Topic: RBI
1. Guidelines for digital lending to protect borrowers issued by RBI.
- As per the new guidelines by RBI, regulated entities cannot store borrowers' data except for some basic minimal information.
- The lender can now only store information like the name, address, contact details of the customer, etc.
- The digital lending apps cannot store the biometric information of the borrower.
- The regulated entities have been given time till 30 November 2022, to implement the guidelines.
- The main objective of these guidelines is to protect borrowers from unscrupulous lending practices.
- As per the guidelines, all data should be stored only in servers located within India.
- Borrowers will get the option to exit the digital loan by paying the principal and the proportionate APR without penalty during this period.
- The guidelines will be applicable to all commercial banks, primary (urban) co-operative banks, state co-operative banks, district central co-operative banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies, including housing finance companies.
Topic: Infrastructure and Energy
2. Blue Energy Motors launched India’s first LNG-fuelled truck.
- Union Minister Nitin Gadkari inaugurated the manufacturing facility, near Pune, with a capacity to make 10,000 trucks annually.
- The LNG-fuelled trucks will start with the introduction of 5,528 4x2 tractors by the end of September 2022.
- The LNG-fuelled trucks of Blue Energy Motors will be long-haul, and heavy-duty trucks.
- Blue Energy Motors has signed an agreement with Iveco FPT, which will provide engines.
- Various public sector undertakings (PSU) and private oil and gas marketing companies are setting up LNG stations.
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is a change-maker for the transport sector. This is a very good alternative to petrol and diesel.
- Blue Energy Motors is a Singapore-based firm.
Topic: Miscellaneous
3. Tata Group Ex-Chairman Cyrus Mistry passed away.
- He died in a road accident while he was travelling from Gujarat's Udwada to Mumbai.
- Cyrus Mistry was the sixth chairman of Tata Sons. He became the Chairman in December 2012, after the retirement of Ratan Tata.
- He was an Indian-born Irish businessman. He was the first person who was not directly from the Tata family but became the chairman of Tata Sons.
- He served as head of the Shapoorji Pallonji Group. He joined the board of Tata Sons on 1 September 2006.


Topic: RBI
4. RBI to run pilot project for full digitalization of Kisan Credit Card lending.
- The Reserve Bank of India will run the pilot project from September 2022 in selected districts of Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- The aim of this initiative is to making the lending under Kisan Credit Card scheme more efficient through reduction of costs and turn-around time for borrowers and improvement in credit flow to people living in rural areas.
- RBI said that this pilot project is being developed by the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH).
- In Madhya Pradesh, Union Bank of India is the partner bank while in Tamil Nadu, Federal Bank is the partner bank.
- There will be active cooperation of the state governments in the implementation of the pilot projects.
- Rural Credit is an important aspect of inclusive economic growth in India. It caters to the needs of various activities in rural areas like agriculture, small scale industries, etc.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Scheme:
- It was launched in 1998 to issue Kisan Credit Cards to farmers based on their holdings for uniform adoption by the banks so that they may use these cards to purchase agricultural inputs and withdraw cash for production requirements.
- In 2004, it was further extended for investment credit needs of farmers.
- In 2012, the scheme was revisited by a working group chaired by Shri T M Bhasin to simplify the scheme and promote issue of e-Kisan Credit Cards.
- In 2019, it was extended for fisheries and animal husbandry sector.
- Aim of the KCC scheme: To provide credit to farmers to meet short term credit needs for growing crops; Post-harvest expenses; Produce marketing loans; Consumption requirements of farmer household; working capital for maintenance of farm assets and activities; investment credit requirement for agriculture.
- Eligibility: Farmers (joint/individual borrowers) who are owner cultivators, tenant farmers, oral lessees and share croppers and SHGs or Joint Liability Groups of farmers including tenant farmers, share croppers, etc.
- The scheme provides the facility of ATM enabled Rupay card.
- A flexible limit of Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 50,000 has been provided to farmers under the scheme based on the land holding and crops grown and other factors.
- Most of the banks has set a validity of 5 years after which Kisan Credit Card can be renewed.

