Planets in Solar System | Inner and Outer Planets | Asteroids, Meteors, Comets, Constellations, Our Galaxy
The basic knowledge of our universe, our galaxy, our solar system and its planets, other celestial bodies present in solar system is important for all candidates preparing for various government exams like State PCS, CDS, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, CCS GD Constable, RRB NTPC and other exams. This basic knowledge helps in understanding the recent developments in the field of science and technology.
1. Solar system
- The totality of everything that exists is defined as Universe. Cosmology is the study of Universe.
- The solar system is part of Universe that comprises various celestial bodies including the sun, planets, moon, asteroids, meteors, comets, etc.
- At the centre of the Solar system lies the sun around which all these bodies revolve. The gravitational force of the sun governs the motion of these bodies.
- The Solar system planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical path.
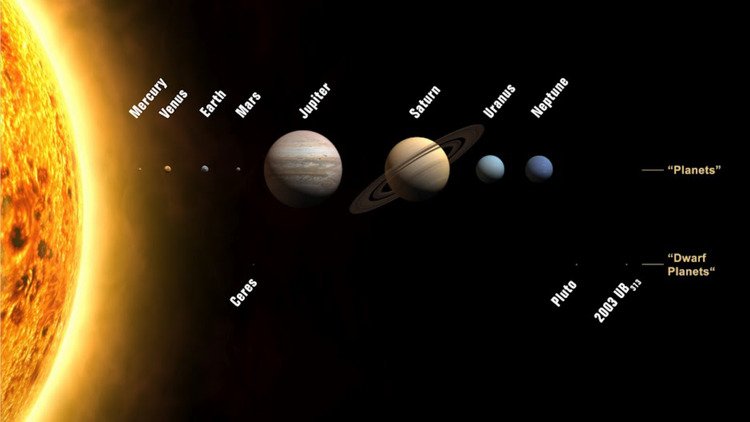
Fig.1: Solar System and its planets (Source: NOAO)
2. Features of Solar System
- Size of Solar system- 105 Astronomical unit
- There are eight planets in our solar system. Ceres and Pluto are dwarf planets as per the definition by International Astronomical Union (IAU). Ceres is part of the asteroid belt and Pluto is part of the Kuiper belt.
- In 2005, Kuiper belt object Eris was discovered.
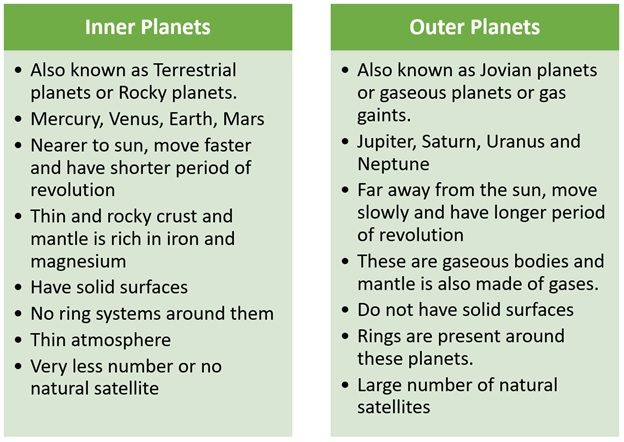
- The solar system planets are divided into two groups- Inner planets or Terrestrial planets and Outer or Jovian planets or gaseous planets.
- Inner planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars while Outer Plantes include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
2.1. The Sun
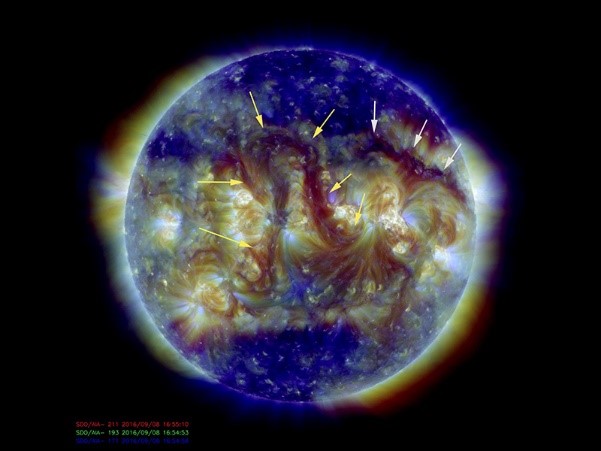

