Topic: Regulatory Bodies/Financial Institutions
1. IRDAI has taken steps to stop sharp increases in health insurance premiums.
- It has prohibited insurers from increasing premiums for policyholders of 60 and above age by over 10% annually without getting prior approval.
- This will keep the health insurance accessible to senior citizens and prevent them from vulnerability due to medical inflation.
- Earlier, policyholders had raised concerns that premiums were being doubled within a year.
- As per the IRDAI mandate, insurers will now offer health plans as well as riders for all age groups. This will include those more than 65 years of age.
- IRDAI has lowered the waiting period with regard to pre-existing conditions from earlier 4 years to 3 years.
- Customer Information Sheet (CIS) must be provided by insurers with every policy document.
- This CIS shall, in simple terms, provide an explanation on details like sum insured, coverage, exclusions and waiting periods.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
2. In the week ending January 24, India's foreign exchange reserves increased by $5.57 billion to $629.55 billion.
- The foreign exchange reserves in the week that ended on January 17 were at 623.98 billion, down 1.8 billion dollars from the previous week.
- The main cause of the increase was a rise in Foreign Currency Assets (FCA), which makes up a large portion of the reserves.
- Over the course of the week, the FCA increased by 4.75 billion dollars to surpass 537.89 billion dollars.
- Gold reserves also increased by 704 million dollars, bringing the total to over 69.65 billion dollars.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
3. In the fiscal year 2025, it is estimated that India's real GDP will increase by 6.4%.
- According to the Economic Survey, India's growth in the fiscal year 2026 is projected to be between 6.3 and 6.8 percent.
- According to survey, India's GDP increased by 6.7% in the first quarter and 5.4% in the second quarter of the fiscal year 2025 at constant prices (2011–12).
- During the first half of the current fiscal year, real GDP grew by 6%.
- In the first half of the fiscal year 2025, agriculture grew steadily, with a growth rate of 3.5 percent in the second quarter.
- The first half of the fiscal year 2025 saw a 6% growth in the industrial sector.
- In the first half of the fiscal year 2025, the services sector grew by 7.1 percent.
- Retail headline inflation decreased from 5.4 percent for the fiscal year 2024 to 4.9 percent between April and December of the same year.
- According to the 2023-24 annual Periodic Labour Force study (PLFS) report, the unemployment rate for people 15 years of age and older has been progressively declining, said the survey.
- This unemployment rate was 6.2 percent in 2017–18.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
4. Retail inflation declined from 5.4% in FY24 to 4.9% in FY25.
- Various government initiatives and monetary policy measures have helped in reducing retail inflation in India from 5.4% in FY24 to 4.9% in FY25 (April-December).
- On January 31, this was stated in the Economic Survey 24-25 presented in Parliament by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
- The survey said the decline in retail inflation is mainly due to a 0.9 percentage point reduction in core inflation between FY2024 and FY2025 (April-December), driven mainly by moderation in core services inflation and fuel price inflation.
- The survey said that India's food inflation rate remained stable, led by some food items like vegetables and pulses.
- Vegetables and pulses contributed 32.3% to the overall inflation in FY25 (April to December).
- Excluding these items, the average food inflation rate for FY25 (April-December) was 4.3%, lower than the overall food inflation of 4.1%.
- The Economic Survey highlights that the deficient production of tur in 2022-23 and 2023-24 caused high price pressures in tur dal during FY24 and FY25.
- To ensure adequate supply, the government imposes stock limits and monitors stocks while importing 7.7 lakh tonnes of tur in FY24.
- The Economic Survey stated that despite challenges, the RBI and IMF project India's consumer price inflation to align towards the 4% target by FY26.
- RBI expects 4.2% inflation in FY26, while IMF forecasts 4.4% in FY25 and 4.1% in FY26.
- The survey mentioned that according to the World Bank's Commodity Market Outlook, October 2024, commodity prices are expected to decline by 5.1% in 2025 and 1.7% in 2026.

(Source: PIB)
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
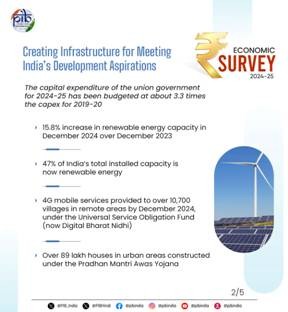
5. According to the Economic Survey 2024-25, government capital expenditure on key infrastructure sectors grew by 38.8% between FY20 and FY25.
- The Union Government’s capital expenditure on key infrastructure sectors grew by 38.8% from 2019-20 to 2023-24.
