Daily Current Affairs and GK | 29 October 2020

Main Headlines:
- 1. Government notified new land laws for Jammu and Kashmir, removed ‘permanent resident’ as criteria.
- 2. IAEA: Iran building an Underground nuclear facility.
- 3. President issued an ordinance for setting up Commission to manage Air Quality in NCR & adjoining areas.
- 4. Foreign secretary started his 7-day visit to France, Germany, UK.
- 5. ASER Survey: 20% of rural school children had no textbooks due to COVID-19.
- 6. Government releases Consolidated FDI Policy circular of 2020.
- 7. India and UK sign agreements at 10th India-UK Economic and Financial Dialogue.
- 8. ‘Electricity Access in India and Benchmarking Distribution Utilities’ report released
- 9. 19th meet of SCO ministers of Foreign Economy and Foreign Trade has been hosted by India.
- 10. CIC issues notices to Central Public Information Officers of MeitY, NIC and NeGD.
Happy February get 35% Off
Use Coupon code FEB26
1. Government notified new land laws for Jammu and Kashmir, removed ‘permanent resident’ as criteria.
- Ministry of Home Affairs has notified new land rules for Jammu and Kashmir. It has removed the permanent resident criteria for buying land.
- These new laws will be called the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Adaptation of Central Laws) Third Order, 2020.
- The notification has omitted the ‘permanent resident’ criteria from section 17 of the Jammu and Kashmir Development Act.
- Now, people and investors outside the state can buy the land in Jammu and Kashmir. It will stimulate development in the state.
- Government has allowed the transfer of land in favour of a person or an institution for the development of healthcare and educational infrastructure.
- The Central government will also bring new separate land laws for the Ladakh.
- Under the new notification, a “strategic area” within a local area cannot be declared by below the rank of Corps Commander.
- It has repealed 12 state laws and modified 26 laws of the state.
- It has completely repealed the J&K Alienation of Land Act, 1995, the J&K Big Land Estates Act and the J&K Common Lands (Regulation) Act, 1956 and the J&K Consolidation of Holdings Act, 1962.
- According to the new amendment in “The Jammu & Kashmir Land Revenue Act, 1996”, only agriculturists of J&K can purchase agricultural land. No transfer of land will be allowed in favour of a person who is not an agriculturist.
- Jammu & Kashmir:
- On 31 October 2019, Jammu and Kashmir was reorganized into Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union Territory of Ladakh.
- Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir is located to the north of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab.
- Its winter capital is Jammu and summer capital is Srinagar.
- Lieutenant Governor: Manoj Sinha
2. IAEA: Iran building an Underground nuclear facility.
- IAEA, the United Nations’ atomic watchdog, has confirmed that Iran has started building an underground nuclear facility.
- According to IAEA, Iran has stockpiled low-enriched Uranium, but it doesn’t appear to possess enough to produce a nuclear weapon.
- Iran had a nuclear facility at Natanz, but it got destroyed in July. After that, Iran stated it would build a more secure nuclear facility around Natanz.
- In 2002 satellites showed an underground facility at Natanz. IAEA visited it in 2003 and found an underground centrifuges nuclear facility.
- In 2015 a landmark deal was agreed between Iran and world powers are known as the P5+1 for a joint Comprehensive Plan of Action. It had allowed Iran to produce a certain amount of uranium.
- According to the IAEA report, Iran has stockpiled 2105 kilograms of low-enriched uranium. It is well above the limit decided in the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action.
- IAEA also stated that Iran doesn’t possess that amount of uranium to produce a bomb.
- Iran is located in Western Asia. Its capital and largest city is Tehran. Its President is Hassan Rouhani.
- Iran’s Nuclear Deal:
- Iran’s nuclear deal, also known as Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), was signed in July 2015.
- The deal was signed between Iran and P5+1+ EU i.e. five permanent members of UNSC viz. China, USA, Britain, France, Russia + Germany + European Union.
- Recently, the USA has withdrawn from the treaty.
3. President issued an ordinance for setting up Commission to manage Air Quality in NCR & adjoining areas.
- President has signed an ordinance brought by the government for setting up a commission to manage air quality in NCR & adjoining areas.
- The commission will be chaired by a government official equivalent to the rank of Secretary or Chief Secretary, and it will also include a representative from the Ministry of Environment, members from the state of Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan and technical experts from Central Pollution Control Board and ISRO.
