Summary of Economic Survey 2021- 2022
2022-02-04 | Priyanka Chaudhary

Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Economic Survey 2021-22 in Parliament on 1 February 2022.
The Agile approach is the central theme of the Economic Survey 2021-22. The art and science of policymaking in situations of extreme uncertainty is another theme covered in this Economic Survey.
This year, Economic Survey has been released in a single volume and there is a separate volume for the Statistical Appendix.
Who prepares Economic Survey?
Economic Survey has been prepared by the Department of Economic Affairs under Chief Economic Adviser.
The Economic Survey of India is an annual document released by the Ministry of Finance. The first Economic Survey in India was presented in 1950-51.
Key Points of Economic Survey 2021-2022
State of the Economy
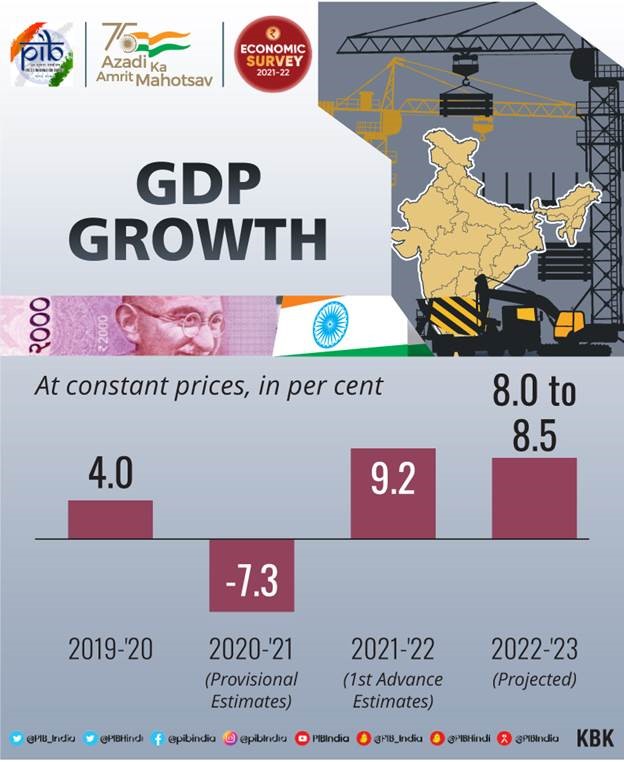
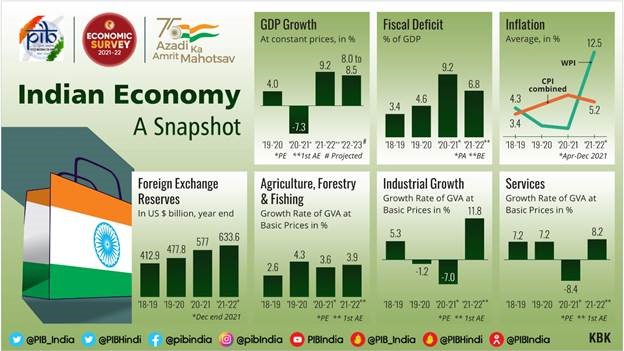
- GDP of India will grow by 8- 8.5 percent in real terms in 2022-23 and is estimated to grow by 9.2 percent in 2021-22.
- Indian Economy has contracted by 7.3 percent in 2020-21.
- In 2021-22, Export and import will grow by 16.5 percent and 29.4 percent respectively.
- Agriculture and allied sectors is expected to grow by 3.9 percent while the services sector will grow by 8.2%.
- Consumption will grow by 7.0 percent on the demand side and Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) grow by 15 percent.
- Macroeconomic stability indicators predict that the Indian Economy is ready to take the challenges of 2022-23.
- World Bank and Asian Development Bank’s latest forecasts of GDP growth are 8.7 percent and 7.5 percent respectively for 2022-23.
- IMF projected a GDP growth of 9 percent for 2021-22 and 7.1 percent for 2023-2024.
- High foreign exchange reserves, foreign direct investment, and export earnings will protect against possible global liquidity tapering in 2022-23.
(Source: PIB)
Fiscal Developments:
- During April to November 2021, Gross Tax Revenue has increased by 50 percent.
- The revenue receipts of the Central Government have also increased by 67.2%.
- In 2020-21, the Central Government debt has increased from 49.1 percent of GDP to 59.3 percent of GDP.
- Capex (Capital Expenditure) has grown by 13.5 percent during April-November 2021 with a focus on infrastructure-intensive sectors.