Fig.2: Two long filaments observed on Sun (Source: NASA)
- Sun is the source of all energy in the solar system. 99.9% of matter in the whole solar system is present in the sun. It is the closest star to the Earth. It is classified as a yellow dwarf star.
- Features:
- Composition of Sun: 71% Hydrogen, 26.5% Helium and 2.5% other elements
- Size of Sun: Around 13 lakh times that of the Earth
- Diameter of Sun: 14 lakh kms
- Temperature of Sun: 5778K (Surface) and 1.57x107 K (Core)
- Distance of Sun from earth: Around 150 million kms
- It takes about 8.5 minutes for the light to reach Earth from the Sun.
- The surface of the Sun is called Photosphere.
- Thin gas layer above the photosphere is called Chromosphere.
- The outer layer of the atmosphere of the Sun is called Corona which can be seen only during the total eclipse of the Sun. Corona can also be seen through a special solar telescope called Coronagraph.
- Solar winds are the extension of Corona. Solar flare is a dense burst of solar wind particles.
2.2. Planets
- The planets are opaque celestial bodies that revolve around the sun and receive light mainly from the Sun.
- Most planets orbit in the same plane.
- Size of planets in ascending order: Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn and Jupiter
- Sequence of planets according to their distance: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Comparison between Inner and Outer Planets
2.2.1. Mercury
Fig.3: Mercury (Source: NASA)
- It is the closest planet to the Sun with almost no atmosphere.
- Mercury has a cratered surface.
- It has an effective temperature of around 350° F.
- No water and gases like CO2, H2 are present on this planet.
- No moons are present on Mercury.
- Thin Sodium atmosphere is present.
- NASA's Mariner 10 was the first mission to explore Mercury.
- NASA’s MESSENGER made history by becoming the first spacecraft ever to orbit Mercury.
- Rotation Period of Mercury (Time taken to rotate on its axis): 59 Days
- Revolution Time of Mercury (Time taken to revolve around the Sun): 88 days
2.2.2. Venus
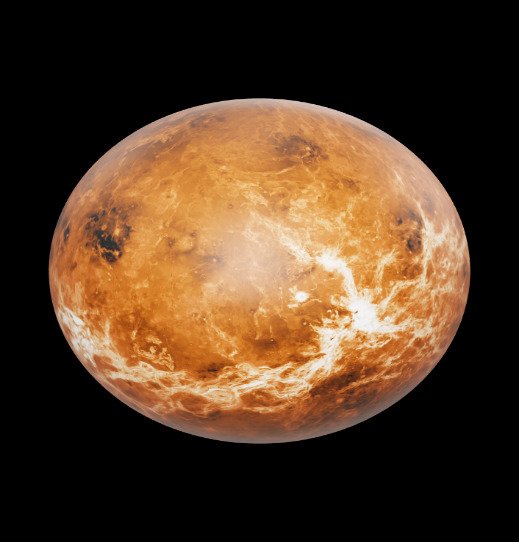

Fig.4: Venus (Source: NASA)
- Venus is also known as Evening Star and Morning Star.
- It is the second closest planet to the Sun.
- It is considered a twin to Earth due to almost the same size and mass.
- Dense carbon dioxide atmosphere causes an extreme greenhouse effect. It is the hottest planet in the solar system.
- The surface temperature of Venus is around 750 K.
- Venus’ clouds contain sulphuric acid, unlike Earth’s clouds which contain water.
- It rotates clockwise similar to Uranus.
- Rotation Period of Venus: 243 days
- Revolution time of Venus: 224.7 days
- No moons are present on Venus.
2.2.3. Earth

Fig 5: Moon moving over the Pacific Ocean (Source: NASA)
- It is the third planet from the Sun where life exists.
- Earth is also known as a blue planet due to the presence of water in large quantities.
- It is a hard, rocky planet with mountains, valleys, volcanoes, and craters.
- It is tilted 23.5° on its axis.
- Rotation period of Earth: 23 hours 56 minutes 4 seconds
- Revolution time of Earth: 365 days, 5 hours and 48 minutes
- The atmosphere of Earth mainly consists of nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Average Surface Temperature: 14° C
- Earth’s Moon: It has one Moon that orbits around it. Its atmosphere is thinner than that of Mercury. The gravitational pull of the Moon is one-sixth that of the Earth. It takes 27 days, 7 hours and 43 minutes to rotate on its own axis and approx. same time to revolve around the Earth.
2.2.4. Mars
- It is smaller than Earth but has an almost Earth like climate.
- Mars is also known as Red Planet as its soil contains iron oxide (rust).
- Thin carbon dioxide atmosphere is present on Mars,
- The temperature here can get as low as -200° F.
- Rotation period of Mars: 24.6 hours
- Revolution time of Mars: 687 days
- It has two moons- Phobes and Demos.
2.2.5. Jupiter

