Daily Current Affairs and GK | 3 April 2025

Main Headlines:
- 1. 4,991 villages were declared as Adarsh Gram under the PM-Ajay scheme in 2024-25.
- 2. The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 has been taken up by Rajya Sabha for consideration and passing.
- 3. The Ministry of Coal achieved record breaking growth in production and dispatch for FY 2024-25.
- 4. DoT strengthened anti-spam measures to curb unsolicited commercial communications (UCC) through Jan Bhagidari.
- 5. India signed a project sanction order for design and development of 6 MW Medium Speed Marine Diesel Engine in New Delhi.
- 6. Odisha topped the Fiscal Health Index launched by NITI Aayog.
- 7. The second edition of Startup Mahakumbh at Bharat Mandapam inaugurated by Union Commerce and Industry Minister Shri Piyush Goyal.
- 8. On 2 April 2025, India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completed three years of its signing.
- 9. As per Copernicus Climate Change Service report, January 2025 was the hottest month on record.
- 10. Measures taken by government of India for digital infrastructure upgradation in villages.
Happy February get 35% Off
Use Coupon code FEB26
Topic: Government Schemes and Initiatives
1. 4,991 villages were declared as Adarsh Gram under the PM-Ajay scheme in 2024-25.
- Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY) is a centrally sponsored scheme launched in 2021-22 to improve the socio-economic conditions of SC communities.
- The scheme has three components: (i) Adarsh Gram (ii) Grant-in-aid for district/State level projects for socio-economic development of Scheduled Caste (SC) communities and (iii) Hostels.
- In the year 2021-22, the earlier Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (launched in 2009–10) was subsumed under the Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY).
- From 2018-19 till now, 29,847 villages have been selected, out of which 11,076 villages have been declared as Adarsh Gram.
- In 2024-25, 4,991 villages have been declared as Adarsh Gram.
- Villages where more than 40% of the Scheduled Caste people live and the total population is 500 or more are eligible to come under this scheme.
- Skill development is an intervention included in the grant-in-aid component of the scheme.
- 25 states have submitted perspective plans for 2023-24, 2024-25, and 2025-26 and Rs 457.82 crore has been released for 8146 projects, including 987 projects for skill development during 2023-24 and 2024-25 under the grant-in-aid component.
- The objective of the hostel component is to promote participation of SC students in the curriculum by providing adequate residential facilities in quality institutions and through residential schools as per the need.
- It is also to encourage enrolment in schools and higher educational institutions.
- So far, 891 hostels have been approved under PM-Ajay Yojana, out of which 27 hostels have been approved in 2024-25.
Topic: Indian Polity
2. The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 has been taken up by Rajya Sabha for consideration and passing.
- The Bill aims to modernise the immigration laws in India.
- It grants the Central Government authority over passports, travel documents, visas, and registration.
- Nityanand Rai, the Minister of State for Home, introduced the Bill in the Rajya Sabha.
- The Bill has already been passed by the Lok Sabha on 27 March 2025.
- It creates a framework to monitor foreigners entering and leaving India in real time.
- The Bill requires carriers, institutions, and service providers to share detailed information with immigration authorities.
- Clause 3(3) gives immigration officers the authority to inspect travel documents at various stages of a foreigner’s stay in India. This includes entry, transit, and stay.
- Clause 3(5) places full control over visa-related matters with the central government.
- Transport providers must share real-time passenger details for air, sea, and land travel.
- Clause 17(7) allows district magistrates and police commissioners to request additional information about passengers or crew from carriers.
- Clause 17(12) prevents carriers from departing without immigration clearance.
- Accommodation providers must report the presence of foreign guests to local authorities under Clause 8(1).
- Clause 9 mandates that universities and educational institutions report foreign students to authorities.
- Clause 10 extends this obligation to hospitals and medical facilities, which must notify authorities when a foreigner is admitted for treatment.
- The Bill introduces tougher penalties for using forged documents or overstaying visas.
- Penalties include up to seven years in jail and fines up to Rs 10 lakh.
- There are also penalties for entering restricted areas without valid documents.
- Such violations could result in up to five years in jail or fines of up to Rs 5 lakh.
- The Bill proposes repealing four existing laws, including the Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920.
- The Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939, the Foreigners Act, 1946, and Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act, 2000 will also be repealed.