- It will help in better coordination among institutions, research and identify problems in improving the air quality in NCR regions.
- It will have all the powers to make any decision to improve the air quality in the National Capital Region and adjoining areas.
- It can also decide the parameters for emission or discharge of pollutants from different sources.
- This commission will be divided into three sub-committees to curb air pollution in the region. Three committees are:
- Committee on Monitoring and identification
- Committee on Safeguarding and Enforcement
- Committee on Research and Development
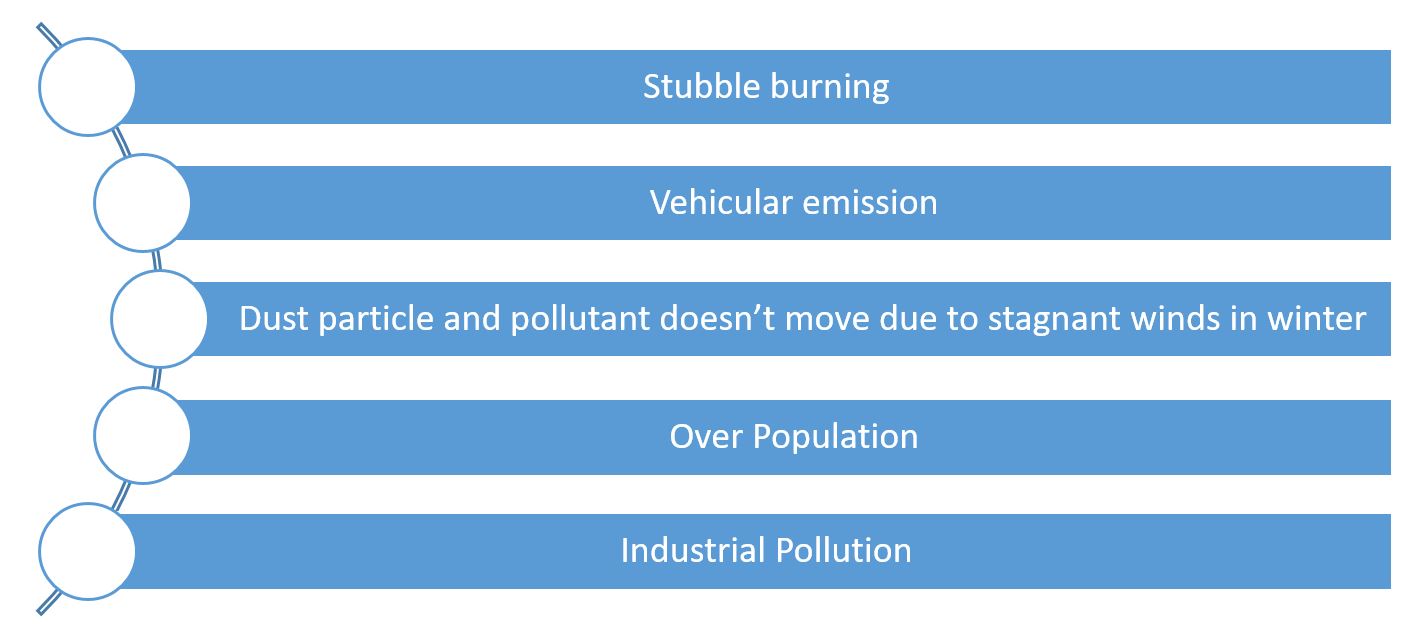
- Reason for the Air pollution problem in NCR & adjoining areas:
- Stubble burning
- Vehicular emission
- Dust particle and pollutant doesn’t move due to stagnant winds in winter
- Over Population
- Industrial Pollution
4. Foreign secretary started his 7-day visit to France, Germany, UK.
- Foreign secretary Harsh Vardhan Shringla has started his seven-day visit to France, Germany and the United Kingdom.
- The visit will start from 29 October and will continue till November 4.
- In this visit, he will discuss many issues, which include the latest development on the border standoff with China, cooperation in dealing with Covid-19, matters of mutual interest and review bilateral relations.
- He will meet with business persons, academics, intellectuals and media persons in these three countries.
- Indian government stated that France, Germany and the UK are strategic partners and India has close and well-established relations with them.
- India has established trade and commercial ties with these countries and works with them on many platforms.
- Issues of robust and reformed multilateralism and open and inclusive Indo-Pacific will also be discussed in the visit.
- France:
- It is a Western European country.
