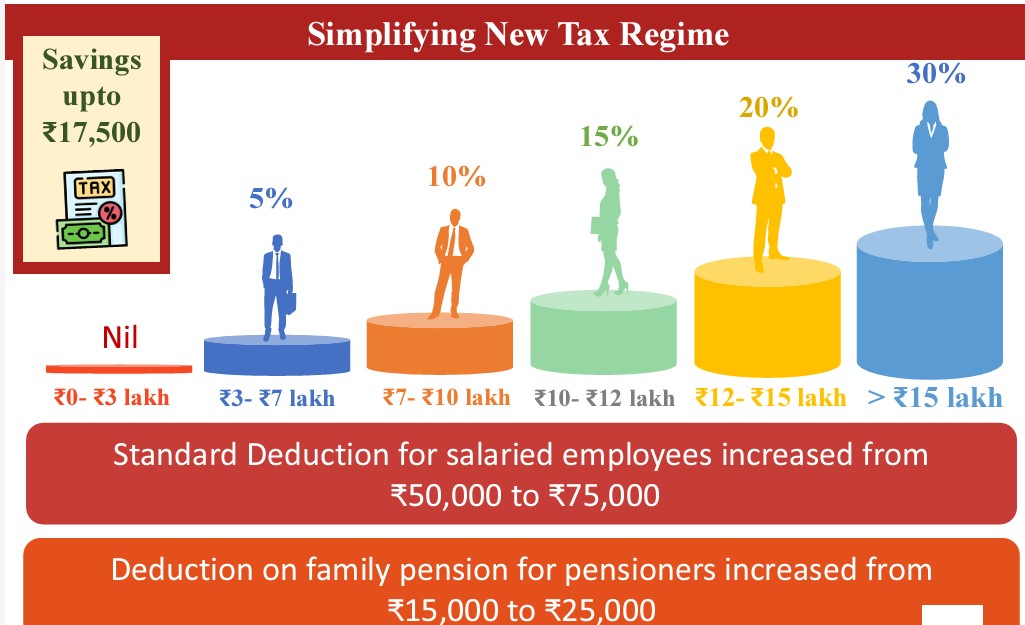
Revised tax rate structure 2024
|
0-3 lakh rupees |
Nil |
|
3-7 lakh rupees |
5 % |
|
7-10 lakh rupees |
10 % |
|
10-12 lakh rupees |
15 % |
|
12-15 lakh rupees |
20 % |
|
Above 15 lakh rupees |
30 % |
Other facts related to the Budget 2024-25
- Rs 1.48 crore has been allocated for imparting skills to citizens to create employment opportunities, with a target to skill 20 lakh youth over five years.
- Union Budget has allocated ₹56 crore to establish the ‘Bhartiya Bhasha Anubhag’ (Indian Languages Department) for the development of a platform to facilitate the translation of various languages into Hindi and vice-versa.
- About ₹88 crore has been allocated for the holistic development of islands in Union Territories.
- The allocation to the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network Systems has been increased from ₹264 crore to ₹520 crore in 2024-25.
- Border Infrastructure Maintenance and Capital Outlay has seen an increase of ₹211 crore.
- ₹1,050 crore has been allocated for the Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP).
- Twelve industrial parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme are to be sanctioned.
- Rental housing with dormitory-type accommodation for industrial workers will be facilitated in PPP mode with VGF support and commitment from anchor industries.
- Land records in urban areas will be digitized with GIS mapping. An IT-based system for property record administration, updating, and tax administration will be established.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Union Budget 2024-25
What will be the new standard deduction for a salaried person in the Income tax?
What will be the new limit for Mudra loans under the ‘Tarun’ category?
What will be the fiscal deficit target for the current financial year?
What will be the new Long-term capital gains tax (LTCG) rate on all financial and non-financial as per budget 2024?
How many cancer drugs have been exempted from the customs duty in the budget 2024?
Share Blog






Comments