Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
1. All India CPI-IW for June increased by 1.1 points.
- All India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (CPI-IW) for June increased by 1.1 points and stood at 121.7.
- It increased by 0.41 % when compared to June 2020. The increase in prices of food and beverages and fuel items is responsible for the rise in CPI-IW.
- Shillong recorded a maximum increase of 6.2 points. Indore recorded a maximum decrease of 1.1 points.
- The year-on-year inflation for June was at 5.57 %. It stood at 5.24 % for May and 5.06 % during June 2020.
- Food inflation was at 5.61 %. It stood at 5.26 % for May and 5.49 % for June 2020.
Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (CPI-IW):
CPI-IW is compiled by Labour bureau every month on the basis of retail prices collected from 317 markets of 88 industrially important centres.
It is released on the last working day of succeeding month. CPI-IW for the month of July 2021 will be released on 31st August 2021 (last working day).
Topic: Indian Economy/Financial Market
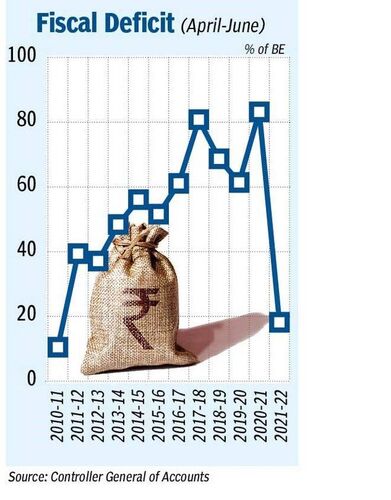
2. Finance Ministry reports a fiscal deficit of 18.2% of Budget Estimate for April-June quarter.
- Finance Ministry has reported a fiscal deficit of 18.2% of Budget Estimate (BE) for April-June quarter.
- This is the lowest since 2010-11. Centre’s receipts increased to more than ₹5.47-lakh crore, which is 27.7 % of the BE.
- The expenditure stood at over ₹8.21-lakh crore, which was 23.6 % of the BE.
- Net tax collection exceeded ₹4.12-lakh crore. Non-tax revenues stood ₹1.27-lakh crore.
- During April-June, revenue expenditure (such as subsidy, interest outgo, salary and pension) declined 2.4 %.
- The government had fixed a fiscal deficit target of ₹15.06-lakh crore (6.8 per cent of GDP) for FY22.
- Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government’s total income and total expenditure.
Topic: Banking System
3. Union Cabinet approves changes to deposit insurance laws.
- Union Cabinet has approved changes to deposit insurance laws to provide funds up to Rs 5 lakh to an account holder within 90 days of the bank being put under moratorium.
- Till now, account holders used to wait for a year till liquidation or restructuring of distressed banks to get their deposits.
- Government has also given permission to raising of the deposit insurance premium by 20 % immediately, and maximum by 50%.
- Banks pay a minimum of 10 paise on every Rs 100 worth of deposits to the DICGC as premium for the insurance cover. This has now been raised to a minimum of 12 paise.
- Government has a plan to introduce the Deposit Insurance & Credit Guarantee Corporation (Amendment) Bill 2021 in the current session of Parliament.
- The proposed law will be implemented prospectively and not retrospectively. However, it will cover banks already under moratorium.
- DICGC would collect all information about deposit accounts within the first 45 days of the bank being put under moratorium. In the next 45 days, the information will be reviewed and depositors will be repaid.
- A depositor can claim up to a maximum of Rs 5 lakh per account as insurance cover even if the deposit in their account far exceeds Rs 5 lakh.
Deposit Insurance & Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC):
It is a fully owned subsidiary of RBI. It was established in July 1978 under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961.
It insures deposits in public and private sector banks, local area banks, small finance banks, regional rural banks, cooperative banks, Indian branches of foreign banks and payments banks.
Topic: MoUs/Agreements
4. Cabinet approves multilateral MoU signed between international finance services agencies.
- Cabinet has approved multilateral MoU signed between IFSCA, International Organisation of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) and International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS).
- It is one of the biggest multilateral forums with several regulators and has 124 signatories.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said that India’s joining this forum will enable exchange of information and ease of doing business for those registering themselves in GIFT City.
- GIFT City at Gandhinagar is India's first operational smart city and International Financial Services Centre (IFSC).
- International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) is a unified regulator of financial products, financial services and financial institutions in the international financial services centres in India.
International Organisation of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) is an association of organizations regulating world's securities and futures markets. It is headquartered in Madrid, Spain.
International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) is a voluntary membership organization of insurance supervisors. It is headquartered in Basel, Switzerland.
Topic: Corporates/Companies
5. Union Cabinet approves amendments to Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008.
- Union Cabinet has approved amendments to Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act 2008 to bring Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) on level playing field with large corporates.
- The amendments propose to decriminalize 12 offences under existing LLP law.
- Once proposed amendments to LLP Act 2008 come into effect, the number of compoundable offences will decrease from 21 to 7 and total number of penal provisions will decrease to 22.
- Government has for the first time proposed amendments to LLP Act since its enactment in 2008.
- The amendments are being proposed on the basis of the recommendations of the Ministry Corporate Affairs-appointed Company Law Committee.