Topic: Reports and Indices
3. The Ministry of Coal achieved record breaking growth in production and dispatch for FY 2024-25.
- The Ministry of Coal reported that it has achieved a historic breakthrough, setting new records in captive and commercial coal production and dispatch for the financial year 2024-25.
- Total coal production increased to 190.95 million tonnes (MT) by 31 March 2025.
- This has registered a significant increase of 29.79% over last year's 147.11 MT.
- There has also been an exceptional growth in coal dispatch.
- It reached 190.42 MT, which is 33.36% higher than the 142.79 MT recorded in FY 2023-24.
- These excellent numbers reflect the sector's resilience, efficiency, and vital role in meeting India's energy needs.
- It drives industries such as power, steel, and cement.
- Captive mines recorded a growth of 24.72% in production and 27.76% in dispatch over last year, ensuring a stable coal supply to core industries.
- Commercial mines demonstrated remarkable progress, with production increasing by 67.32% and dispatch increasing by 76.71% over the previous year, reflecting the rapid expansion and efficiency of India's coal sector.
- List of important Coal Mines in India:
|
Name of Coal Mine / Block |
State |
|
|
1 |
Choritand Tiliaya |
Jharkhand |
|
2 |
Jogeshwar & Khas Jogeshwar |
Jharkhand |
|
3 |
Rohne |
Jharkhand |
|
4 |
Rabodih OCP |
Jharkhand |
|
5 |
Urtan North |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
6 |
North of Arkhapal Srirampur |
Odisha |
Topic: National news
4. DoT strengthened anti-spam measures to curb unsolicited commercial communications (UCC) through Jan Bhagidari.
- In a major step to curb spam calls and cyber fraud, DoT has disconnected approximately 1.75 lakh Direct Inward Dialing (DID)/landline telephone numbers.
- These numbers were identified as being misused for unauthorized promotional and illegal activities.
- A significant rise in spam calls has been detected, originating from telecom identifiers such as 0731, 079, and 080.
- These calls exploit PRIs, lease lines, Internet lease lines, SIP, and IPLC for unauthorized activities.
- Under Jan Bhagidari, citizens are reporting such cases of unsolicited commercial communication (UCC)/spam/fraud calls on the Chakshu module of Sanchar Saathi.
- The DoT has advised Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) to enforce strict adherence to Unified License conditions.
- They are required to prevent the misuse of PRIs, SIP trunks, Lease Lines, Internet Lease Lines, and IPLC, ensuring their proper and authorized usage.
- Handling of cyber-crimes in India:
- Cybercrime-related matters fall under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), as per the allocation of business rules.
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) actively works to prevent the misuse of telecom resources in cyber fraud activities.
- Additionally, under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India, 'Police' and 'Public Order' are classified as State subjects, making state governments responsible for maintaining law and order.
- To strengthen cybercrime enforcement, the MHA has established the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) as an attached office.
- This center provides a structured framework and support system for Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) to address cyber-related offenses effectively.
- Furthermore, the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal (NCRP) has been launched by the MHA, allowing various types of cybercrimes to be reported by citizens through a centralized platform.
Topic: Defence
5. India signed a project sanction order for design and development of 6 MW Medium Speed Marine Diesel Engine in New Delhi.
- On 2 April, the Indian Navy and Kirloskar Oil Engines Limited have inked a Project Sanction Order under the Make-I category for the design and development of a 6MW Medium Speed Marine Diesel Engine.
- This prototype diesel engine will be developed at a cost of Rs 270 crore, with more than 50% indigenous content used and 70% funded by the Government of India.
- The contract also includes detailed design development for a 3-10 MW diesel engine.
- The developed engines will be used for main propulsion and power generation on ships of the Indian Navy and Indian Coast Guard.
- Most of the high-capacity diesel engines were till now being imported from foreign Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
- This project will initiate the process of achieving Aatmanirbharta in marine engine development in the country.
Topic: Report and Indices
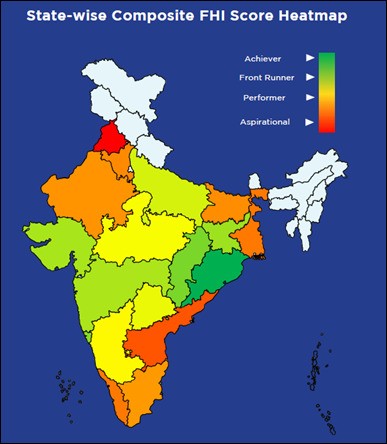
6. Odisha topped the Fiscal Health Index launched by NITI Aayog.
- NITI Aayog developed the Fiscal Health Index (FHI) initiative to improve the understanding of states' fiscal health in India.