Fig.6: Jupiter (Source: NASA)
- Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system.
- It is called the winter planet as its average temperature is -220° F (-140° C).
- Its atmosphere mainly consists of Hydrogen and Helium.
- Its clouds are made of frozen gases like ammonia and water.
- There are thin rings around the planet.
- It has a great red spot that is equivalent to the size of Earth.
- It has 16 or more moons. Ganymede is the largest moon in our solar system. Callisto, Europa and Io are its other moons.
- Rotation period of Jupiter: 9.8 hours
- Revolution time of Jupiter: 11.85 years
2.2.6. Saturn
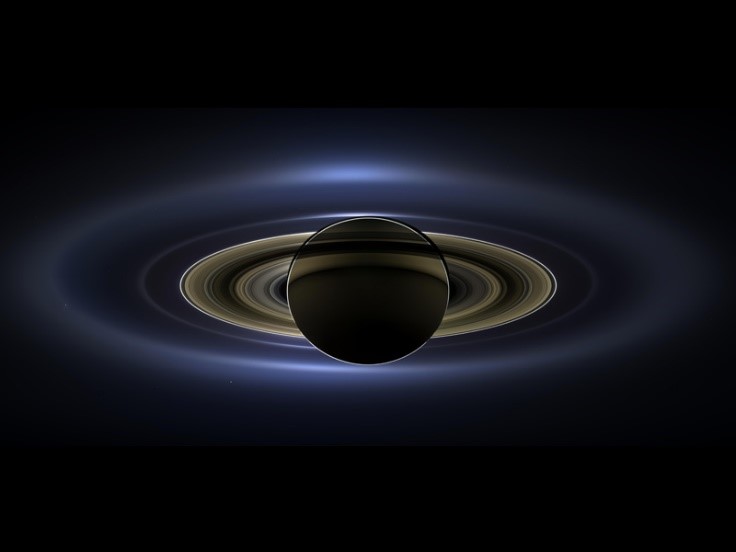

Fig.7: Saturn (Source: NASA)
- Saturn is the second-largest planet in the solar system.
- It has a complex and largest ring system.
- Temperature: -285° F
- It has 18 or more moons. Its largest moon Titan is the second-largest moon of the solar system.
- Rotation period of Saturn: 10.7 hours
- Revolution time of Saturn: 29.42 years
2.2.7. Uranus
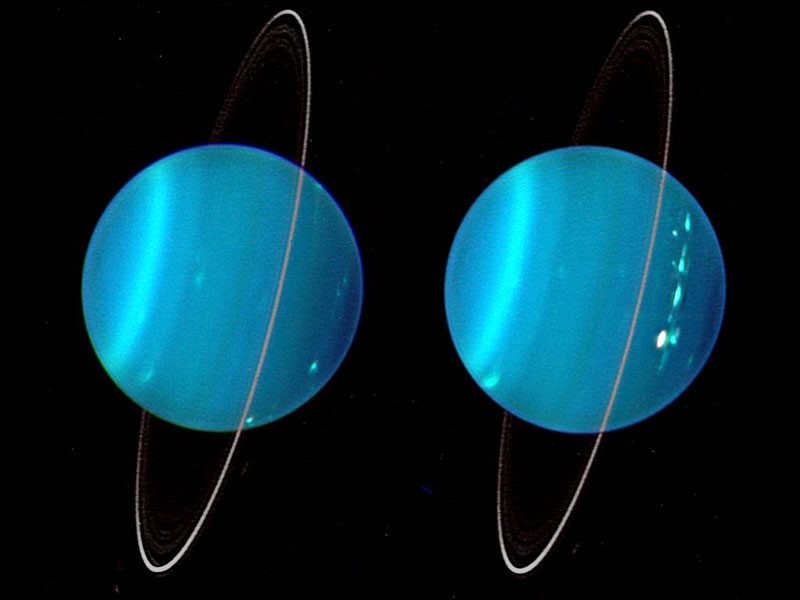