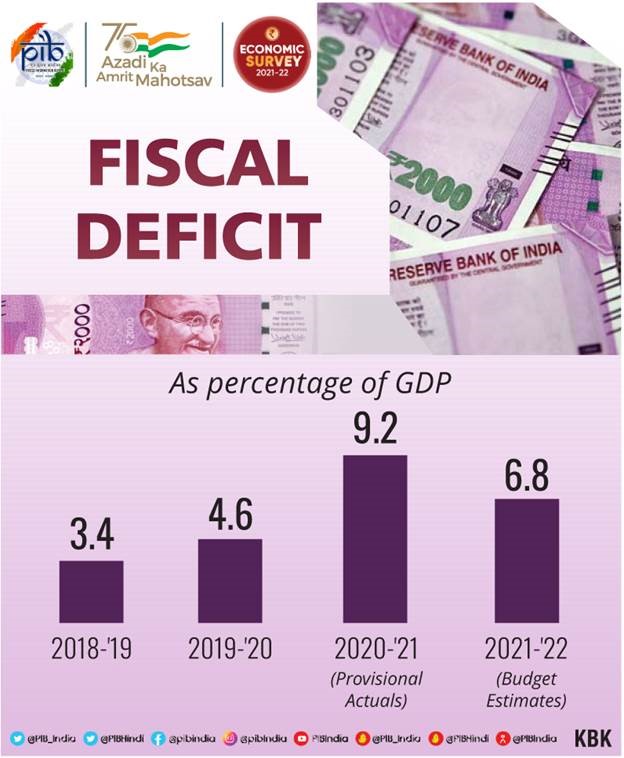
- Government is on course to achieve the fiscal deficit target of 6.8% of GDP for the current fiscal year.
(Source: PIB)
External Sectors:
- India’s external debt had reached US $ 593.1 billion by September 2021.
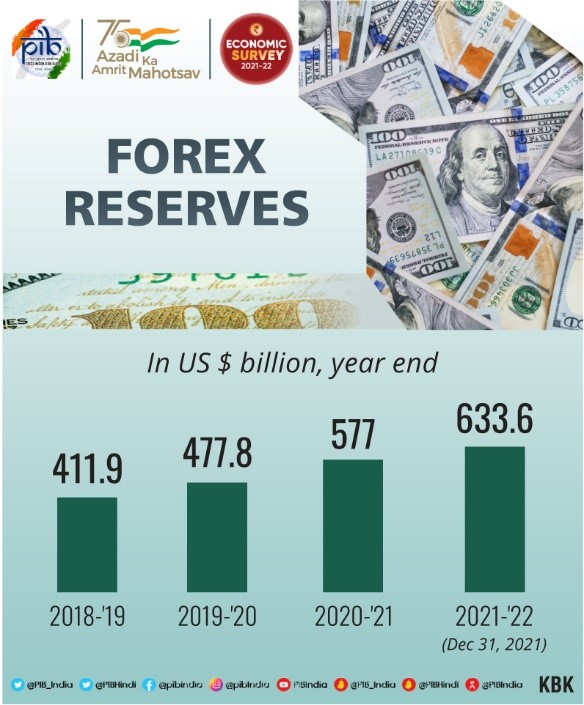
- Foreign Exchange Reserves touched the US $ 633.6 billion till 31 December 2021.
- In the first half of 2021-22, the Net capital flows reached US$ 65.6 billion.
- India has the fourth largest forex reserves after China, Japan, and Switzerland.
(Source: PIB)
Monetary Management and Financial Intermediation:
- In 2021-22, the Repo rate was maintained at 4 percent and the liquidity in the system remained in surplus.
- The Gross Non-Performing Advances ratio of Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) has declined from 11.2 percent to 6.9 percent.
- Net Non-Performing Advances ratio has also declined from 6 percent to 2.2 percent.
- Capital to risk-weighted asset ratio of Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) has increased from 13 percent in 2013-14 to 16.54 percent at the end of September 2021.
- During April-November 2021, Rs 89,066 crores has been raised through 75 Initial Public Offering (IPO).
Prices and Inflation:
- In 2021-22 (April to December), Food inflation averaged at a low of 2.9 percent. The decline in retail inflation was due to low food inflation.
- Effective supply-side management kept the prices of commodities under control.
- The average headline CPI-Combined inflation remain 5.2% in 2021-22 (April-December).
- The government has taken many proactive measures to contain the price of pulses and edible oils.
- Subsequent cuts in Value Added Tax by states and central excise helped in easing the price of petrol and diesel.
- Wholesale inflation rose to 12.5 percent during 2021-22. Low base in the previous year, Pick-up in economic activity, international prices of crude oil are the main factors of increased Wholesale inflation.