- In 2024-25, capital expenditure gained momentum between July and November 2024.
- On January 31, this was stated in the Economic Survey 24-25 presented in Parliament by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
- The power sector network continued to expand, with installed capacity rising by 7.2% to 456.7 GW by November 2024.
- By the end of December 2024, the total renewable energy installed capacity in the country was increased by 15.8% year-on-year (YoY), reaching 209.4 GW from 180.8 GW in December 2023.
- With the implementation of the Restructured Distribution Sector Scheme, the daily average power supply in urban areas has increased from 22.1 hours in FY2014 to 23.4 hours in FY2024 and in rural areas from 12.5 hours in FY2014 to 21.9 hours.
- The gap between demand and supply of energy has also reduced from 4.2% in FY 2014 to just 0.1% by December 2024.
- Talking about infrastructure in rural areas, Jal Jeevan Mission, launched in August 2019, aims to ensure water security for rural households.
- When it was launched in August 2019, only 3.23 crore (%) rural households had tap water connections.
- Since then, over 12.06 crore households have been connected, taking the total to over 15.30 crore (79.1%) out of around 19.34 crore rural households by November 26, 2024.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Grameen (SBM-G) achieved open defecation-free (ODF) status in Phase I. Phase II (2020-25) focuses on upgrading villages to ODF Plus, with 1.92 lakh villages added from April to November 2024, bringing the total to 3.64 lakh.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U), launched in 2015, aims to provide permanent housing in urban areas. As of November 25, 2024, 1.18 crore houses have been approved and construction of over 89 lakh houses has been completed.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
6. As per Economic Survey 2024-25, average growth of agriculture sector in India has been 5 per cent annually from FY17 to FY23.
- The growth rate of India’s agriculture sector was 3.5 per cent in the 2nd quarter of the 2024-25 fiscal year.
- Gross Value Added (GVA) of agriculture and related sectors have increased from 24.38 per cent in FY15 to 30.23 per cent by FY23.
- Agriculture growth at around 5 per cent with a 20 per cent contribution to overall GVA will contribute 1 per cent growth to GVA.
- As per survey, it is projected that kharif foodgrain production in 2024 will reach 1647.05 Lakh Metric Tonnes.
- As per survey, agricultural income has grown at 5.23 per cent annually during the past decade.
- From FY16 to FY25 (Dec. 2024 end), ₹ 21968.75 crore was released to states for implementation of Per Drop More Crop Scheme.
- For FY25, the government raised MSP for arhar and bajra by 59 per cent and 77 per cent, respectively. This raise was over weighted average cost of production.
- MSP for Masur has been increased by 89 per cent. Rapeseed MSP has seen an increase of 98 per cent.
- The livestock sector represented 5.5 per cent of the total GVA, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate of 12.99 per cent.
- Among livestock production, the milk industry generated over ₹11.16 lakh crore.
- Total fish production has increased from 95.79 lakh tonnes in FY14 to 184.02 lakh tonnes in FY 23.
- India's seafood exports have shown a growth of 29.70 per cent.
- India's floriculture exports grew by 14.55 per cent in April-October FY25 over April-October FY24.
- As per survey, India is a leading exporter of fresh grapes globally in 2023-24.
- Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Mizoram contributed over 67 per cent of total output of grapes.
- As per survey, in the fiscal year FY24, the value of agri-food exports constituted about 11.7 per cent of India’s total exports.
- The share of processed food exports grew from 14.9 per cent in FY18 to 23.4 per cent in FY24.
(Source: PIB)
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
7. In the Economic Survey 2024-25, the Service Sector has been termed the ‘Old War Horse’.
- The contribution of the services sector to total GVA at current prices has grown from 50.6% in FY14 to nearly 55% in FY25.
- The service sector growth has been above 6% in each year in the last decade. This growth is measured by YoY change in the real GVA by services.
- The exception has been FY21 that was affected by the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Before the pre-pandemic year, the average services growth rate was 8%.
- In the post-pandemic years (FY23 to FY25), average services growth has increased to 8.3%.
- India represents a 4.3% share in global services export.
- Economic Survey 2024-25 referred to HSBC’s India services PMI.
- It highlighted that the services sector has been in expansion for 41 months in a row since August 2021.
- HSBC’s India services PMI was above 60 mark for first five months of FY25. In September, the index reached a ten-month low level.
- India’s services export growth increased from 5.7% in FY24 to 12.8% in April-November FY25.
- Computer services and business services exports contributed about 70% of India’s services exports.
- In April-November FY25, services imports increased by 13.9%. In the same period in FY24, there was a decline of 2.9%.