Fig. 8: Uranus (Source: NASA)
- It is the seventh planet from the Sun.
- It is also known as a "sideways planet" as it rotates on its side.
- It rotates east to west like Venus.
- Uranus is an ice giant. Most of the mass of Uranus is a hot, dense fluid of water, methane and ammonia. It is the coldest planet in our solar system.
- Its atmosphere is made of hydrogen, helium and methane. The presence of methane makes Uranus blue.
- It was the first planet that was discovered with a telescope.
- It is four times larger than the Earth.
- It has 27 known moons.
- Its obliquity is 98 degrees. Obliquity is the angle between the rotation axis and the orbit plane.
- Temperature at the top of clouds is -370° F (-220° C).
- Rings system is present-13 known rings
- Rotation period of Uranus: 17 hours
- Revolution time of Uranus: 84 years
2.2.8. Neptune
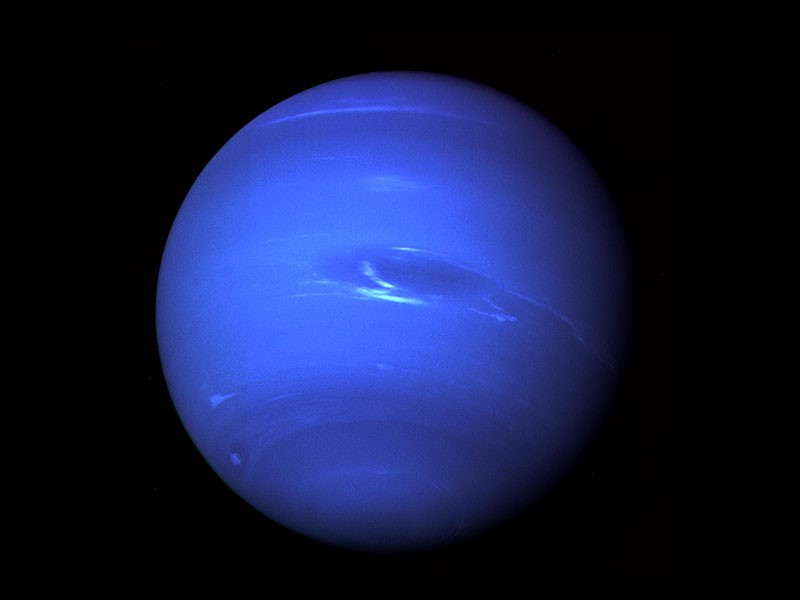

Fig. 9: Neptune (Source: NASA)
- It is the eighth and farthest planet in our solar system.
- It is dark, cloud and windy.
- It has 18 known Moons and 5 rings. Its largest moon is Triton.
- Temperature at the top of clouds is -355° F (-215° C).
- Its clouds are made of frozen methane, therefore appear blue.
- Like Jupiter, it has a Great Dark Spot.
- Rotation period of Neptune: 16.1 hours
- Revolution time of Neptune: 164 years
3. Other Celestial Bodies
Apart from the eight planets in our solar system, there are other celestial bodies that orbits the Sun. These are explained below:
3.1. Asteroids
They are small objects that revolve around the Sun in the gap between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. These are called minor planets because of their small size. They can only be seen through large telescopes.

Fig.10: Asteroid Bennu (Source: NASA)
3.2. Meteoroids
These are smaller than asteroids and orbit the sun like other celestial bodies. These can be formed due to the collision of asteroids or from comets.
3.3. Meteors
They are commonly known as shooting stars. They occasionally enter the earth’s atmosphere at a very high speed and glow brightly due to friction caused by the atmosphere.
3.4. Meteorite
Sometimes meteors reach the Earth and are called meteorites. Scientists study about the nature of solar system forming materials with the help of meteorites.
3.5. Meteor showers
They are swarms of meteors visible when Earth crosses the tail of a Comet.
3.6. Comets
They revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. Their period of revolution around the Sun is usually very long. Their tail is always directed away from the Sun.
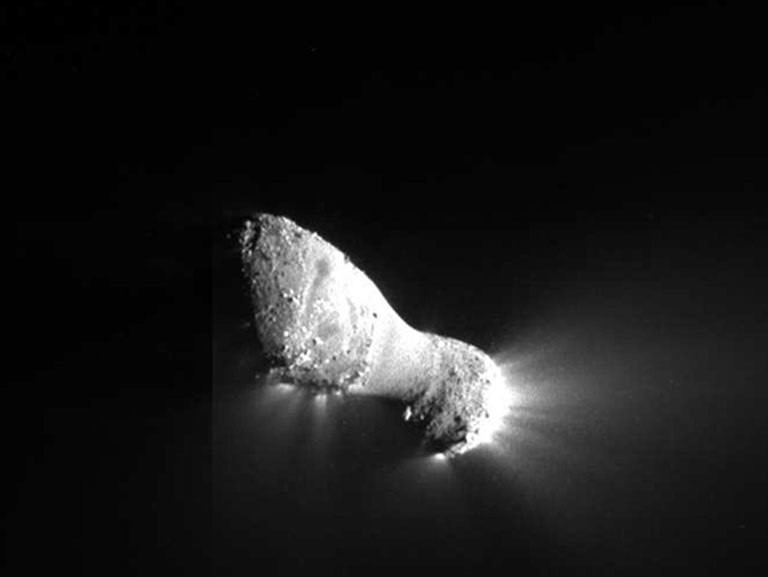