- Capital: Paris
- President of France: Emmanuel Macron
- Prime Minister: Jean Castex
- Currency of France: Euro
- Germany: It is located in the central and western region of Europe. Its capital and largest city is Berlin.
- United Kingdom: It is a group of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland nations. It is located in northwestern Europe. Its capital is London and the currency is Pound sterling.

(Source: PIB)
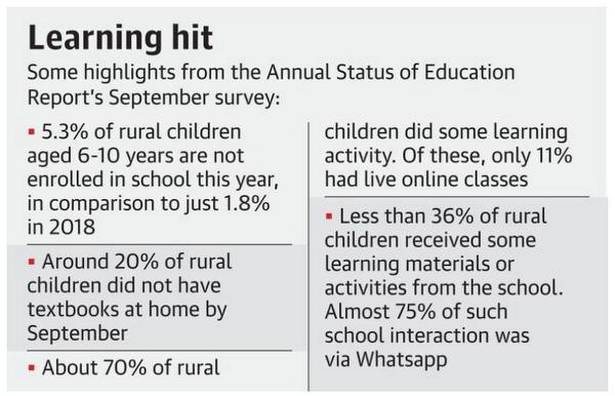
5. ASER Survey: 20% of rural school children had no textbooks due to COVID-19.
- According to the Annual State of Education Report (ASER) survey, around 20% of the rural children do not have textbooks at home due to the impact of COVID-19 pandemic.
- Due to COVID-19 and subsequent lockdown, schools remained closed for more than six months across the country.
- The survey was conducted in September and about one in three rural children had done no learning activity at all in the survey week.
- Although the number of smartphones has doubled from 2018, 1/3rd of children with access to smartphones did not get any learning materials.
- The schools have been permitted to reopen if they follow safety measures.
- The survey highlights the learning loss of rural students with different levels of access to technology, school and family resources that are leading to the digital divide in education.
- ASER is a nationwide survey conducted by the NGO Pratham of rural education and learning outcomes in reading and arithmetic skills.
(Source: The Hindu)
6. Government releases Consolidated FDI Policy circular of 2020.
- FDI Division of Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has released the Consolidated FDI Policy circular of 2020.
- Consolidated FDI Policy circular of 2020 has become effective from October 15, 2020.
- Before the Consolidated FDI Policy circular of 2020, the Consolidated FDI Policy circular was released in 2017.
- Consolidated FDI Policy circular of 2020 is a single document that provides all the FDI policy decisions taken by the government.
- The circular includes restrictions applied by the government on investments from land boundary sharing countries in April 2020.
- Government has also permitted a maximum of 26% FDI through government approval route in uploading or streaming news and current affairs through digital media.
- Persons who are resident outside India can make the foreign investment either through Foreign Direct Investment or Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI). FDI is a source of non-debt financial resources.
- FDI means investment by residents outside India through shares, bonds, etc. in an unlisted Indian company.
- FDI also means investment by residents outside India in 10% or more of post-issue paid-up equity capital (paid-up share capital after issuance of shares) of a listed Indian company.
7. India and UK sign agreements at 10th India-UK Economic and Financial Dialogue.
- India and UK have signed agreements on financial services, infrastructure and sustainable finance at 10th India-UK Economic and Financial Dialogue.
- Agreements include a new strategic partnership for faster development of Gujarat International Finance Tech (GIFT) City in the form of an international financial centre.
- The agreements also include support for developing the regulatory capacity of International Financial Services Centre Authority, a statutory body under the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance.
- Two countries also agreed to establish a new UK-India Sustainable Finance Forum, new Financial Markets Dialogue and new UK-India Partnership on Infrastructure Policy and Financing to support the Indian National Infrastructure Pipeline.
- India has allowed Indian companies to directly list on the London Stock Exchange.
- SIDBI and the UK Government supported UK-India Fast Track Start-up Fund will fund early-stage tech start-ups.
- UK will be the president of G7 in 2021. Along with Italy, it will jointly host COP26 in November 2021. India will be the president of G20 in 2022.
