Highlights of Interim Budget 2024
2024-02-03 | Rituraj
The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2024-25 in Parliament on 1 February 2024. This was the Interim Budget before the 2024 Lok Sabha Elections.

The interim Budget following the British tradition is called a vote on account. The interim Budget provides an overview of the expected receipts and expenditures of the government until a newly elected government presents a fully-fledged Budget.
The Union Budget is referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in Article 112 of the Indian Constitution.
Article 116 of the Indian Constitution defines a vote on account as an advance grant to the government from the Consolidated Fund of India to cover short-term expenditure requirements until the new financial year begins.
Key Highlights of the Union Budget 2024-25
1. Budget Estimates 2024-25
- The capital expenditure outlay for the next year will be Rs 11,11,111 crore, which would be 3.4 percent of the GDP.
- The capital expenditure outlay has been increased by 11.1 percent as compared to the previous year.
- The tax receipts are estimated to be Rs 26.02 lakh crore. The total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at Rs 30.80 and 47.66 lakh crore respectively.
- The gross and net market borrowings through dated securities during 2024-25 are estimated at Rs14.13 and 11.75 lakh crore respectively.
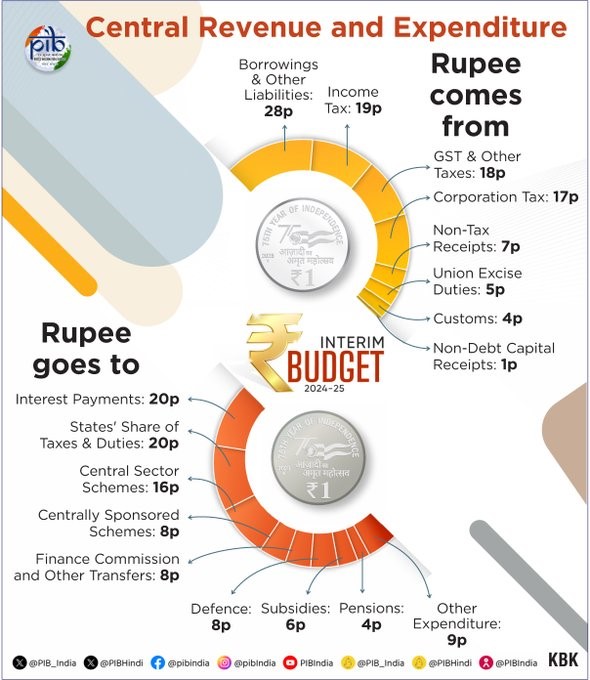
(Source: PIB)
2. Growth Projections in Interim Budget 2024
- India’s real GDP is projected to grow at 7.3 percent in FY 2023-24.
- India has registered the highest growth among major advanced and emerging market economies during this period.
- As per the IMF, India is likely to become the third-largest economy in 2027 in USD at market exchange rate.
- India’s contribution to global growth will rise by 200 basis points in 5 years.
- The fiscal deficit in 2024-25 is estimated to be 5.1 percent of GDP. It will reduce to below 4.5 percent by 2025-26.
- The Finance Minister said that the government is committed to making India a ‘Viksit Bharat’ by 2047.
3. Revised Estimates (RE) 2023-24 in Interim Budget
- RE of the total receipts other than borrowings is Rs.27.56 lakh crore, of which the tax receipts are Rs.23.24 lakh crore.
- RE of the total expenditure is Rs.44.90 lakh crore.
- RE of the fiscal deficit is 5.8 percent of GDP for 2023-24.
4. Social Justice
- The government is committed to the upliftment of four major castes, that is, ‘Garib’ (Poor), ‘Mahilayen’ (Women), ‘Yuva’ (Youth) and ‘Annadata’(Farmer).
5. Women Empowerment
- Female enrolment in higher education has increased by 28%.
- 30 crore Mudra Yojana loans given to women entrepreneurs and more than 70% of houses under PM Awas Yojana have been given to women from rural areas.
- 43 percent of female enrolment in STEM courses.
- The government plan is to increase the Lakhpati Didi target from 2 crore to 3 crore.
6. Railways and Aviation sector
- Three major economic railway corridor-energy, mineral and cement corridors, port connectivity corridors, and high traffic density corridors will be implemented.
- 40000 normal rail bogies will be converted to the Vande Bharat standards. It will enhance the safety, convenience and comfort of passengers.
- The number of airports has doubled to 149. Indian carriers have placed orders for over 1000 new aircraft.
- The projects have been identified under the PM Gati Shakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity.

(Source: PIB)
7. Energy Sector
- The Government has announced several schemes to turn Net Zero by 2070.
- 1 crore households to obtain 300 units of free electricity every month through rooftop solarization.
- A coal gasification and liquefaction capacity of 100 MT will be set up by 2030.
- Phased mandatory blending of CNG, PNG and compressed biogas has been proposed in the budget.
8. Sustainable Development
- The government will strengthen the e-vehicle ecosystem by supporting manufacturing and charging.
- Financial assistance is provided for the procurement of biomass aggregation machinery.
- Adoption of e-buses for public transport networks will be promoted.
- A new scheme of biomanufacturing and bio-foundry will be launched to support environment-friendly alternatives.