Sustainable Development and Climate Change:
- India’s overall score on the NITI Aayog SDG India Index and Dashboard has improved. It has reached 66 in 2020-21 from 60 in 2019-20. The number of front runners states has increased to 22.
- 39 districts of North East India were the Performers in the NITI Aayog North-Eastern Region District SDG Index 2021-22.
- The government had notified the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021 in August 2021.
- Effluent discharge has reduced from 349.13 million liters per day (MLD) in 2017 to 280.20 MLD in 2020.
- India ranked third globally in increasing its forest area during 2010 to 2020. India has the tenth largest forest area in the world.
Agriculture and Food Management:
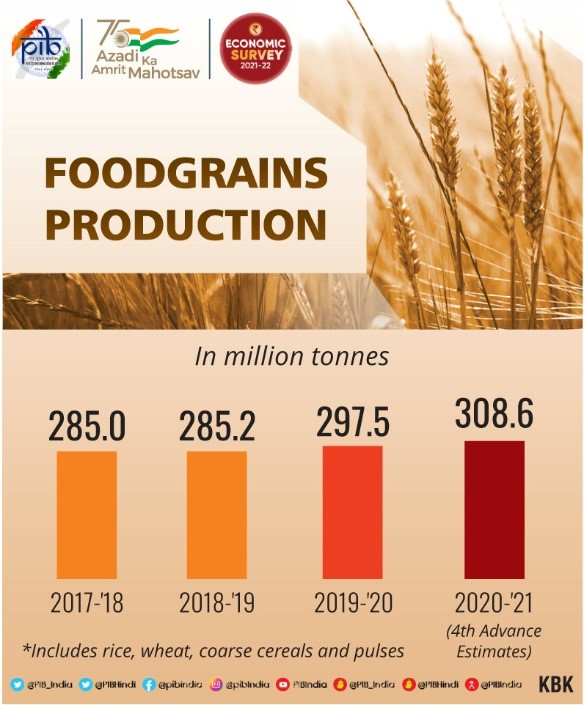
- In the last two years, the Agriculture sector has shown growth. Minimum Support Price (MSP) policy is used for promoting crop diversification.
- According to the latest Situation Assessment Survey (SAS), the Net receipts from crop production have increased by 22.6%.
- The Livestock sector has grown at a CAGR of 8.15% over the last five years. Livestock has become an important source of revenue for agricultural households.
- The government has extended the food security network through various schemes including PM Gareeb Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY).
- Government has supported food processing through infrastructure development, subsidized transportation and support to micro food enterprises.
- India is running one of the largest food management programmes in the world.
(Source: PIB)
Industry and Infrastructure:
- Index of Industrial Production (IIP) has grown by 17.4 percent as compared to last year.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme provided support to many industries for the speedy recovery.
- In 2020-21, the Capital expenditure of Indian railway has increased to Rs. 1,55,181 crores.
- Road construction per day has increased from 28 Kms per day in 2019-20 to 36.5 Kms per day in 2020-21.
Services:
- Services Sector GVA is expected to grow by 8.2 percent in 2021-22.
- The Service sector received over US$ 16.7 as FDI in the first half of 2021-22, which is around 54 percent of the total received FDI.
- Removing telecom regulations in IT-BPO sector and opening up of space sector to private players were the major reform by the government.
- India has become 3rd largest start-up ecosystem in the world after US and China.
- In India, the number of newly recognized start-ups has increased to over 14000 in 2021-22. 44 Indian start-ups become unicorns in 2021.
Social Infrastructure and Employment:
- Expenditure on social services by center and state has increased by 6.2 % in 2014-15 to 8.6% in 2021-22.
- According to the National Family Health Survey-5, the Total Fertility Rate (TFR) came down to 2 in 2019-21.
- Employment in the urban sector affected by pandemics has recovered almost to the pre-pandemic level.
- The adverse impact of COVID on the formalization of jobs was less during the second wave than the first COVID wave.
- 83 districts have become ‘Har Ghar Jal’ districts under the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM).
- The government has increased the allocation of funds to MNREGS to give employment to unorganized labour in rural areas.
(Source: PIB)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Summary of Economic Survey 2021- 2022
What is the central theme of the Economic Survey 2021-22?
What will be the GDP growth rate of India for fiscal year2022-23?
Which country has the largest forex reserves after China, Japan, and Switzerland in the world?
According to the economic survey, which country has become the 3rd largest start-up ecosystem in the world?
What is the fiscal deficit target of the government for the 2021-22 fiscal year?
Share Blog





Comments