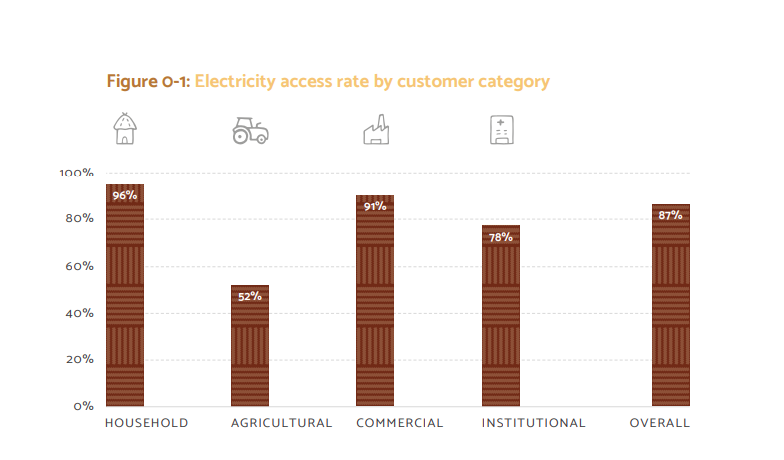
8. ‘Electricity Access in India and Benchmarking Distribution Utilities’ report released
- ‘Electricity Access in India and Benchmarking Distribution Utilities’ report has been launched by the NITI Aayog, the Ministry of Power, Rockefeller Foundation and Smart Power India.
- Highlights of the report:
- This report is based on a survey conducted in ten states, representing about 65% of the rural population of India.
- The Sample size of the survey is more than 25,000, it includes households, commercial enterprises and institutions.
- 92% people have access to electricity infrastructure within 50 meters of their premises.
- 87% people have access to grid-based electricity.
- Nearly 85% of customers reported to have a metered electricity connection.
- Average electricity supply is about 17 hours per day.
- Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana and Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana had played a significant role in improving the accessibility of electricity.
- This report has recommended some measures in the areas of policy and regulation, infrastructure development, sustainable electricity accessibility, etc.
- Recommendations of the report:
- Revamp new electricity connection process
- Direct Benefit Transfer implementation for electricity subsidies to consumers
- Enable capacity building of regulatory commissions to resolve utility viability challenges on account of widening cost coverage.
- Digitalize the metering, billing, and collection (MBC) cycle through the implementation of smart metering and demand-side management measures
- Enable technology for system-led reporting and decision-making for regulatory filings and reporting on Standards of Performance.
(Source: Electricity access in India report)
9. 19th meet of SCO ministers of Foreign Economy and Foreign Trade has been hosted by India.
- India hosted the 19th Meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Ministers responsible for Foreign Economy and Foreign Trade Activities.
- It was attended by the Secretary-General of SCO and Ministers from Kyrgyz Republic, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
- India stated that intra SCO trade and investment would help in the speedy recovery from the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- In the meeting, four documents were adopted. These are:
- Statement of Cooperation in the response of COVID-19 pandemic: It will focus on the cooperation for access to medicines and facilitation of trade.
- Statement on Cooperation on Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): It will help in sharing information and experience related to IPR, cooperation in international organizations and other areas.
- Statement on the Multilateral Trading System of Ministers of SCO Countries who are WTO Members.
- Action Plan for Implementation of MOU to stimulate cooperation within the framework of SCO in the field of MSMEs.
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO):
- Its creation was announced in 2001 by leaders of six nations.
- Currently, it has eight members as India and Pakistan joined it in June 2017.
- Other six members are China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- It is headquartered in Beijing, China.
10. CIC issues notices to Central Public Information Officers of MeitY, NIC and NeGD.
- Central Information Commission (CIC) has issued notices to Central Public Information Officers (CPIOs) of Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), National Informatics Centre (NIC) and National E-Governance Division (NeGD).
- CIC issued notices to CPIOs of MeitY, NIC and NeGD as they did not provide information about creation of Aarogya Setu app.
- The complainant has sought information about the laws under which Aarogya Setu was created and is handled.
- CIC ordered CPIOs of MeitY, NIC and NeGD to appear on November 24.
- Section 20 of the RTI Act, 2005 provides for penalties if CPIOs do not provide information within the specified time.
- Aarogya Setu app: Government has launched Aarogya Setu app on April 2. NIC under MeitY has developed it. It is available in 11 languages.
- Central Information Commission (CIC):
- CIC is a statutory body that was constituted under the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- It includes the Chief Information Commissioner and not more than 10 Information Commissioners. They are appointed by the President.
- The first Chief Information Commissioner of India was Wajahat Habibullah.
- Last CIC: Bimal Julka





 28 October 2020 Current Affairs
28 October 2020 Current Affairs 








Comments