(Source: PIB)
9. Health Sector
- U-WIN platform for immunisation efforts of Mission Indradhanush will be implemented.
- Government will encourage Cervical Cancer Vaccination for girls (9-14 years).
- Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 will be implemented for improved nutrition delivery, early childhood care and development.
- Healthcare coverage under the Ayushman Bharat scheme will be extended to all ASHA workers, Anganwadi Workers and Helpers.
10. Infrastructure
- The Housing for Middle-Class scheme will be launched by the government to encourage the middle class to buy/build their own houses.
- 2 crore houses will be built under the PM Awas Yojana (Grameen) in the next 5 years.
- The Government will subsidize the construction of 30 million affordable houses in rural areas.
- The length of National highways increased from 97,991 km in FY15 to 1,44,634 km in FY22.
- The urban transformation via Metro Rail and NaMo Bharat will be promoted.
11. Agriculture and food processing sector
- The government will encourage ‘Nano DAP’ for various crops and expand its use for all agro-climactic zones.
- The government will also formulate policies to support dairy farmers and defeat the Foot and Mouth Disease.
- A strategy will be formulated to achieve ‘Atmanirbharta’ for oil seeds such as mustard, groundnut, sesame, soybean, and sunflower. It will cover research for high-yielding varieties, procurement, value addition and crop insurance.
- A comprehensive programme for supporting dairy farmers will be formulated.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced five integrated aquaparks in the interim budget.

(Source: PIB)
12. Taxation Reforms
- GST collection stood at ₹1.65 lakh crore in December 2023. This is the seventh time that gross GST revenues have crossed ₹1.6 lakh crore.
- Average monthly Gross GST collections doubled to ₹1.66 lakh crore in FY24
- Increase in tax buoyancy of State revenue from 0.72 (2012-16) to 1.22 in the post-GST period (2017-23).
- A provision of Rs.75,000 crore rupees as a fifty-year interest-free loan is proposed to support reforms by the State Governments.
- Tax exemption on certain income of IFSC units has been extended till 31st March 2024.
- It has been proposed to withdraw the outstanding direct tax demands up to Rs 25,000 relating to the period up to 2009-10 and up to Rs 10,000 relating to the financial year 2011 to 2014-15.

(Source: PIB)
13. Upskilling and reskilling
- More than 1.4 crore youth were trained under the Skill India Mission.
- 43 crore loans sanctioned under PM Mudra Yojana.
- PM-Vishwakarma Yojana was launched to provide support to artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades.
14. Tourism sector
- States will be encouraged to take up comprehensive development of iconic tourist centres, branding and marketing them at a global scale.
- Long-term interest-free loans are to be provided to States for financing such development on a matching basis.
- To promote domestic tourism, projects for port connectivity, tourism infrastructure, and amenities will implemented on different islands, including Lakshadweep.
15. Research and Innovation
- A corpus of INR 1 Lakh Cr will be established with a fifty-year interest-free loan. It will encourage the private sector to scale up research and innovation significantly in sunrise domains.
- A new scheme will be launched for strengthening deep-tech technologies for defence purposes and expediting ‘Atmanirbharta’.
16. Education
- More medical colleges will be set up by utilizing the existing hospital infrastructure.
- Rs 73,008.10 crore has been allocated to the Education Ministry’s Department of School Education and Literacy for the financial year 2024-25.
- The total allocation for the Higher Education Department is ₹47,619.77 crore.
17. Retention of same tax rates
- For direct and indirect taxes, including import duties.
- For Corporate Taxes-22% for existing domestic companies, 15% for certain new manufacturing companies.
- No tax liability for taxpayers with income up to ₹7 lakh under the new tax regime.
Major achievements of the union government
- Over the last ten years, the government has helped 25 crore people escape multidimensional poverty.
- FDI Inflow doubled from 298 USD Billion during 2005-14 to 596 USD Billion during 2014-23.
- Credit assistance to 78 lakh street vendors has been provided under PM-SVANidhi.
- 7 IITs, 16 IIITs, 7 IIMs, 15 AIIMS and 390 universities have been set up since 2014.
- Direct Benefit transfer has led to savings of ₹2.7 lakh crore.
- Direct financial assistance haven been provided to 11.8 crore farmers under PM-KISAN.
- 1,361 mandis under eNAM have been integrated with a trading volume of ₹ 3 lakh crores.
- Direct Tax Collections more than trebled in the last 10 years.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana has benefitted 38 lakh farmers and generated 10 lakh employment.
- Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Yojana has assisted 2.4 lakh SHGs and 60000 individuals with credit linkages.
Other facts related to the Budget 2024-25
- The average processing time of tax returns has been reduced to 10 days from 93 days in 2013-14.
- The government will come out with a White Paper on the mismanagement of the economy before 2014.
- The Government will form a high-powered committee for an extensive consideration of the challenges arising from fast population growth and demographic changes.
- In Budget 2024, the biggest allocation is for defence and the lowest for agriculture.
|
Ministry |
Budget |
|
Defence |
₹6.1 lakh crore |
|
Road Transport and Highways |
₹2.78 lakh crore |
|
Railways |
₹2.55 lakh crore |
|
Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution |
₹2.13 lakh crore |
|
Home Affairs |
₹2.03 lakh crore |
|
Rural Development |
₹1.77 lakh crore |
|
Chemicals and Fertilizers |
₹1.68 lakh crore |
|
Communications |
₹1.37 lakh crore |
|
Agriculture and Farmer's Welfare |
₹1.27 lakh crore |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Interim Budget 2024-25
Was there any rebate in personal income tax in Budget 2024?
Was the Interim Budget 2024-25 paperless?
How many Budgets have presented so far by the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman?
What is the duration of the shortest budget speech ever?
Who holds the distinction for delivering the longest duration Budget speech?
Which article defines the Vote on Account?
Share Blog





Comments