- The FHI analysis covers eighteen major states that drive the Indian economy in terms of their contribution to India’s GDP, demography, total public expenditure, revenues, and overall fiscal stability.
- Odisha topped the index, followed by Chhattisgarh, Goa, Jharkhand, and Gujarat.
- Since states are responsible for approximately two-thirds of public expenditure and one-third of total revenue, their fiscal performance is critical to the overall economic stability of the country.
- NITI Aayog developed the Composite Fiscal Health Index using data from the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) for the financial year 2022-23.
- The objective of the Fiscal Health Index is to provide a comparative analysis of the fiscal health of Indian states using standardized metrics, thereby identifying both strengths and concerns in their fiscal management practices.
- It also aims to promote transparency, accountability and prudent fiscal management and enable policymakers to make informed decisions to enhance fiscal sustainability and resilience.
- The Fiscal Health Index 2025 is based on a comprehensive set of indicators, grouped into five broad categories:
- Revenue Generation and Mobilization
- Expenditure Management and Prioritization
- Debt Management
- Fiscal Deficit Management
- Overall Fiscal Sustainability
- List of Fiscal Health Index 2025:
|
Achiever |
Front Runner |
Performer |
Aspirational |
|
Odisha (1) |
Maharashtra (6) |
Tamil Nadu (11) |
Kerala (15) |
|
Chhattisgarh (2) |
Uttar Pradesh (7) |
Rajasthan (12) |
West Bengal (16) |
|
Goa (3) |
Telangana (8) |
Bihar (13) |
Andhra Pradesh (17) |
|
Jharkhand (4) |
Madhya Pradesh (9) |
Haryana (14) |
Punjab (18) |
|
Gujarat (5) |
Karnataka (10) |
(Source: News on AIR)
Topic: National News
7. The second edition of Startup Mahakumbh at Bharat Mandapam inaugurated by Union Commerce and Industry Minister Shri Piyush Goyal.
- It will continue from April 3-5, 2025 and aims to boost India's economic growth.
- Shri Jitin Prasada, Minister of State, delivered a special address during the inauguration.
- Startup Mahakumbh is a platform for entrepreneurs, investors, and thought leaders.
- More than 45 tribal entrepreneurs are taking part in it. It features representation from over 50 countries.
- Its focal theme is 'Startup India @ 2047—Unfolding the Bharat Story'.
- A made-in-India flying taxi will be on display at the event.
- Nepal will have the largest pavilion at Startup Mahakumbh.
- It will show a two-stage rocket powered by sustainable hybrid propulsion.
- Startup Mahakumbh is organized by FICCI, ASSOCHAM, Indian Venture and Alternate Capital Association, and Bootstrap Advisory & Foundation.
- The event is supported by SIDBI, GEM, ECGC, Meity, and DPIIT Startup India.
Topic: MoUs/Agreements
8. On 2 April 2025, India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completed three years of its signing.
- The agreement was signed on April 2, 2022. It has significantly strengthened the economic relationship between India and Australia.
- The ECTA has benefited businesses, entrepreneurs, and created jobs in both nations.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 24 billion in 2023-24.
- India’s exports to Australia grew by 14% compared to the previous year.
- From April 2024 to February 2025, exports grew by 4.4% compared to the same period in 2023.
- The ECTA has delivered benefits in sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and agriculture.
- Exports of products such as Calcined Petroleum Coke, High-Capacity Diesel Generating Sets, and Air Liquefaction Machinery show grown trade opportunities.
- India-Australia diplomatic relations:
- India and Australia established diplomatic relations with setting up of India Trade Office in Sydney in 1941.
- Bilateral relationship between India and Australia was upgraded from ‘Strategic Partnership’ in 2009 to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) in 2020.
- 1st India-Australia Annual Summit was held in New Delhi on 10 March 2023.
- India is Australia’s sixth largest trading partner. Bilateral trade between two nations grew from US$ 22.2 billion in 2021 to US$ 31.4 billion in 2022.