Topic: Indian Economy
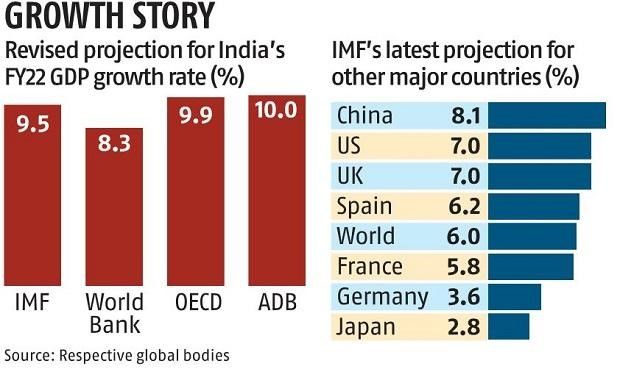
6. IMF slashed India's economic growth forecast for FY22 to 9.5%.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has reduced India’s economic growth projection by 300 basis points to 9.5% for the financial year 2022 from 12.5%.
- However, IMF has projected India's economy to grow at 8.5 percent in 2023.
- The global growth forecast remained unchanged at 6% for the financial year 2021.
- It has also projected the global economy to grow by 4.9% in 2022. China’s growth forecast has been cut by 0.3%.
- According to the IMF, the growth prospects in emerging markets and developing economies will remain low for the year 2021.
- The World Bank projected India's economy to grow at 8.3 percent in 2021 and 7.5 percent in 2022.
Topic: Miscellaneous
7. Finance Minister introduced a bill in the Lok Sabha to sell a part of government's stake in public sector general insurance companies.
- Finance Minister has introduced a bill in the Lok Sabha to sell a part of the government's stake in public sector general insurance companies.
- The bill will amend General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, 1972. It removes a clause that requires the government to hold at least 51 % of equity capital in an insurer.
- The bill will insert a new Section 24 B, which provides for the Act’s application to a specific insurer to stop as soon as government stops having control of insurer.
- The bill makes the director of the insurer, who is not a whole-time director, liable for any acts of omission or commission committed with his knowledge and consent.
- The bill contains a new section to make the director liable for acting in connivance or for not practicing his/her duties diligently.
- General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, 1972 was last time amended in 2002.
- Currently, there are four public sector general insurance companies in India. Their names are given below.
- National Insurance Company Limited
- New India Assurance Company Limited
- Oriental Insurance Company Limited
- United India Insurance Company Limited
- General insurance business in India was nationalized with effect from 1st January, 1973 after the passing General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act in 1972. !07 insurers were grouped into four companies.
Topic: RBI
8. RBI decides to align provisions for HFCs relating to the rating of deposits taken by them with provisions for NBFCs.
- RBI has decided to align provisions for Housing Finance Companies (HFCs) relating to the rating of deposits taken by them with provisions for NBFCs.
- As a result, RBI has approved seven Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs) and their respective minimum investment-grade credit rating.
- The names of seven CRAs are Crisil, ICRA, CARE Ratings, Fitch Ratings India Pvt Ltd, Brickwork Ratings, Acuite Ratings & Research and Infomerics Valuation and Rating.
- For example, a HFC’s fixed deposit programme should have a minimum investment-grade credit rating of ‘FA-’ from Crisil or ‘MA–’ from ICRA or ‘BBB’ from CARE Ratings.
Topic: RBI
9. RBI allows authorised non-bank Payment System Providers (PSPs) to take part in RTGS and NEFT in the first phase.
- RBI has allowed authorised non-bank Payment System Providers (PSPs) to take part in RBI-operated Centralised Payment Systems (CPS) like RTGS and NEFT in the first phase.
- Authorised non-bank Payment System Providers (PSPs) include PPI Issuers, Card Networks and White Label ATM Operators.
- Non-banks getting direct access to CPS will be allotted a separate Indian Financial System Code (IFSC).
- They can open a Current Account with the Reserve Bank in its core banking system (e-Kuber) and maintain a settlement account with RBI. They will get membership of Indian Financial Network (INFINET).
- Non-bank PSPs would require a valid certificate of authentication by the RBI under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 and net worth of at least ₹25 crore.
Centralised Payment Systems (CPS):
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) and National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) are Centralised Payment Systems (CPS) in India.
They are both owned and operated by Reserve Bank. They were made available 24x7x365 with effect from December 2019 and December 2020 respectively.
Topic: RBI
10. RBI announces Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI) for March 2021.
- RBI has announced Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI) for March 2021.
- Reserve Bank of India–Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI) for March 2021 increased to 270.59 from 207.84 for March 2020.
- As per RBI, the index has shown significant growth representing the rapid adoption and deepening of digital payments across the country.
- RBI-DPI:
- It aims to capture the extent of digitisation of payments across the country. It has March 2018 as a base.
- It was launched on January 1, 2021. It comprises of five broad parameters given below.
- Payment enablers
- Payment infrastructure – demand side factors
- Payment infrastructure – supply-side factors
- Payment performance
- Consumer centricity


 Previous
Previous 
 Latest
Latest 








Comments