Fig.11: Comet Hartley 2 (Source: NASA)
4. Stars
Stars are celestial bodies that are made up of hot burning gases prominently hydrogen and helium. These produce heat and light due to the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to form helium.
Massive stars with 100 or more times huger than the Sun are known as Hypergiants. These emit 1000 times more energy than Sun but their lifetime is a few million years. As per NASA, the closest star to Earth after Sun is Proxima Centauri.
Examples of Stars- Sun, Pole star, Sirius, Alpha centauri, Beta centauri, Proxima centauri, Arcturus, Spica, Regulus
4.1. Constellations
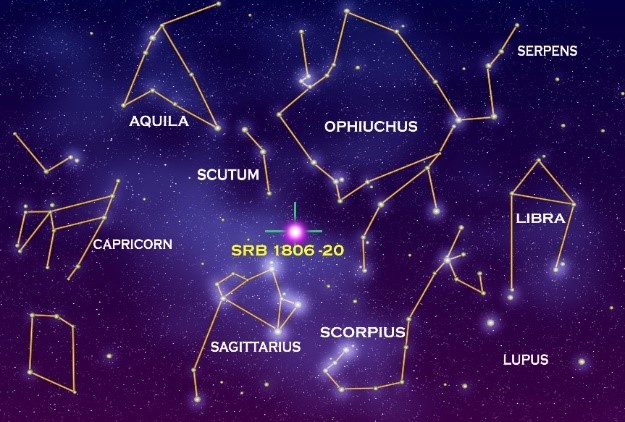
Fig.12: Types of Constellations (Source: NASA)
- It is a group of stars forming a certain pattern.
- There are 88 constellations in the Universe identified by IAU.
- Constellations and their Indian names are given below:
- Ursa Major (Great Bear) – Saptarishi
- Ursa Minor (Little Bear) – Dhruva Matsya
- Orion (Hunter) – Mriga
- Draco (Dragon) – Kaleya
- Aries – Mesh
- Taurus – Vrish
- Gemini – Mithun
- Cancer – Kark
- Leo – Simha
- Virgo – Kanya
- Libra – Tula
- Scorpio – Vrishchika
- Sagittarius – Dhanu
- Capricorn – Makar
- Aquarius – Kumbh
- Pisces – Meen
5. Our Galaxy

Fig.13: Hubble Space Telescope picture showing thousands of galaxies (Source: NASA)
Galaxy is a large collection of star, gas, dust and solar systems which are bounded together by gravity. Some galaxies are spiral shaped, some are elliptical or irregular. Our Earth is part of the Milky Way Galaxy (Spiral shaped galaxy). It takes almost 250 million years to complete one revolution.
Andromeda is the closest neighbor of our galaxy.
Current Facts related to Solar System
- Chandrayaan 1 Mission was launched in 2008 by ISRO. Chandryaan-2 mission was launched on 22 July 2019 by GSLV Mk III M1 but the contact was lost with its lander carrying the rover. ISRO will launch Chandrayaan-3 mission in 2022.
- Mars Orbiter Mission or Mangalyaan was launched by ISRO in 2013 to explore and observe Mars’ surface features.
- Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover mission is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program.
- NASA’s Juno mission was launched in 2011 to explore Jupiter.
- Cassini Huygens Spacecraft launched in 1997 was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit.
- NASA's Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to fly by Uranus and Neptune.
- NASA’s OSIRIS-Rex spacecraft (Mission launched in 2016) briefly touched asteroid Bennu.




 Latest
Latest 



Comments