Topic: Committees/ Commissions/ Taskforces
5. SEBI restructured the panel on cyber security.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has restructured its high-level panel on cyber security.
- The panel was formed to suggest measures to safeguard the capital markets from cyberattacks.
- The members in committee have been increased from 4 to 6.
- The committee will be chaired by DG at National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) Navin Kumar Singh.
- The other members include Sanjay Bahl DG at CERT-In, H Krishnamurthy, Chief Scientist at IISc Bengaluru, Sandeep Shukla, Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, and Sugata Gangopadhyay.
- The panel will find measures to enhance cyber resilience and related business continuity and disaster recovery process in Indian securities market.
- The National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) is the nodal agency to protect the Critical Information Infrastructure in India. It was formed in 2014.
Topic: Reports and Indices/ Rankings
6. Department of Economic Affairs released 28th edition of Status Report on India’s External Debt 2021-22.
- External Debt Management Unit in Department of Economic Affairs under Ministry of Finance released Status Report on India’s External debt.
- The external debt has increased by 8.2% from US$ 573.7 billon (end-March 2021) to US$ 620.7 billion (end-March 2022).
- The largest part of the external debt is denominated in US dollar (53.2%) followed by Indian rupee denominated debt (31.2%).
- External debt as a ratio to GDP has decreased marginally from 21.2% to 19.9% during FY2021-22.
- Foreign currency reserves as a ratio to external debt was 97.8 percent as compared to 100.6 percent a year ago.
- Long-term debt is about 80.4% of the total external debt which stood at US$ 499.1 billion while short-term debt is 19.6% of the total debt.
- 90% of the total external debt is due to-
- Commercial borrowings
- NRIs deposits
- Short-term trade credit
- Multilateral loans
- Commercial lenders are the biggest creditors accounting for 36.7% of the debt, followed by NRI depositors (22.4%), short-term trade creditors (19.6%), and multilateral lenders (11.7%).
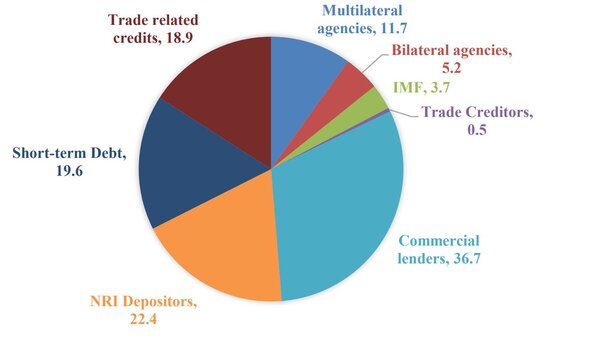
(Source: RBI and Ministry of Finance)
- During end-March 2021 and end-March 2022, NRI deposits contracted marginally while Commercial Borrowings, short-term trade credit and multilateral loans expanded.
- The sovereign external debt (SED) has increased by 17.1% to US$ 130.7 billion which shows the additional allocation of Special Drawing Rights (SDR) by IMF. SDR increased to US$ 22.9 billion (end-March 2022).
- Sovereign External Debt (SED) comprises external assistance (from multilateral and bilateral sources) on government account, defence debt, investment in treasury bills/government securities by FPIs, foreign central banks and international institutions, and SDR allocations by the IMF.
- Non-sovereign external debt is estimated at US$ 490.0 billion and CBs, NRI deposits, and short-term trade credit accounts for 95% of non-sovereign debt.
- The debt service ratio has declined to 5.2% due to buoyancy in current receipts and decline in debt service payments.
- Debt service ratio is measured by the proportion of gross debt service payments (both principal and interest) to external current receipts. It indicates the extent of pre-emption of forex resources for the purposes of repayment of principal and interest on the stock of foreign debt.
- Comparing with other countries, India’s external debt is modest and stands at 23rd position globally.
- In terms of various debt vulnerability indicators, India’s sustainability was better than Low and Middle Income countries.