Topic: Environment and Ecology
9. As per Copernicus Climate Change Service report, January 2025 was the hottest month on record.
- Global surface temperatures during January 2025 were 0.79°C above the 1991-2020 average.
- In India, the average temperature was the second highest since 1901.
- It was 0.98°C higher than the 1991-2020 average.
- The primary cause of these higher temperatures is global warming.
- Global warming is closely linked to climate change and driven by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels.
- Burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Greenhouse gases trap heat, leading to an increase in the Earth's temperature.
- Typically, La Niña years bring above-average rainfall to the Indian summer monsoon.
- Currently, neutral El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) conditions are present in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- The eastern and far western Pacific Ocean have higher-than-average sea surface temperatures.
- The central Pacific Ocean has cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures.
- As per forecasts, neutral ENSO conditions will continue through the 2025 southwest monsoon season.
- No La Niña impact is expected on the Indian monsoon in 2025.
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) will release the initial seasonal rainfall forecast for the 2025 Southwest monsoon by mid-April.
- IMD tracks global Sea Surface Temperature (SST) changes, especially in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- IMD uses the Monsoon Mission Climate Forecasting System (MMCFS) to generate forecasts.
- It releases monthly ENSO/Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) reports.
- IMD provides monthly and seasonal outlooks for rainfall and temperature.
- IMD also offers agriculture-specific advisories to help farmers prepare for extreme weather conditions related to El Niño and La Niña.
Topic: Government Schemes and Initiatives
10. Measures taken by government of India for digital infrastructure upgradation in villages.
- The BharatNet project is being implemented for broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats (GPs) and villages beyond GPs on demand basis.
- The amended BharatNet program, approved in August 2023, is improving the current network.
- It also promotes the use of the network through BharatNet Udyamis.
- BSNL is the sole Project Management Agency for operation and maintenance.
- On January 17, 2025, the government launched National Broadband Mission 2.0.
- The mission aims to accelerate the expansion of digital infrastructure and bridge the digital gap.
- It focuses on ensuring high-speed internet and meaningful connectivity for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) was launched by MeitY to provide digital literacy to 6 crore rural households.
- The scheme was executed by CSC e-Governance Services India Limited through Common Service Centres in Gram Panchayats.
- Instead of 6 crore, 6.39 crore people were successfully trained.
- PMGDISHA training and certification officially ended on March 31, 2024.
- A survey by NSSO in its 79th round revealed that 78.4% of young people aged 15-24 can send messages with attachments.
- This reflects a rise in digital skills.
- About 94.2% of rural households and 97.1% of urban households have a mobile phone or telephone.
- The increase in smartphone usage and internet access in rural areas highlights PMGDISHA's success.
- Evaluation by IIT Delhi, Council for Social Development (CSD) and Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA) confirmed the positive effects of PMGDISHA on ICT adoption.
- Launched in December 2019, the National Broadband Mission (NBM) aims to improve digital communications infrastructure.
- NBM seeks to close the digital divide and ensure affordable broadband for all.
- Key initiatives under NBM include the Centralized Right of Way (RoW) Portal GatiShakti Sanchar.
- The 'Call Before u Dig' mobile app is another key initiative.
- The PM GatiShakti National Master Plan (NMP) Platform is also part of the mission.
- Progress under NBM 1.0 since the launch:
- Broadband subscribers has increased from 66 crore to 94.49 crore.
- Average monthly wireless data consumption per person has risen from 10 GB to 21.10 GB.
- Median mobile broadband download speed has grown from 10.71 Mbps in 2019 to 144.33 Mbps in February 2025.
- Median fixed broadband speed has increased from 29.25 Mbps in 2019 to 61.66 Mbps in February 2025.
- The length of Optical Fiber Cable has grown from 19.35 lakh route km to 42.13 lakh route km.
- Number of mobile towers has risen from 5.37 lakh to 8.23 lakh.
- Base Transceiver Stations have grown from 21.80 lakh to 29.97 lakh, including 4.69 lakh 5G Base Transceiver Stations.
| Monthly Current Affairs eBooks | |
|---|---|
| February Monthly Current Affairs 2025 | January Monthly Current Affairs 2025 |
| December Monthly Current Affairs 2024 | October Monthly Current Affairs 2024 |





 2 April 2025 Current Affairs
2 April 2025 Current Affairs 








Comments