- As of November 2024, total outstanding credit to the banking sector was 48.5 lakh crore rupees.
- The highest YoY credit growth was recorded in computer software and professional services.
- The highest FDI inflows was received in insurance services in FY25 (April- September), followed by the financial sector.
- The Survey classifies services into four categories. This is based on performance analysis of the various service sub-sectors across certain key dimensions.
- During FY23, road transport contributed 78 per cent of total GVA of transport services.
- Growth of passenger traffic of Indian Railways stood at 8 per cent over the previous year.
- As of October 2024, India has 26 operational waterways.
- The tourism sector’s contribution to GDP reached the pre-pandemic level of 5% in FY23.
- India is second largest telecommunications market.
- India has an overall tele density of 84% as of 31st October 2024.
- India has 941 million broadband users as of 31st October 2024.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
8. Finance Minister presented the Union Budget 2025-26 with the theme “Sabka Vikas”.
- The Budget aims to make reforms in Taxation, Power Sector, Urban Development, Mining, Financial Sector, and Regulatory Reforms.
- Union Budget highlights that Agriculture, MSME, Investment, and Exports are engines in the journey to Viksit Bharat.
- The government will launch a 6-year “Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses.
- A comprehensive multi-sectoral ‘Rural Prosperity and Resilience’ programme will be launched in partnership with states.
- In the budget 2025, the Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced establishment of Cancer Center in each district.
- The Government announced the increase in loan limits from Rs. 3 lakhs to Rs. 5 lakhs for loans taken through Kisan Credit Cards.
- The government will also launch a new scheme for 5 lakh women, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes first-time entrepreneurs.
- Under this scheme, loans up to Rs. 2 crores will be provided during the next 5 years.
- Government will also launch a scheme to make India a global hub for toys representing the 'Made in India' brand.
- Five National Centres of Excellence for skilling will be set up with global expertise and partnerships.
- A Centre of Excellence in Artificial Intelligence for education will be set up with a total outlay of 500 crore.
- Budget proposed Gyan Bharatam Mission, for survey, documentation and conservation of more than 1 crore manuscripts in academic institutions.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
9. Government target Fiscal Deficit of 4.4% of GDP.
- In the budget 2025–26, the government has kept the budget deficit target on a declining path to 4.4 percent of GDP.
- It was 4.8 per cent of GDP in 2024-25.
- The net market borrowing for the budget 2025-26 has been fixed at Rs 11.54 crore. The rest of the funds will come from small savings schemes.
- The government’s gross borrowing target for FY25-26 was revised upwards by 5.7 per cent to Rs 14.82 lakh crore.
- In FY 2025-26, the government projected gross tax revenue at Rs 38.40 lakh crore. It is 11.72 percent more than FY24.
- The net tax receipts are estimated at Rs 28.37 lakh crore.
- The total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at Rs 34.96 lakh crore and Rs 50.65 lakh crore, respectively.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
10. The finance minister announced that no income tax will be payable for those with an income up to ₹12 lakh.
- On 1 February, the Union Budget 2025-2026 was presented in the Parliament by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, introducing a massive relief for income taxpayers.
- Giving a big relief to the taxpayers, the finance minister made income up to Rs 12 lakh tax-free, which was earlier Rs 7 lakh.
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented her record eighth consecutive Union Budget in Parliament.
- Nirmala Sitharaman proposed to revise the tax rate structures as follows:
- ₹0 to ₹4 Lakhs – Nil
- ₹4 Lakhs to ₹8 Lakhs – 5%
- ₹8 Lakhs to ₹12 Lakhs – 10%
- ₹12 Lakhs to ₹16 Lakhs – 15%
- ₹16 Lakhs to ₹20 Lakhs – 20%
- ₹20 Lakhs to ₹24 Lakhs – 25%
- Above ₹24 Lakhs – 30%
- Considering the standard deduction of₹75,000 for the salaried class, income up to₹12.75 lakh will be tax-free.
- However, this income does not include capital gains, which are taxed at different short-term and long-term tax rates.
- The minister said these proposals would result in the government losing revenue of about Rs 1 trillion from direct taxes and Rs 2,600 crore from indirect taxes.
- Taxpayers have the option to choose between two tax systems: the old tax regime and the new tax regime.
- In the old tax system, exemptions are available on house rent, insurance, and other long-term investment plans.
- The new tax system introduced in the year 2020 has given slightly lower rates, but no exemption has been given in this.
- The finance minister has not announced any change in the old tax system.






 Previous
Previous 
 Latest
Latest 








Comments