Topic: Infrastructure and Energy
7. India’s overall coal production increased to 58.33 million tonnes in August 2022.
- As compared to the overall coal production in Aug 2021, the total coal production in India has increased by 8.27%.
- According to the provisional statistics of Ministry of Coal, Coal India Limited and captive mines/ others have shown growth by producing 46.22 MT and 8.02 MT respectively.
- Out of the top 37 coal producing mines in India, 25 mines have produced more than 100% while the production level of 5 mines remained between 80 and 100%.
- The power utilities despatch has increased by 10.84% to 54.09 MT owing to rise in power demand.
- The overall electricity production in Aug 2022 has registered a growth of 3.14% as compared to that in Aug 2021.
- Coal based power generation has registered marginally negative growth of 0.3%.
- Status of Coal in India:
- Coal accounts for 55% of India’s energy demand.
- In India, coal has been mined since 1774. After China, India is the second largest producer and consumer of coal.
- Coal can be imported by consumers themselves freely under Open General License based on the commercial needs. Coking Coal is being imported by SAIL and other steel manufacturing companies.
- Non-coking coal is imported by coal based power plants, captive power plants, industrial consumers, coal traders, etc. Pig-iron manufacturers and iron and steel sector consumers using mini blast furnace mainly import coke.
- Coal India Limited (CIL) is the largest producer of Coal in India. Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL) is the main source for supply of coal to the southern region. Small quantities of coal are also produced by TISCO, IISCO, DVC and others.
- As per Geological Survey of India data, Jharkhand has the largest coal reserves followed by Odisha, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh.
Topic: Corporates/ Companies
8. Reliance Industries Limited will acquire majority stake in SenseHawk.
- RIL signed definitive agreements with SenseHawk to acquire majority stake in the company for $32 million including funding for future growth, commercial launch of products and R&D.
- SenseHawk was founded in 2018. It is California-based software based management tools developer for solar projects. Swarup Mavanoor is the CEO and Co-Founder of SenseHawk.
- RIL is committed to revolutionise the Green Energy sector and has a vision to enable 100 GW of solar energy by 2030.
Topic: Corporates/ Companies
9. Binance decided to convert USDC of users into its Stablecoin.
- Binance will convert existing user balances and new deposits of USD Coin (USDC), Pax Dollar (USDP) and True USD (TUSD) into its own stablecoin starting from 29 September 2022.
- The step is taken to enhance liquidity and capital efficiency for users.
- Binance is the largest cryptoexchange in terms of volume. Binance’s stable coin is the third ranked stablecoin with a market value of around $19.3 billion.
- After Tether, USDC is the second ranked stablecoin issued by Cricle Internet Financial.
- What is Stablecoin?
- Stablecoins are the cryptocurrencies whose market value is pegged or attached to another asset like fiat money, exchange-traded commodity, a cyptocurrency or financial instrument. These are designed to reduce volatility. These are open, global and accessible to anyone. These are fast, cheap and secure to transmit.
- Dai (DAI), Digix Gold Token (DGX), Havven’s Nomin, and Paxos Standard are the other examples of stablecoins.
Topic: Corporates/ Companies
10. CCI approved acquisition of Bill Desk by PayU India.
- Competition Commission of India has approved acquisition of BillDesk by Prosus-backed PayU India for $4.7 billion.
- This is the largest fintech combination ever approved by CCI.
- The deal was announced in August 2021. This approval will help PayU become a leading online payment providers globally in terms of payment volume.
- Indiaideas.com Limited is an unlisted company that uses name “BillDesk” for trading/business/brandname in India.
- PayU is a Netherlands based payment service provider. It was founded in 2002. PayU India was founded in 2014 and acquired Citrus Pay in 2016.
- In 2017, it launched LazyPay and acquired ZestMoney and PaySense. In 2018, PayU India got NBFC license for credit business. In 2019, the company acquired Wibmo, leading online authentication provider for card payments.
- PayU India operates across three businesses—payments for domestic and across border transactions, credit solutions for consumers and small businesses and strategic investments in fintech companies.




 Previous
Previous 
 Latest
Latest 








Comments