Topic: Banking System
1. Government has raised maximum tenure of Managing Director and other whole-time directors of PSU Banks to 10 years.
- Finance Ministry has issued a notification on 17 November to amend Nationalised Banks (Management and Miscellaneous Provisions) Scheme, 1970.
- Maximum tenure of the Managing Director and other whole-time directors of PSBs has been raised from 5 years to 10 years, while superannuation (retirement) age has been retained at 60.
- Earlier, maximum tenure of MD or the executive director of a PSU bank was 5 years or until they reach 60, whichever was earlier.
- Government appoints Managing Directors from Whole-time Directors (WTD) of a public sector banks.
- Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB) recommends the names of Whole-time Directors (WTDs).
Topic: RBI
2. DSP Investment Managers’ acquisition of up to 9.99% stake in Equitas Small Finance Bank has been approved by RBI.
- The approval is valid for one year, till November 15, 2023.
- DSP Investment Managers will take over up to 9.99% of the paid-up equity capital of the bank.
- As of end of September 2022, Mutual funds held 13.17% stake in Equitas Small Finance Bank. The largest share was held by Nippon Life Mutual Fund.
- Equitas Small Finance Bank is a small finance bank. It is headquartered in Chennai.


Topic: RBI
3. India’s GDP is likely to grow at a growth rate of about 7% in 2022-23 according to a RBI report.
- As per the RBI report, India’s GDP is expected to grow at growth rate between 6.1% and 6.3% in the June-September quarter of the current fiscal.
- In its report, RBI said that Indian Economy has shown resilience to multiple shocks since early 2020. However, India is still sensitive to global headwinds.
- RBI has released seventh edition of its statistical publication titled “Handbook of Statistics on Indian States 2021-22”.
- This seventh edition incorporates two new sections-Health and Environment. It also incorporates nine new tables.
Topic: Reports and Indices
4. State Bank of India and some private sector banks will record profitability more sharply than the system as per a report from S&P Global Ratings.
- In a report titled ‘Global Bank Country-By-Country Outlook 2023’, with special reference to India, S&P said polarisation will be prevalent in the performance of commercial banks in India.
- In the report, S&P said SBI and leading private-sector banks have largely addressed their asset quality challenges.
- It said their profitability is improving more sharply than the system’s.
- It said many large public-sector banks are facing challenges of weak assets, high credit costs, and poor earnings.
- India has 12 public sector banks (PSBs) and 22 private sector banks.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
5. Government has removed export duty on certain steel products and iron ore.
- Exports of iron ore lumps and fines with ‘less than 58% Fe’ will attract nil export duty. Exports of iron ore pellets will also attract nil export duty.
- Exports of iron ore lumps and fines with more than ‘58% Fe’ will attract duty at the rate of 30%.
- Exports of pig iron and steel products classified under HS 7201, 7208, 7209, 7210, 7213, 7214, 7219, 7222 & 7227 will attract nil export duty. HS stands for Harmonised System.
- In May, the government had imposed an export duty varying from 15% for steel exports to around 50% for iron-ore.
- Steel prices in domestic markets have been falling since May.
- India’s steel exports declined 66% in October to 360,000 tonnes on weak global demand and increased prices compared with competitors.
- The industry blamed higher duties for lower export. India turned net importer of steel in October.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
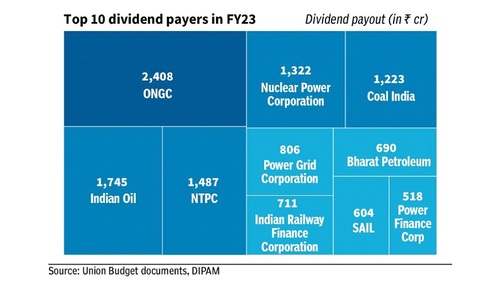
6. According to DIPAM data, the total dividend received from CPSEs now stand at ₹18,719 crore or 46% of FY23 budget estimate.
- For the current fiscal, the Centre has budgeted ₹40,000 crore from dividends from Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs).
- In FY21, the Centre raised ₹39,750 crore in dividend receipts from CPSEs. This was against the revised estimate of ₹34,717 crore for the year.
- In FY22, the Centre received dividend receipts of ₹59,101 crore. This was 28% more than revised estimate of ₹46,000 crore.
- Under the current norms, every CPSE is required to pay a dividend of 30% of profit after tax or 5% of the net-worth, whichever is higher.
- DIPAM stands for Department of Investment and Public Asset Management.
Topic: Miscellaneous
7. Creditors realised ₹2.43 lakh crore through the resolution plans approved by NCLT under IBC till end September 2022.
- The creditors mainly include banks and financial institutions.
- The total claims of the creditors amounted to ₹7.91 lakh crore whose liquidation value is estimated at ₹1.37 lakh crore.
- Data available with Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) showed creditors have realised 177.55% of the liquidation value.
- The provisions relating to Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) became effective on December 1, 2016.
- Total 5,893 CIRPs commenced by September end 2022. 1,807 CIRPs have ended in orders for liquidation.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) has led to behavioural change in the debtor-creditor relationship.
- National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT):
- NCLT was formed under the provisions of Companies Act, 2013.
- NCLT adjudicates cases filed under IBC, 2016.
- Chief Justice (Retd) Ramalingam Sudhakar is its current chairman.
Topic: Miscellaneous
8. Some of India’s top medicine brands will be required to have QR or bar codes from August 2023.
- Total 300 brands are included in the list. Centre has issued order on 17 November under the new Drugs Rules or Drugs (Eighth Amendment) Rules.
- According to the order, mentioning bar codes or QR codes on the packaging will be mandatory from August 1, 2023.
- Union Health Ministry notification said that manufacturers of drug formulation products shall print or affix Bar Code or Quick Response Code on its primary package label, on secondary package label.
- This Bar Code or QR Code shall store data and information legible with software application to facilitate authentication.
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
9. India's foreign exchange reserves gained their biggest weekly rise in the last 1 year.
- The foreign exchange reserve of India has risen by 14.72 billion dollars to 544.715 billion dollars.
- India's foreign exchange recorded its biggest weekly rise in the week that ended on 11 November.
- For the week ending October 28, the foreign exchange reserves had jumped 6.56 billion dollars to 531.08 billion dollars.
- The sharp increase is primarily due to an increase of $11.8 billion in the central bank’s foreign currency assets.
- The main reason for the increase in foreign exchange reserves is the weakening of the US dollar and purchases of dollars in the spot market by the central bank.
- Due to the softening of the prices of global crude and commodities the demand for the dollar has decreased.
- The rupee climbed 2.3% between October 21 and November 11.
- To ensure the rupee's stability, RBI sold a net of $10.3 billion in the spot market and another $9.7 billion in the forwards market in September.
Topic: Reports and Indices
10. India to invest $840 billion to upgrade its urban infrastructure over the next 15 years: World Bank report.
- World Bank has released a report titled ‘Financing India's Infrastructure Needs: Constraints to Commercial Financing and Prospects for Policy Action’.
- The report has highlighted the need to improve the financing avenues for India's urban local bodies.
- At present, only 5% of the infrastructure needs of Indian cities are getting financed through private sources.
- The state government and Central government finance more than 75% of the city’s infrastructure projects.
- Urban local bodies (ULB) finance 15% of their projects through surplus revenues.
- By 2036, around 40% of the population will live in urban cities in India.
- Indian cities need financing in large amounts to promote green, smart, inclusive, and sustainable urbanization.
- The population pressure on Indian cities will increase the demand for clean drinking water, power supply, and road transport.
- The report has recommended increasing the capacities of city agencies to deliver infrastructure projects.
- The weak regulatory environment and weak revenue collection increase the challenges of cities in accessing more private financing.



 Previous
Previous 
 Latest
Latest 








Comments